Top-down management centralizes decision-making within upper leadership, ensuring clear directives and streamlined execution but potentially limiting employee engagement and innovation. Participatory management encourages input and collaboration from employees at all levels, fostering higher motivation and creativity while sometimes complicating consensus and slowing decision-making processes. Balancing these approaches depends on organizational goals, culture, and the need for agility or control in management practices.
Table of Comparison
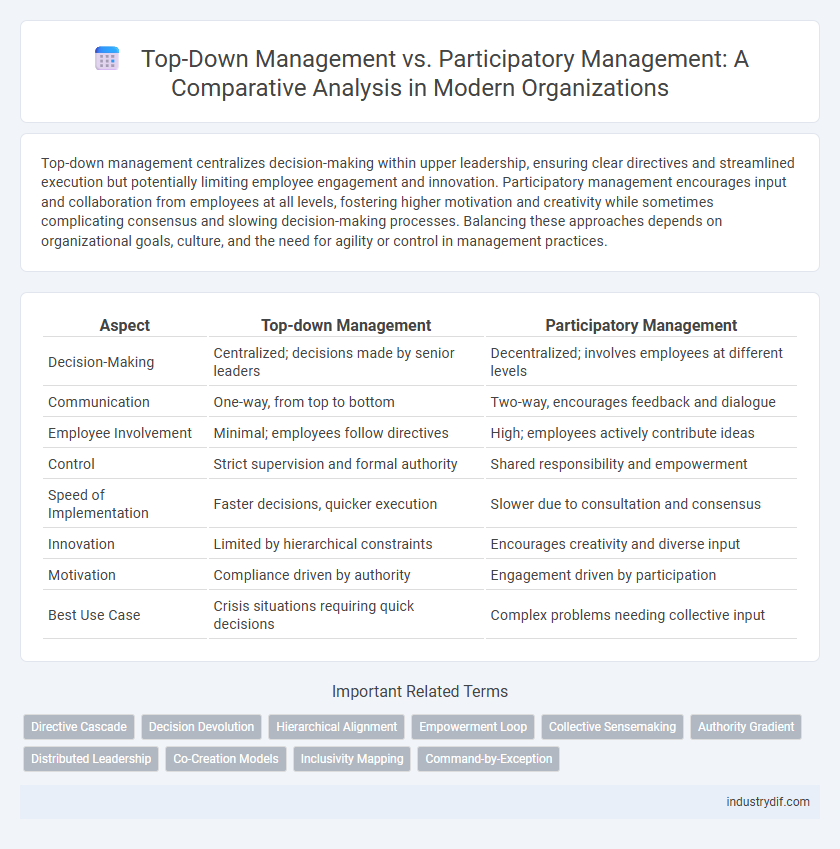
| Aspect | Top-down Management | Participatory Management |
|---|---|---|
| Decision-Making | Centralized; decisions made by senior leaders | Decentralized; involves employees at different levels |
| Communication | One-way, from top to bottom | Two-way, encourages feedback and dialogue |
| Employee Involvement | Minimal; employees follow directives | High; employees actively contribute ideas |
| Control | Strict supervision and formal authority | Shared responsibility and empowerment |
| Speed of Implementation | Faster decisions, quicker execution | Slower due to consultation and consensus |
| Innovation | Limited by hierarchical constraints | Encourages creativity and diverse input |
| Motivation | Compliance driven by authority | Engagement driven by participation |
| Best Use Case | Crisis situations requiring quick decisions | Complex problems needing collective input |
Introduction to Management Styles
Top-down management centralizes decision-making authority within upper management, ensuring clear directives and streamlined execution across organizational levels. Participatory management encourages collaboration by involving employees in decision processes, fostering innovation, and enhancing job satisfaction. Both styles impact organizational culture, communication flow, and responsiveness to change, shaping management effectiveness.
Defining Top-down Management
Top-down management is a hierarchical approach where decision-making authority rests with senior leaders who set directives and goals that flow downward through organizational levels. This management style emphasizes control, clear lines of responsibility, and efficient implementation of strategies by middle and lower-level managers. It often results in faster decision execution but may limit employee input and innovation.
Explaining Participatory Management
Participatory management empowers employees by involving them in decision-making processes, fostering a collaborative organizational culture and enhancing motivation. This management style encourages open communication, shared responsibility, and team-based problem solving, which can lead to increased innovation and job satisfaction. Research shows organizations implementing participatory management often experience higher productivity levels and improved employee retention rates compared to traditional top-down approaches.
Decision-Making Processes
Top-down management centralizes decision-making authority within senior leadership, ensuring quick, uniform decisions but often limiting employee input and innovation. Participatory management involves employees at various levels in decision-making, fostering collaboration and diverse perspectives, which can enhance commitment and creativity but may slow down the process. Effective organizations balance these approaches by aligning decision-making frameworks with strategic goals and organizational culture.
Communication Flow in Each Approach
Top-down management relies on a hierarchical communication flow where directives and information move downward from leaders to employees, ensuring clear authority but often limiting feedback. Participatory management emphasizes two-way communication, encouraging dialogue and collaboration between all organizational levels to enhance engagement and decision-making. Efficient communication flow in participatory management fosters transparency and responsiveness, while top-down management prioritizes control and consistency.
Employee Engagement and Motivation
Top-down management often results in limited employee engagement and reduced motivation due to centralized decision-making that restricts autonomy. Participatory management fosters higher employee motivation by involving staff in decision processes, increasing ownership and commitment. Research shows that organizations practicing participatory management experience up to 30% higher employee engagement scores compared to top-down approaches.
Impact on Organizational Culture
Top-down management centralizes decision-making authority, often resulting in a hierarchical organizational culture that may limit employee engagement and innovation. Participatory management fosters collaboration and empowerment, cultivating a culture of trust and shared responsibility that enhances motivation and adaptability. Organizations adopting participatory approaches typically experience higher employee satisfaction and improved communication across all levels.
Efficiency and Innovation Outcomes
Top-down management often enhances efficiency through centralized decision-making and clear directives, enabling faster execution of tasks. Participatory management fosters innovation by engaging employees in problem-solving and idea generation, which promotes diverse perspectives and creative solutions. Balancing these approaches can lead to optimal performance by combining streamlined processes with adaptive innovation strategies.
Challenges and Limitations
Top-down management often faces challenges such as limited employee engagement and slower adaptability due to centralized decision-making, which can stifle creativity and reduce motivation. Participatory management struggles with potential inefficiencies, longer decision cycles, and difficulties in reaching consensus among diverse team members. Both styles require balancing control and collaboration to address organizational complexity and dynamic market demands effectively.
Choosing the Right Management Style
Top-down management centralizes decision-making, ensuring quick execution and clear accountability, ideal for crisis situations or hierarchical organizations. Participatory management fosters employee engagement and innovation by involving team members in decision processes, which boosts morale and long-term commitment. Selecting the right management style depends on organizational goals, culture, and the need for adaptability versus control.
Related Important Terms
Directive Cascade
Directive Cascade in Top-down Management ensures clear command flow from executives to frontline employees, enhancing decision control but limiting employee input. In Participatory Management, the cascade adapts to incorporate feedback loops, promoting collaboration and empowering teams for improved innovation and commitment.
Decision Devolution
Top-down management centralizes decision-making authority within senior leadership, facilitating quick, uniform execution but often limiting employee input and innovation. Participatory management devolves decision-making power to lower organizational levels, enhancing team engagement, accountability, and adaptability through collaborative problem-solving and shared responsibility.
Hierarchical Alignment
Top-down management enforces hierarchical alignment by centralizing decision-making authority at upper levels, ensuring uniformity and rapid execution of strategic initiatives. Participatory management fosters hierarchical alignment through collaborative input across ranks, promoting employee engagement and adaptive problem-solving within the organizational structure.
Empowerment Loop
Top-down management concentrates decision-making authority at the executive level, often limiting employee autonomy and slowing the feedback process, whereas participatory management fosters an empowerment loop by actively engaging employees in decision-making, enhancing motivation, innovation, and organizational agility. The empowerment loop in participatory management creates continuous feedback and development cycles, driving higher commitment, improved problem-solving, and sustained performance growth.
Collective Sensemaking
Top-down management centralizes decision-making authority, often limiting employee input, which can hinder collective sensemaking by reducing diverse perspectives in interpreting complex situations. Participatory management encourages collaborative dialogue and shared understanding among team members, enhancing collective sensemaking and enabling more adaptive and informed decision-making processes.
Authority Gradient
Top-down management establishes a steep authority gradient where decisions flow unilaterally from senior leaders to subordinates, often hindering open communication and innovation. Participatory management flattens the authority gradient by involving employees at all levels in decision-making, enhancing collaboration, accountability, and overall organizational agility.
Distributed Leadership
Distributed leadership integrates elements of both top-down management and participatory management by empowering multiple team members to share decision-making responsibilities, enhancing collaboration and innovation. This approach distributes authority across various organizational levels, promoting agility and responsiveness compared to the centralized control of top-down management.
Co-Creation Models
Co-creation models in management emphasize collaborative decision-making, integrating insights from both top-down leadership and participatory team involvement to foster innovation and shared ownership. These models leverage structured strategic directives while encouraging employee input, enhancing adaptability and driving sustainable organizational growth.
Inclusivity Mapping
Top-down management centralizes decision-making authority, often limiting inclusivity by restricting input from lower organizational levels. Participatory management fosters inclusivity through active employee involvement in decision processes, enhancing collaboration and diverse perspectives in organizational planning.
Command-by-Exception
Command-by-exception in top-down management empowers leaders to intervene only when deviations from standards occur, streamlining decision-making and maintaining control. In participatory management, this approach shifts towards collaborative exception reporting, enhancing responsiveness and employee engagement in problem-solving processes.
Top-down Management vs Participatory Management Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com