Public accountability ensures organizations answer to stakeholders through regular reporting and oversight, promoting trust and ethical behavior. Radical transparency goes further by making almost all internal processes and decisions openly accessible, encouraging deeper scrutiny and participation. Balancing these approaches can enhance credibility while protecting sensitive information from misuse.
Table of Comparison
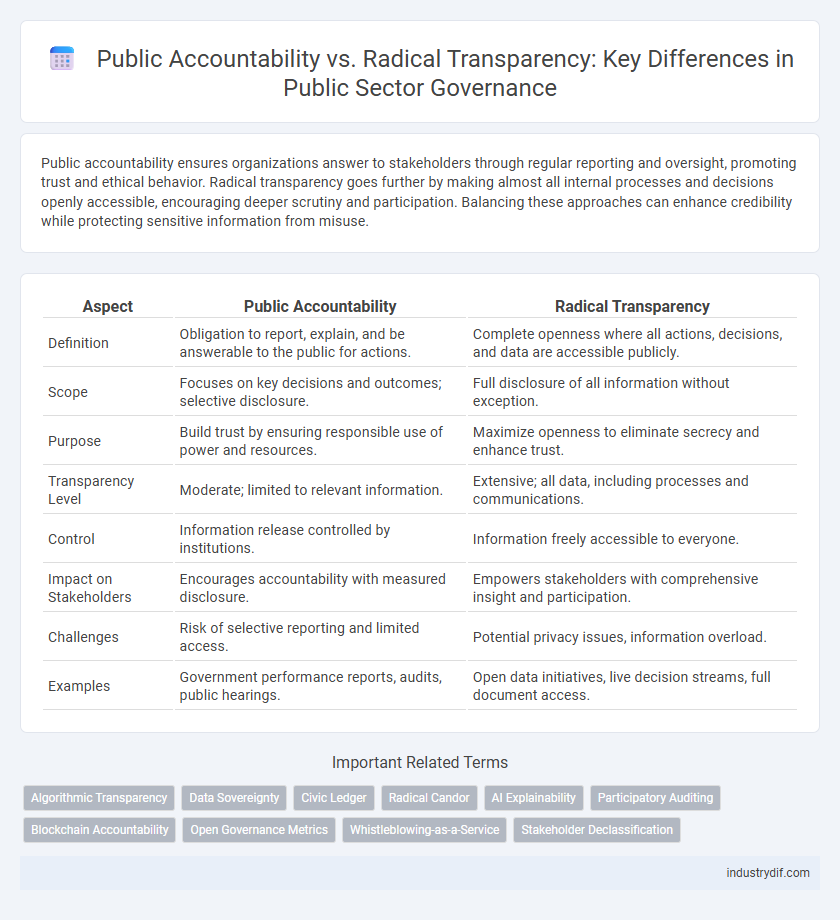
| Aspect | Public Accountability | Radical Transparency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Obligation to report, explain, and be answerable to the public for actions. | Complete openness where all actions, decisions, and data are accessible publicly. |
| Scope | Focuses on key decisions and outcomes; selective disclosure. | Full disclosure of all information without exception. |
| Purpose | Build trust by ensuring responsible use of power and resources. | Maximize openness to eliminate secrecy and enhance trust. |
| Transparency Level | Moderate; limited to relevant information. | Extensive; all data, including processes and communications. |
| Control | Information release controlled by institutions. | Information freely accessible to everyone. |
| Impact on Stakeholders | Encourages accountability with measured disclosure. | Empowers stakeholders with comprehensive insight and participation. |
| Challenges | Risk of selective reporting and limited access. | Potential privacy issues, information overload. |
| Examples | Government performance reports, audits, public hearings. | Open data initiatives, live decision streams, full document access. |
Understanding Public Accountability
Public accountability requires officials to answer for their decisions and actions to stakeholders, ensuring responsibility through established legal and ethical frameworks. Radical transparency extends this by promoting open access to all processes and information, often beyond standard accountability mechanisms. Understanding public accountability involves recognizing its role in maintaining trust, guiding ethical governance, and balancing transparency with privacy and security concerns.
Defining Radical Transparency
Radical transparency involves openly sharing all organizational processes, decisions, and data with the public to foster complete visibility and trust. Unlike traditional public accountability, which focuses on reporting and justification after actions, radical transparency emphasizes proactive disclosure and continuous access to information. This approach aims to minimize information asymmetry and empower stakeholders with real-time insights into governance and operational practices.
Key Differences Between Public Accountability and Radical Transparency
Public accountability involves stakeholders holding organizations or individuals responsible for their actions through established reporting and oversight mechanisms, emphasizing answerability and corrective measures. Radical transparency requires the continuous and open disclosure of all internal processes, decisions, and data, promoting unrestricted access and minimizing information asymmetry. The key difference lies in accountability's reactive nature rooted in responsibility frameworks versus radical transparency's proactive sharing aimed at fostering trust and participation.
Historical Evolution of Accountability in the Public Sector
The historical evolution of accountability in the public sector traces a progression from basic fiscal responsibility to complex mechanisms of public scrutiny and performance evaluation. Early accountability models emphasized hierarchical control and compliance with legal standards, while contemporary shifts emphasize radical transparency, inviting citizens to access comprehensive governmental data and decision-making processes. This transition reflects broader societal demands for openness, enhanced trust, and participatory governance in democratic institutions.
The Rise of Radical Transparency in Modern Organizations
The rise of radical transparency in modern organizations challenges traditional notions of public accountability by promoting open access to decision-making processes, financial disclosures, and internal communications. This approach enhances trust and stakeholder engagement through real-time visibility, yet demands rigorous data governance and ethical standards to prevent misuse. Organizations adopting radical transparency often experience increased pressure to maintain consistent integrity across all operations, redefining accountability beyond regulatory compliance.
Benefits and Challenges of Public Accountability
Public accountability ensures that government actions are subject to oversight, promoting trust and ethical governance by requiring officials to report and justify decisions to citizens. Benefits include increased transparency that deters corruption and fosters informed public participation, while challenges involve potential bureaucratic delays and the difficulty of balancing openness with privacy or security concerns. Maintaining effective public accountability systems requires robust legal frameworks, clear reporting standards, and active citizen engagement to achieve genuine democratic accountability.
Advantages and Pitfalls of Radical Transparency
Radical transparency promotes greater trust by openly sharing information and decision-making processes, fostering accountability and reducing corruption risks. However, its pitfalls include potential information overload, privacy concerns, and the risk of misinterpretation or manipulation of shared data. Balancing openness with strategic confidentiality remains crucial to maximizing the benefits of radical transparency in public governance.
Case Studies: Accountability vs. Transparency in Practice
Case studies comparing public accountability and radical transparency reveal distinct impacts on governance and public trust. Accountability mechanisms often involve structured reporting and oversight, as seen in government audit systems, ensuring decision-makers answer for outcomes. Radical transparency initiatives, such as Iceland's crowd-sourced constitution, emphasize open access to information but may challenge privacy and operational efficiency.
Impact on Stakeholder Trust and Engagement
Public accountability ensures stakeholders receive accurate and reliable information, fostering trust through consistent oversight and responsibility. Radical transparency promotes deeper engagement by exposing real-time data and decision-making processes, though it can sometimes overwhelm or alienate stakeholders due to information overload. Effective stakeholder trust emerges from balancing clarity and openness, enabling informed participation without compromising confidence or security.
Future Trends: Balancing Accountability and Transparency in Public Institutions
Future trends in public institutions emphasize a nuanced balance between public accountability and radical transparency, leveraging advanced technologies such as blockchain and AI for real-time data verification and citizen engagement. Enhanced transparency initiatives focus on open data platforms that empower stakeholders to monitor governmental performance while safeguarding sensitive information to prevent misuse. Institutional reforms will continue to integrate ethical frameworks and predictive analytics to ensure accountability measures adapt dynamically to public expectations and evolving democratic norms.
Related Important Terms
Algorithmic Transparency
Algorithmic transparency enhances public accountability by enabling citizens to understand and scrutinize automated decision-making processes, reducing biases and ensuring fairness. Radical transparency in algorithms demands open access to source codes and data, promoting trust but raising concerns over privacy and security in public governance.
Data Sovereignty
Public accountability ensures institutions responsibly manage data while respecting citizens' Data Sovereignty, emphasizing control over personal information within legal frameworks. Radical transparency advocates for open access to data, challenging traditional privacy boundaries and raising critical questions about how sovereign data rights are preserved or compromised.
Civic Ledger
Civic Ledger leverages blockchain technology to enhance public accountability by ensuring immutable, auditable records while balancing the principles of radical transparency to protect sensitive information. Their platform facilitates trust between governments and citizens through secure data sharing that promotes openness without compromising privacy or operational security.
Radical Candor
Radical Candor emphasizes direct, honest communication while maintaining personal respect, fostering an environment of trust and accountability that goes beyond traditional public accountability by promoting open feedback and continuous improvement. This approach encourages leaders and teams to engage transparently without fear, enhancing organizational effectiveness and morale.
AI Explainability
Public accountability in AI demands clear explanations of decision-making processes to ensure trust and ethical compliance, whereas radical transparency advocates for open access to AI algorithms and data, enhancing scrutiny but raising privacy concerns. Balancing explainability with transparency is crucial for aligning AI systems with societal values and regulatory standards.
Participatory Auditing
Participatory auditing enhances public accountability by involving citizens directly in evaluating governmental actions, promoting transparency beyond traditional reporting methods. This approach balances radical transparency with practical oversight, enabling communities to actively monitor resource allocation and policy implementation.
Blockchain Accountability
Blockchain accountability enhances public accountability by providing immutable, transparent records of transactions that prevent data tampering and enable verifiable audits. Radical transparency, while promoting full disclosure of information, may conflict with privacy concerns, making blockchain's cryptographic security a balanced approach to accountable governance.
Open Governance Metrics
Open Governance Metrics enhance public accountability by providing measurable standards for transparency, participation, and responsiveness in government operations. Unlike radical transparency, which demands full disclosure without filters, these metrics balance openness with practical governance, enabling stakeholders to evaluate performance and trustworthiness effectively.
Whistleblowing-as-a-Service
Whistleblowing-as-a-Service platforms enhance public accountability by providing secure, anonymous channels for reporting corruption and misconduct, bridging the gap between traditional confidential disclosures and radical transparency. These services empower citizens and employees to expose unethical practices while ensuring protection, fostering trust in institutions through verified, actionable information.
Stakeholder Declassification
Stakeholder declassification enhances public accountability by clearly defining which parties have access to sensitive information, balancing openness with privacy concerns. Radical transparency demands full disclosure, often challenging this classification by advocating for broader stakeholder inclusion in information sharing.
public accountability vs radical transparency Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com