Public budgeting involves government officials designing and controlling the allocation of funds based on public needs and policy priorities. Participatory budgeting empowers citizens to directly influence spending decisions by proposing and voting on budgetary initiatives. This democratic approach enhances transparency and community engagement in fiscal management.
Table of Comparison
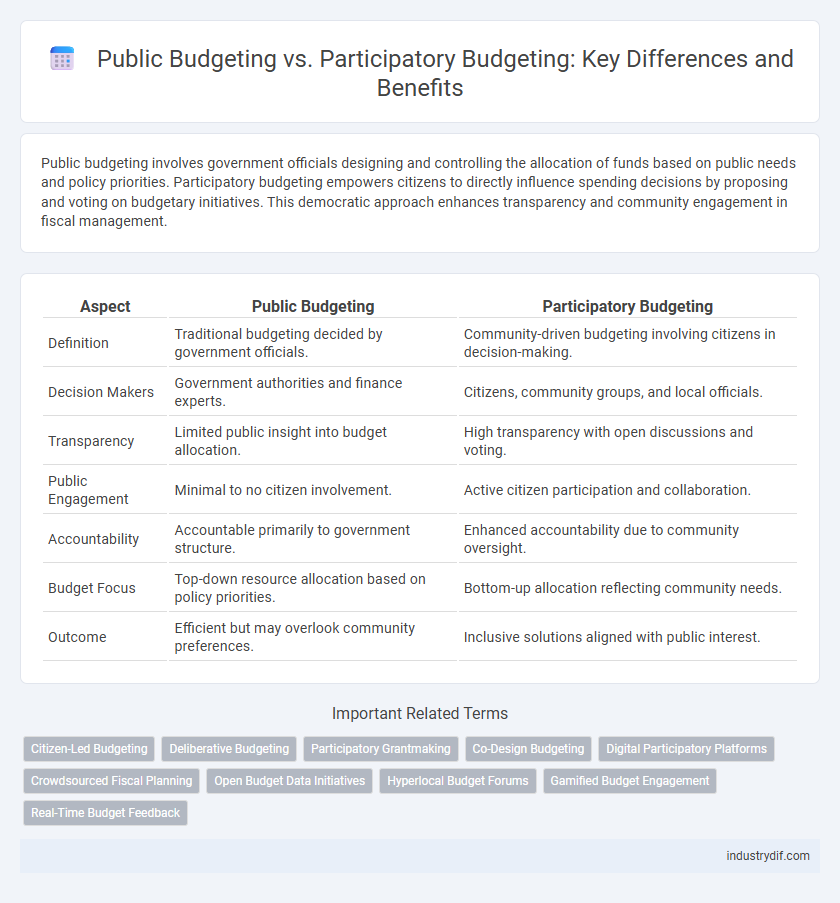
| Aspect | Public Budgeting | Participatory Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional budgeting decided by government officials. | Community-driven budgeting involving citizens in decision-making. |
| Decision Makers | Government authorities and finance experts. | Citizens, community groups, and local officials. |
| Transparency | Limited public insight into budget allocation. | High transparency with open discussions and voting. |
| Public Engagement | Minimal to no citizen involvement. | Active citizen participation and collaboration. |
| Accountability | Accountable primarily to government structure. | Enhanced accountability due to community oversight. |
| Budget Focus | Top-down resource allocation based on policy priorities. | Bottom-up allocation reflecting community needs. |
| Outcome | Efficient but may overlook community preferences. | Inclusive solutions aligned with public interest. |
Understanding Public Budgeting: Key Concepts
Public budgeting involves the allocation of government resources based on legislative priorities and fiscal policies, ensuring transparency and accountability in managing public funds. Participatory budgeting engages citizens directly in decision-making, allowing community input to influence spending allocations and priorities. Understanding public budgeting requires grasping key concepts such as revenue sources, expenditure planning, and fiscal constraints that govern the budgeting process.
Defining Participatory Budgeting: An Overview
Participatory budgeting is a democratic process in which community members directly decide how to allocate part of a public budget. This approach promotes transparency, inclusiveness, and citizen engagement by allowing residents to propose and vote on funding priorities. Unlike traditional public budgeting managed solely by officials, participatory budgeting empowers the public to influence government spending decisions.
Core Differences Between Public and Participatory Budgeting
Public budgeting typically involves government officials allocating funds based on policy priorities and expert analysis, while participatory budgeting actively engages citizens in decision-making, allowing them to vote on or propose specific projects. The core difference lies in the level of citizen involvement: public budgeting is top-down, whereas participatory budgeting is bottom-up and democratic. This shift results in increased transparency, community empowerment, and projects that better reflect local needs.
The Role of Citizens in Public Budgeting
Citizens play a crucial role in public budgeting by influencing the allocation of resources through feedback and voting mechanisms. Participatory budgeting empowers residents to directly propose and decide on budget priorities, enhancing transparency and accountability. This active involvement fosters community engagement, ensuring that public funds address local needs effectively.
Stakeholder Engagement in Participatory Budgeting
Participatory budgeting enhances stakeholder engagement by involving citizens directly in decision-making processes, fostering transparency and community empowerment. This approach encourages diverse input from residents, local organizations, and government officials, which leads to more equitable allocation of public funds. Increased stakeholder participation in participatory budgeting has been linked to higher civic trust and improved public satisfaction with budget outcomes.
Transparency and Accountability in Budgeting Processes
Public budgeting ensures transparency by making financial allocations and expenditures accessible to citizens through official reports and audits. Participatory budgeting enhances accountability by actively involving community members in decision-making, fostering oversight and alignment with local priorities. Both approaches aim to reduce corruption and improve trust in public financial management.
Advantages of Public Budgeting Systems
Public budgeting systems ensure transparent allocation of resources aligned with government priorities, enhancing accountability and fiscal discipline. These systems facilitate long-term financial planning and efficient management of public funds, supporting sustainable economic growth. Centralized control in public budgeting reduces duplication of efforts and optimizes allocation across various public sectors.
Benefits of Participatory Budgeting Approaches
Participatory budgeting fosters increased transparency and accountability by directly involving citizens in allocating public funds, leading to more equitable and community-driven outcomes. This approach enhances civic engagement and trust in government by empowering residents to prioritize projects that address their specific needs. Evidence shows participatory budgeting can improve resource efficiency and promote social inclusion, particularly in marginalized communities.
Challenges Faced in Implementing Participatory Budgeting
Implementing participatory budgeting often faces challenges such as limited public awareness, insufficient funding, and resistance from traditional political structures. Ensuring diverse and inclusive community engagement proves difficult, as marginalized groups may lack resources or trust in the process. Additionally, administrative complexity and the need for transparency in decision-making can hinder effective implementation and long-term sustainability of participatory budgeting initiatives.
Future Trends in Public and Participatory Budgeting
Future trends in public and participatory budgeting emphasize increased digital integration through AI-driven platforms that enhance transparency and citizen engagement. Data analytics will play a crucial role in forecasting community needs and optimizing resource allocation. Collaborative governance models are expected to evolve, promoting inclusivity and real-time feedback mechanisms to drive more responsive and equitable budget decisions.
Related Important Terms
Citizen-Led Budgeting
Citizen-led budgeting empowers residents to directly influence allocation of public funds, fostering transparency and accountability in government spending. Unlike traditional public budgeting, participatory budgeting actively involves community members in decision-making processes, enhancing civic engagement and ensuring budget priorities reflect local needs.
Deliberative Budgeting
Deliberative budgeting emphasizes structured citizen discussions to prioritize public fund allocation, fostering transparent decision-making and community consensus beyond traditional public or participatory budgeting models. This approach leverages informed dialogue and collective reasoning to enhance democratic legitimacy and budget effectiveness.
Participatory Grantmaking
Participatory grantmaking empowers community members to directly influence funding decisions by involving them in grant allocation processes, enhancing transparency and inclusivity beyond traditional public budgeting frameworks. This approach fosters equitable resource distribution by tapping into local knowledge and priorities, contrasting with conventional top-down public budgeting that often lacks grassroots input.
Co-Design Budgeting
Co-Design Budgeting integrates public input and expert collaboration to create more transparent and inclusive financial plans, enhancing civic engagement beyond traditional Public Budgeting methods. Unlike Participatory Budgeting, Co-Design emphasizes iterative feedback loops and joint decision-making between officials and community members for optimal resource allocation.
Digital Participatory Platforms
Digital participatory platforms enhance public engagement by enabling transparent, real-time collaboration between citizens and government in budgeting decisions. These platforms utilize interactive tools and data visualization to streamline input collection, increase inclusivity, and improve accountability compared to traditional public budgeting methods.
Crowdsourced Fiscal Planning
Crowdsourced fiscal planning leverages public input to allocate budgets more transparently and equitably, differentiating participatory budgeting by emphasizing mass digital engagement and real-time data analytics. This approach increases accountability and inclusivity, enabling diverse citizen voices to influence municipal spending priorities effectively.
Open Budget Data Initiatives
Public budgeting often relies on traditional top-down approaches with limited transparency, whereas participatory budgeting emphasizes citizen involvement through open budget data initiatives that enhance accountability and foster trust in government spending. Open budget data initiatives provide accessible, real-time financial information, enabling communities to monitor allocations and influence funding decisions for social programs and infrastructure projects.
Hyperlocal Budget Forums
Hyperlocal budget forums enhance public engagement by allowing community members to directly deliberate and decide on local funding priorities, making participatory budgeting more targeted and transparent. These forums improve resource allocation efficiency by aligning budget decisions with the specific needs of neighborhoods, increasing accountability and fostering civic trust.
Gamified Budget Engagement
Gamified budget engagement transforms traditional public and participatory budgeting processes by incorporating interactive elements and game mechanics that increase citizen participation and transparency. This approach leverages digital platforms with point systems, leaderboards, and real-time feedback to motivate continuous community involvement and enhance decision-making quality.
Real-Time Budget Feedback
Real-time budget feedback in public budgeting enables transparent allocation of funds by providing instant visibility into revenue and expenditure data, fostering accountability and trust among citizens. Participatory budgeting enhances this process by integrating community input directly, allowing residents to prioritize projects and track implementation progress in real time.
Public vs Participatory Budgeting Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com