Public consultation gathers a broad range of opinions from the community to inform decision-making, emphasizing inclusivity and transparency. Deliberative polling goes further by combining surveys with structured discussions, allowing participants to become more informed and reconsider their views. This method aims to capture more thoughtful and reflective public preferences for complex policy issues.
Table of Comparison
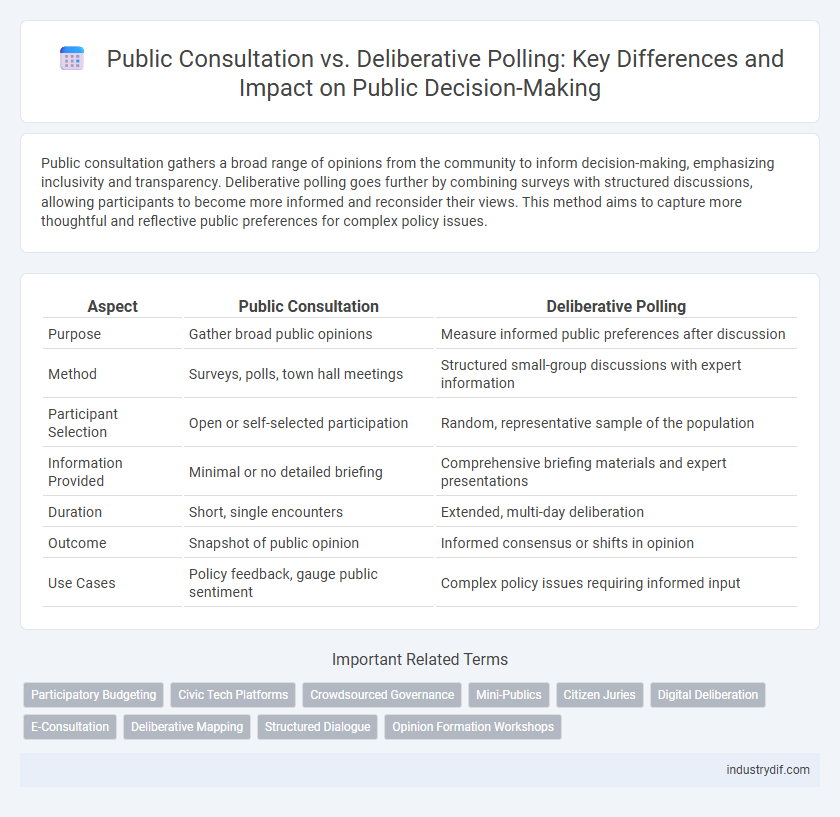
| Aspect | Public Consultation | Deliberative Polling |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Gather broad public opinions | Measure informed public preferences after discussion |
| Method | Surveys, polls, town hall meetings | Structured small-group discussions with expert information |
| Participant Selection | Open or self-selected participation | Random, representative sample of the population |
| Information Provided | Minimal or no detailed briefing | Comprehensive briefing materials and expert presentations |
| Duration | Short, single encounters | Extended, multi-day deliberation |
| Outcome | Snapshot of public opinion | Informed consensus or shifts in opinion |
| Use Cases | Policy feedback, gauge public sentiment | Complex policy issues requiring informed input |
Understanding Public Consultation: Key Definitions
Public consultation involves gathering diverse opinions from a broad audience through surveys, focus groups, or town hall meetings to inform decision-making processes. It emphasizes inclusivity and transparency by allowing stakeholders to express their views without requiring consensus. Unlike deliberative polling, which engages a smaller, representative group in structured, in-depth discussions to reach informed judgments, public consultation prioritizes collecting widespread feedback to guide policy development.
Deliberative Polling Explained: Core Concepts
Deliberative Polling involves gathering a representative sample of citizens to engage in informed discussions about specific policy issues, enabling them to weigh evidence and diverse viewpoints before expressing their opinions. This method enhances public understanding and produces more reflective judgments compared to traditional opinion polls, which often capture immediate reactions without in-depth consideration. By combining random sampling with facilitated deliberation, Deliberative Polling aims to reveal informed public preferences that can guide democratic decision-making effectively.
Goals and Objectives: Public Consultation vs Deliberative Polling
Public Consultation aims to gather diverse stakeholder input and assess public opinion on policy proposals, ensuring transparency and community engagement. Deliberative Polling focuses on informed decision-making by providing participants with balanced information and facilitating structured discussions to reflect considered public judgments. Both approaches seek to enhance democratic legitimacy but differ in depth of engagement and the quality of collective reasoning.
Methods and Processes: A Comparative Analysis
Public consultation typically involves gathering input from a broad audience through surveys, town halls, or online platforms to inform decision-making, emphasizing inclusivity and accessibility. Deliberative polling engages a smaller, representative sample selected randomly to deliberate extensively on issues after receiving balanced information, aiming for informed public opinion. The key methodological difference lies in the depth of engagement and informed deliberation, with deliberative polling fostering reflective discussions, while public consultation captures immediate, diverse viewpoints.
Stakeholder Engagement: Levels of Participation
Public consultation typically allows for broad stakeholder engagement through open forums, surveys, and feedback mechanisms, enabling a wide range of participants to express opinions with limited interaction. Deliberative polling involves a select group of stakeholders representing a larger population who engage deeply through informed discussions and expert briefings, fostering higher-quality participation and more considered judgments. The level of participation in deliberative polling is more intensive and interactive compared to the generally more passive and extensive input gathered in public consultations.
Representativeness and Inclusivity in Both Approaches
Public Consultation often faces challenges in achieving true representativeness, as participation tends to skew toward more vocal or organized groups, limiting inclusivity of marginalized populations. Deliberative Polling actively addresses this by using randomized sampling methods to ensure a statistically representative subset of the population, fostering inclusivity across diverse demographics. Both approaches aim to inform policy, but Deliberative Polling's structured format enhances the legitimacy of outcomes through balanced representation and equitable participation.
Advantages and Limitations: Public Consultation
Public consultation facilitates broad citizen engagement, allowing diverse perspectives to inform policy decisions and enhance democratic legitimacy. Its advantages include inclusivity and accessibility, enabling policy-makers to gather qualitative insights from a wide audience. Limitations involve potential biases from unrepresentative participation and challenges in synthesizing large volumes of input into actionable outcomes.
Strengths and Weaknesses: Deliberative Polling
Deliberative Polling excels in gathering informed public opinion by engaging a representative sample of participants in structured discussions after receiving balanced information, which enhances the quality and legitimacy of the results. Its strengths include fostering deep understanding and reducing misinformation, but weaknesses involve high costs, time consumption, and limited scalability compared to broader public consultations. The method's structured format may also exclude spontaneous public input, potentially overlooking diverse viewpoints outside the selected sample.
Measuring Impact: Outcomes of Each Method
Public Consultation often yields qualitative insights from diverse community opinions, enhancing policymaker responsiveness but with limited measurable impact on decision shifts. Deliberative Polling provides quantifiable data on how informed discussion changes participants' views, demonstrating statistically significant attitude transformations and increased public legitimacy. Both methods contribute uniquely to democratic engagement, yet Deliberative Polling offers stronger evidence of impact on public opinion dynamics.
Choosing the Right Approach for Policy Development
Public consultation gathers broad community input through surveys, meetings, or online platforms to capture diverse opinions rapidly, ideal for identifying general public preferences in early policy stages. Deliberative polling engages a representative sample in in-depth discussions and information sessions to refine opinions, fostering informed consensus suitable for complex policy decisions requiring nuanced understanding. Selecting the right approach depends on the policy complexity, desired depth of engagement, and resource availability for effective stakeholder involvement.
Related Important Terms
Participatory Budgeting
Participatory budgeting empowers communities to directly influence public spending decisions through inclusive public consultations, ensuring diverse stakeholder input in resource allocation. Deliberative polling complements this by combining random sampling and informed deliberation, enhancing the legitimacy and depth of public opinion reflected in budgeting processes.
Civic Tech Platforms
Civic tech platforms enhance public consultation by enabling broad citizen input through surveys and forums, while deliberative polling leverages these technologies to facilitate informed discussions and representative sampling for more nuanced policy feedback. Both methods use digital tools to increase transparency and democratic participation, but deliberative polling emphasizes quality of opinion over quantity, fostering deeper civic engagement.
Crowdsourced Governance
Public Consultation gathers diverse citizen input through surveys and forums, providing broad but often surface-level feedback for policymakers. Deliberative Polling engages a representative sample in informed discussions to elicit more thoughtful, consensus-driven insights, enhancing the effectiveness of crowdsourced governance.
Mini-Publics
Mini-publics, including public consultations and deliberative polling, serve as democratic tools to engage citizens in policymaking by providing structured platforms for informed discussion and collective decision-making. While public consultations gather broad input from participants on specific issues, deliberative polling combines representative sampling with in-depth deliberation to reflect public opinion changes after exposure to balanced information.
Citizen Juries
Citizen Juries offer a focused approach to public consultation by engaging a representative group of citizens in in-depth deliberation on complex policy issues, fostering informed decision-making. Unlike broader public consultations, Citizen Juries emphasize thoughtful dialogue and consensus-building, enhancing the quality of democratic participation and providing policymakers with nuanced public perspectives.
Digital Deliberation
Digital deliberation enhances public consultation by enabling more diverse participation and real-time feedback through online platforms, improving the quality of collective decision-making. Unlike traditional deliberative polling, digital tools facilitate continuous dialogue and data-driven insights, increasing transparency and inclusiveness in policy development processes.
E-Consultation
E-Consultation enhances public consultation by enabling real-time, large-scale digital engagement, increasing accessibility and diversity of participant input. Unlike deliberative polling which focuses on informed opinion shifts through moderated discussions, e-consultation prioritizes broad stakeholder participation and rapid feedback collection to inform policy decisions.
Deliberative Mapping
Deliberative Mapping integrates diverse public values and expert knowledge through structured dialogue and real-time feedback, enhancing the depth of public consultation beyond traditional surveys or opinion polls. This method enables more informed and reflective citizen participation by combining qualitative discussions with quantitative ratings, thereby improving the legitimacy and quality of policy decisions.
Structured Dialogue
Public Consultation and Deliberative Polling both employ structured dialogue to engage citizens but differ in scope and methodology; Public Consultation gathers diverse opinions through guided discussions, whereas Deliberative Polling combines polling with intensive information exchange and deliberation to reveal informed public preferences. Structured dialogue in these processes fosters mutual understanding and informed decision-making by encouraging participants to collaboratively explore issues, evaluate evidence, and consider diverse perspectives.
Opinion Formation Workshops
Opinion Formation Workshops in public consultation engage diverse stakeholders in structured discussions to explore informed viewpoints, enhancing the depth of public input. Unlike Deliberative Polling, which quantitatively measures opinion shifts post-deliberation, these workshops prioritize qualitative understanding of evolving attitudes through collaborative dialogue.
Public Consultation vs Deliberative Polling Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com