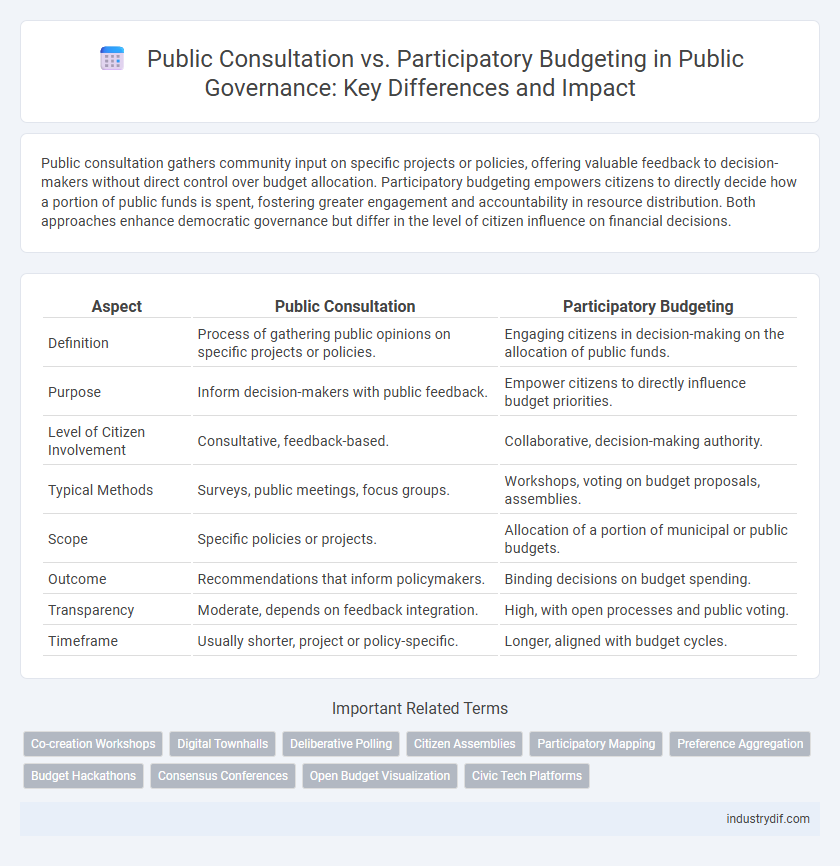
Public consultation gathers community input on specific projects or policies, offering valuable feedback to decision-makers without direct control over budget allocation. Participatory budgeting empowers citizens to directly decide how a portion of public funds is spent, fostering greater engagement and accountability in resource distribution. Both approaches enhance democratic governance but differ in the level of citizen influence on financial decisions.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Public Consultation | Participatory Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of gathering public opinions on specific projects or policies. | Engaging citizens in decision-making on the allocation of public funds. |
| Purpose | Inform decision-makers with public feedback. | Empower citizens to directly influence budget priorities. |
| Level of Citizen Involvement | Consultative, feedback-based. | Collaborative, decision-making authority. |
| Typical Methods | Surveys, public meetings, focus groups. | Workshops, voting on budget proposals, assemblies. |
| Scope | Specific policies or projects. | Allocation of a portion of municipal or public budgets. |
| Outcome | Recommendations that inform policymakers. | Binding decisions on budget spending. |
| Transparency | Moderate, depends on feedback integration. | High, with open processes and public voting. |
| Timeframe | Usually shorter, project or policy-specific. | Longer, aligned with budget cycles. |
Understanding Public Consultation
Public consultation involves gathering feedback from community members on specific issues, policies, or projects to inform decision-making. It typically seeks opinions and suggestions through surveys, meetings, or online platforms, prioritizing transparency and inclusivity. Understanding public consultation helps differentiate it from participatory budgeting, which empowers citizens to directly allocate portions of a public budget.
Defining Participatory Budgeting
Participatory budgeting is a democratic process in which community members directly decide how to allocate a portion of a public budget, enhancing transparency and civic engagement. Unlike general public consultation, which gathers input and opinions without guaranteeing implementation, participatory budgeting empowers citizens with decision-making authority over specific financial resources. This approach fosters inclusivity, accountability, and ensures that public funds address community priorities effectively.
Key Differences Between Public Consultation and Participatory Budgeting
Public consultation involves gathering community feedback on policies or projects to inform decision-making, whereas participatory budgeting empowers citizens to directly allocate portions of a public budget. Public consultation primarily serves as an advisory process, while participatory budgeting grants participants decision-making authority over financial resources. The key difference lies in the level of citizen influence, with participatory budgeting enabling active budget control and public consultation focusing on input collection.
Objectives and Outcomes: A Comparative Overview
Public consultation aims to gather citizen input to inform policymakers and improve transparency, resulting in more inclusive decision-making processes. Participatory budgeting directly involves community members in allocating public funds, enhancing democratic engagement and ensuring resources align with local priorities. Both approaches foster civic participation but differ in their scope of influence and tangible impact on budgetary decisions.
Stakeholder Engagement in Public Processes
Public consultation involves gathering feedback from stakeholders to inform decision-making, while participatory budgeting empowers community members to directly allocate public funds, enhancing transparency and accountability. Effective stakeholder engagement in these public processes fosters inclusive dialogue, ensuring diverse perspectives influence policy outcomes and resource distribution. Integrating both approaches strengthens democratic governance by promoting active citizen participation and trust in public institutions.
Methods and Tools Used in Each Approach
Public consultation primarily employs surveys, focus groups, and town hall meetings to gather citizen feedback on specific policies or projects, ensuring broad input with relatively low resource investment. Participatory budgeting utilizes digital platforms, workshops, and deliberative forums to engage residents directly in decision-making on budget allocation, promoting deeper involvement and transparent resource distribution. Both methods leverage online tools and data analytics to enhance accessibility and analyze community priorities efficiently.
Benefits and Challenges of Public Consultation
Public consultation offers a platform for diverse stakeholder input, enhancing transparency and community trust in decision-making processes. It facilitates early identification of potential issues and promotes informed policymaking by incorporating a wide range of perspectives. Challenges include limited public engagement due to lack of awareness or interest, and potential dominance by vocal minority groups, which can skew outcomes and reduce representativeness.
Impact and Effectiveness of Participatory Budgeting
Participatory budgeting directly involves citizens in allocating public funds, increasing transparency and accountability in decision-making processes. Studies show this approach boosts community engagement, leading to more equitable resource distribution and enhanced public trust. Compared to traditional public consultation, participatory budgeting delivers tangible impact by empowering residents to prioritize projects that address local needs effectively.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Public consultation in urban planning is exemplified by New York City's EngageNYC platform, where residents provide feedback on development projects through surveys and public forums. Participatory budgeting, as seen in Porto Alegre, Brazil, empowers citizens to directly allocate municipal funds, enhancing transparency and community engagement. Case studies from these cities demonstrate how public consultation gathers input broadly, while participatory budgeting enables tangible decision-making power at the community level.
Future Trends in Civic Participation
Emerging trends in civic participation highlight a shift from traditional public consultation toward more inclusive participatory budgeting models that empower citizens with direct decision-making authority over local expenditures. Digital platforms and AI-driven tools enhance transparency and facilitate real-time feedback, fostering greater community engagement and accountability. Future developments focus on integrating data analytics and collaborative governance to tailor budgeting processes, ensuring equitable resource allocation aligned with diverse community priorities.
Related Important Terms
Co-creation Workshops
Public consultation gathers community feedback through surveys and meetings, while participatory budgeting actively involves citizens in allocating public funds. Co-creation workshops serve as a dynamic platform within participatory budgeting, enabling stakeholders to collaboratively design budget priorities and ensure more inclusive, transparent decision-making.
Digital Townhalls
Digital Townhalls enhance public consultation by enabling widespread citizen input through virtual meetings and surveys, fostering transparent communication between governments and communities. Participatory budgeting leverages these digital platforms to directly involve residents in allocating funds, increasing accountability and promoting inclusive decision-making.
Deliberative Polling
Deliberative Polling enhances public consultation by combining representative sampling with informed deliberation, providing a statistically robust reflection of public opinion that improves decision-making accuracy. Participatory budgeting focuses on direct allocation of funds by citizens, while Deliberative Polling emphasizes deep engagement and considered judgment to guide policy priorities beyond mere budget distribution.
Citizen Assemblies
Citizen Assemblies empower residents to engage deeply in decision-making, fostering inclusive deliberation beyond traditional public consultations by promoting collective judgment on budget priorities. Unlike participatory budgeting, which often limits input to financial allocations, Citizen Assemblies integrate diverse perspectives to shape broader policy frameworks and community goals.
Participatory Mapping
Participatory mapping enhances public consultation by actively involving community members in spatial data creation, fostering more inclusive decision-making processes. This approach strengthens participatory budgeting by visually identifying local priorities and resource allocations, thereby increasing transparency and accountability in public fund distribution.
Preference Aggregation
Public consultation involves gathering diverse opinions from citizens to inform decisions, while participatory budgeting actively engages community members in allocating public funds, enhancing preference aggregation by directly linking expressed preferences to budgetary outcomes. This democratic process improves transparency and accountability, ensuring resource distribution aligns with collective priorities.
Budget Hackathons
Budget Hackathons foster intense public consultation by engaging citizens directly in designing and prioritizing budget allocations through collaborative workshops and digital platforms. These events enhance participatory budgeting by crowdsourcing innovative solutions, increasing transparency, and empowering communities to influence fiscal decisions effectively.
Consensus Conferences
Consensus Conferences serve as a structured public consultation method that actively involves citizens in evaluating complex policy issues, fostering informed deliberation and collective decision-making. Unlike participatory budgeting, which allocates financial resources based on direct citizen input, Consensus Conferences emphasize consensus-building through expert presentations and facilitated discussions to guide policy formulation.
Open Budget Visualization
Open Budget Visualization enhances transparency by transforming complex budget data into accessible, interactive graphics that empower citizens to understand and monitor public spending. Unlike public consultation, which gathers citizen feedback, participatory budgeting leverages these visual tools to actively involve residents in decision-making, fostering informed community engagement and equitable resource allocation.
Civic Tech Platforms
Civic tech platforms enhance public consultation by facilitating real-time feedback and data collection from diverse communities, while participatory budgeting employs these technologies to empower citizens in decision-making over budget allocations. Integrating both processes through digital platforms increases transparency, accountability, and active civic engagement, driving more inclusive and informed governance outcomes.
public consultation vs participatory budgeting Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com