Public tech emphasizes broad accessibility and user-friendly solutions designed for the general population, while civic tech targets government-related services and policy engagement to enhance democracy. Public tech projects prioritize inclusivity and ease of use across diverse communities, whereas civic tech focuses on tools that facilitate communication between citizens and public institutions. Both spheres aim to improve public life but differ in their core objectives and stakeholder involvement.
Table of Comparison
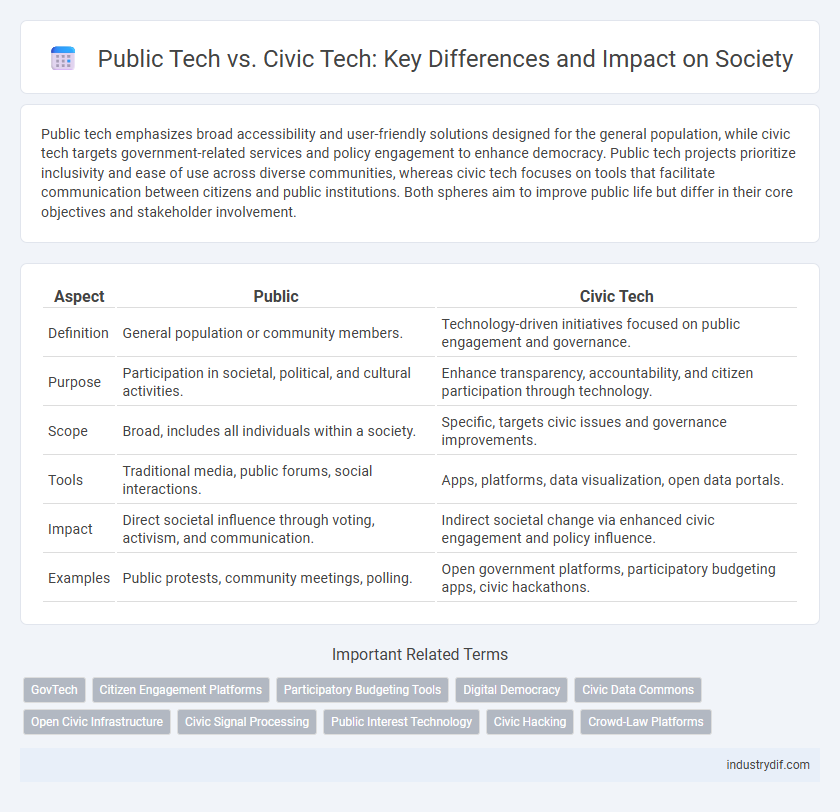
| Aspect | Public | Civic Tech |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | General population or community members. | Technology-driven initiatives focused on public engagement and governance. |
| Purpose | Participation in societal, political, and cultural activities. | Enhance transparency, accountability, and citizen participation through technology. |
| Scope | Broad, includes all individuals within a society. | Specific, targets civic issues and governance improvements. |
| Tools | Traditional media, public forums, social interactions. | Apps, platforms, data visualization, open data portals. |
| Impact | Direct societal influence through voting, activism, and communication. | Indirect societal change via enhanced civic engagement and policy influence. |
| Examples | Public protests, community meetings, polling. | Open government platforms, participatory budgeting apps, civic hackathons. |
Defining Public Tech: Scope and Applications
Public Tech encompasses digital tools and platforms developed to improve government functions, public services, and citizen engagement, with a primary focus on enhancing transparency and accessibility in the public sector. Its applications range from digital identity systems and e-governance portals to public health monitoring and disaster response technologies. Unlike Civic Tech, which centers on grassroots participation and citizen-driven initiatives, Public Tech is institutionally driven and integrated within official government workflows.
Understanding Civic Tech: Key Features
Civic tech leverages digital tools and platforms to enhance citizen engagement, transparency, and government accountability, distinguishing it from traditional public services. Key features include open data access, participatory decision-making, and real-time communication between officials and the public. This technology fosters collaboration, enabling communities to influence policy and improve public service delivery effectively.
Historical Evolution of Public and Civic Tech
Public tech originated from government-driven initiatives aimed at improving administrative efficiency and public service delivery, evolving through the digital revolution with technologies like e-governance and digital identity systems. Civic tech emerged later as a grassroots movement leveraging open-source platforms, social media, and participatory apps to enhance citizen engagement, transparency, and collaboration in governance. The historical evolution of both domains reflects a shift from top-down institutional control toward decentralized, community-driven innovations that empower public participation.
Primary Stakeholders in Public vs Civic Tech
Primary stakeholders in public technology typically include government agencies, public sector employees, and citizens who directly interact with government services. In contrast, civic technology emphasizes engagement from non-governmental organizations, community groups, and individual citizens actively participating in governance and societal problem-solving. Public tech focuses on service delivery efficiency, while civic tech prioritizes collaborative innovation and public involvement.
Main Objectives: Public Tech vs Civic Tech
Public Tech primarily aims to enhance government service delivery and improve administrative efficiency through digital solutions, focusing on transparency, data management, and public sector innovation. Civic Tech centers on empowering citizens by facilitating participation, engagement, and collaboration in governance, addressing community needs through open data platforms and digital tools for activism. Both fields leverage technology but differ in their core objectives: Public Tech targets institutional improvement while Civic Tech fosters grassroots involvement.
Technology Implementation in Public Services
Technology implementation in public services transforms citizen engagement and streamlines administrative processes through digital platforms, mobile applications, and data analytics. Public tech focuses on deploying scalable, secure IT infrastructure, while civic tech emphasizes participatory tools that empower community-driven problem solving. Integrating these approaches enhances transparency, efficiency, and responsiveness in government operations.
Community Engagement in Civic Tech
Civic Tech leverages digital platforms to enhance community engagement by facilitating direct citizen participation in local governance and decision-making processes. Tools such as open data portals, participatory budgeting apps, and online forums empower residents to voice opinions, collaborate on public projects, and monitor government performance. This technology-driven approach fosters transparency, accountability, and inclusive dialogue between government entities and the communities they serve.
Funding Models: Public vs Civic Tech Initiatives
Public tech initiatives typically rely on government funding, grants, and taxpayer resources to ensure sustainable development and broad accessibility, emphasizing accountability and regulatory compliance. Civic tech projects often depend on a mix of crowdfunding, philanthropic donations, and volunteer contributions, fostering community engagement and innovative problem-solving outside traditional bureaucratic structures. This divergence in funding models shapes the scope, scalability, and impact of each approach in addressing public needs.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Public and Civic Tech
Case studies in public tech highlight transformative projects like Estonia's e-Residency program, which revolutionized digital identity and government services for global users. Civic tech successes include Code for America's initiatives, where community-driven platforms improve local government transparency and citizen engagement. These examples illustrate how technology fosters efficient public administration and empowers civic participation worldwide.
Future Trends in Public and Civic Technology
Future trends in public and civic technology emphasize increased integration of artificial intelligence and blockchain to enhance transparency, security, and citizen engagement. Smart city initiatives will leverage IoT sensors and data analytics to improve urban planning and public services efficiently. The rise of decentralized platforms aims to empower communities with direct participation in governance and decision-making processes, fostering more inclusive and responsive public systems.
Related Important Terms
GovTech
GovTech refers to technologies specifically designed to improve government services, enhance public sector efficiency, and foster transparent governance. Unlike Civic Tech, which emphasizes citizen engagement and grassroots innovation, GovTech prioritizes the digital transformation of government operations and policy implementation.
Citizen Engagement Platforms
Citizen engagement platforms in public tech primarily facilitate direct interaction between government bodies and residents, enhancing transparency and participation in decision-making processes. Civic tech platforms often expand on this by integrating open data tools and collaborative features that empower communities to co-create solutions and drive local innovation.
Participatory Budgeting Tools
Participatory budgeting tools within public technology enable citizens to directly influence how government funds are allocated, promoting transparency and community engagement. Civic tech platforms specifically designed for participatory budgeting integrate features like real-time voting, proposal submissions, and budget tracking to increase public accountability and inclusiveness.
Digital Democracy
Public Tech emphasizes government-led digital services designed to improve administrative efficiency and public access, while Civic Tech empowers citizens to actively participate in digital democracy by facilitating collaboration, transparency, and community engagement through open-source platforms and participatory tools. Digital democracy thrives on Civic Tech's ability to harness technology such as e-voting systems, online deliberation, and crowdsourced policy-making to foster inclusive decision-making and strengthen democratic processes.
Civic Data Commons
Civic Data Commons serve as centralized repositories that enable municipalities, nonprofits, and citizens to access, share, and utilize public datasets for enhanced transparency and community-driven decision-making. Unlike traditional public technologies often limited to administrative functions, Civic Tech initiatives leveraging these data commons empower grassroots innovation and collaborative problem-solving through open data ecosystems.
Open Civic Infrastructure
Open Civic Infrastructure forms the backbone of Civic Tech by providing transparent, interoperable, and reusable digital tools that empower public participation and government accountability. Public Tech often refers to broader governmental technology strategies, while Civic Tech specifically leverages open-source platforms to enhance community engagement and collaborative decision-making.
Civic Signal Processing
Civic signal processing leverages advanced data analytics and machine learning to interpret and amplify public feedback for improving governance and community engagement. This approach contrasts with traditional public technology by prioritizing real-time, context-aware analysis of civic signals to facilitate transparent decision-making and responsive policy development.
Public Interest Technology
Public Interest Technology bridges the gap between Public and Civic Tech by applying technology solutions specifically designed to address societal challenges and improve public services. It emphasizes collaboration among government, nonprofits, and technologists to create ethical, inclusive, and impactful innovations that serve the common good.
Civic Hacking
Civic hacking leverages open data and community collaboration to develop innovative technological solutions that address public issues, contrasting with traditional public sector approaches that often rely on formal bureaucratic processes. By empowering citizens to co-create tools and services, civic tech fosters transparency, accountability, and enhanced civic engagement beyond institutional frameworks.
Crowd-Law Platforms
Crowd-law platforms empower public participation by harnessing collective intelligence to co-create legislation, bridging the gap between public and civic tech through transparent, inclusive policymaking. These platforms utilize digital tools to facilitate dialogue, gather feedback, and enhance governmental accountability, making lawmaking more democratic and data-driven.
Public vs Civic Tech Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com