Public consultation gathers input from citizens through structured feedback mechanisms, providing authorities with data to inform decision-making. Participatory foresight engages stakeholders in collaborative envisioning of future scenarios, fostering collective creativity and long-term strategic planning. Both approaches enhance democratic involvement but differ in scope and depth of engagement, with participatory foresight emphasizing proactive and anticipatory participation.
Table of Comparison
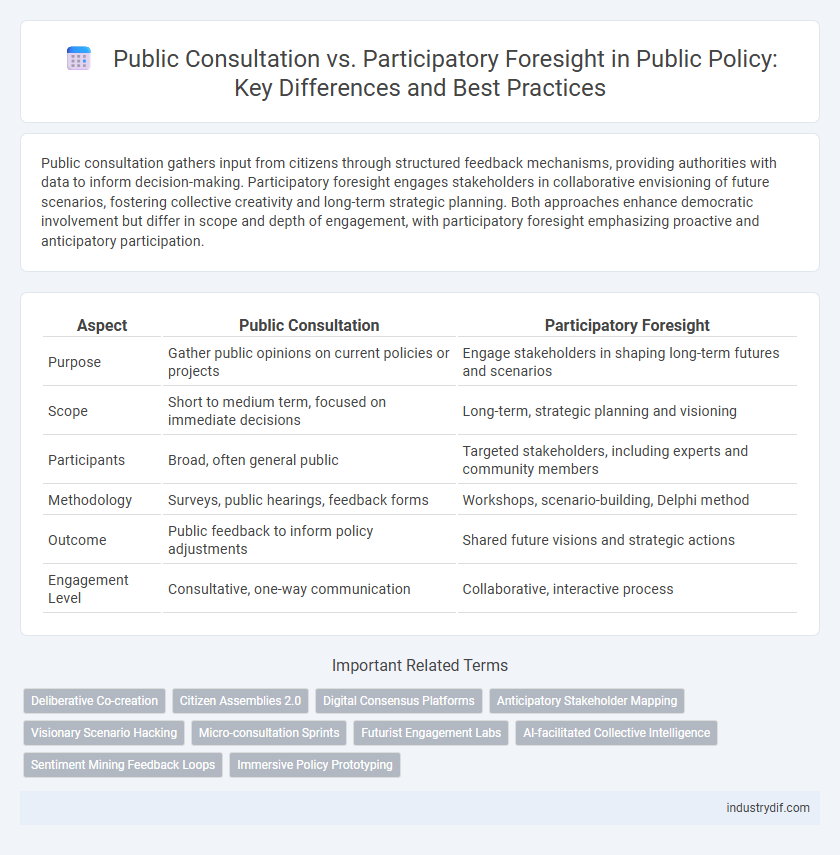
| Aspect | Public Consultation | Participatory Foresight |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Gather public opinions on current policies or projects | Engage stakeholders in shaping long-term futures and scenarios |
| Scope | Short to medium term, focused on immediate decisions | Long-term, strategic planning and visioning |
| Participants | Broad, often general public | Targeted stakeholders, including experts and community members |
| Methodology | Surveys, public hearings, feedback forms | Workshops, scenario-building, Delphi method |
| Outcome | Public feedback to inform policy adjustments | Shared future visions and strategic actions |
| Engagement Level | Consultative, one-way communication | Collaborative, interactive process |
Understanding Public Consultation: Definition and Importance
Public consultation involves systematically gathering input from citizens to inform policymaking, ensuring transparency and democratic engagement. It plays a crucial role in legitimizing decisions by incorporating diverse perspectives and promoting accountability. Unlike participatory foresight, which emphasizes future-oriented scenario planning, public consultation primarily focuses on current issues and stakeholder feedback.
What Is Participatory Foresight? Key Concepts Explained
Participatory foresight is a collaborative approach to anticipating and shaping future scenarios by engaging diverse stakeholders in the decision-making process. This method integrates collective intelligence, scenario planning, and long-term visioning to co-create adaptable strategies that address complex social, economic, and environmental challenges. Unlike traditional public consultation, participatory foresight emphasizes continuous dialogue, shared ownership, and proactive innovation to foster resilient and inclusive futures.
Core Objectives: Public Consultation vs Participatory Foresight
Public consultation primarily aims to gather diverse public opinions to inform decision-making processes, ensuring transparency and inclusiveness. Participatory foresight focuses on collaboratively envisioning future scenarios to guide strategic planning and innovation, emphasizing co-creation and anticipatory governance. While both engage stakeholders, public consultation collects feedback on current issues, whereas participatory foresight actively shapes long-term policies through collective foresight exercises.
Methodological Approaches: Comparing Tools and Techniques
Public consultation primarily employs surveys, focus groups, and town hall meetings to gather stakeholder opinions efficiently, emphasizing quantitative and qualitative data collection. Participatory foresight integrates scenario planning, Delphi methods, and visioning workshops, fostering collective anticipation of future trends through iterative dialogue and expert facilitation. These methodological approaches differ in their scope and depth, with public consultation targeting immediate feedback and participatory foresight enabling strategic, long-term decision-making.
Stakeholder Engagement: Who Gets Involved and How
Public consultation typically involves a broad range of stakeholders providing feedback on specific proposals through surveys, forums, or comment periods, ensuring inclusivity but often limited to reactive participation. Participatory foresight engages stakeholders more proactively and repeatedly, including experts, community members, and policymakers collaborating in scenario-building and future planning processes. This method fosters deeper involvement by emphasizing co-creation, iterative dialogue, and long-term commitment to shared visions and adaptive strategies.
Outcome Differences: Short-Term Feedback vs Long-Term Visioning
Public consultation often generates immediate, short-term feedback focused on current issues, enabling policymakers to address urgent community needs quickly. Participatory foresight emphasizes long-term visioning, engaging stakeholders in envisioning future scenarios and strategic planning that shapes sustainable development over decades. The outcome difference lies in consultation providing actionable insights for present decisions, while foresight cultivates adaptive, forward-looking policies anticipating complex future challenges.
Integration in Policy-Making: Use Cases and Impacts
Public consultation often gathers stakeholder feedback on existing policies, while participatory foresight engages diverse groups in envisioning future scenarios to inform long-term strategies. Integration of participatory foresight in policy-making enhances adaptive governance by anticipating emerging trends and uncertainties, leading to more resilient and forward-looking decisions. Case studies in urban planning and climate policy demonstrate significant impacts, such as increased stakeholder buy-in and improved policy relevance through co-created knowledge and scenario-based deliberation.
Strengths and Limitations of Public Consultation
Public consultation offers broad stakeholder input, enhancing decision-making through diverse perspectives and democratic legitimacy. However, it often faces limitations such as superficial engagement, limited influence on policy outcomes, and potential biases from vocal minority groups. Despite these constraints, public consultation remains a valuable tool for capturing immediate public opinions but may lack the forward-looking, integrative approach found in participatory foresight.
Strengths and Limitations of Participatory Foresight
Participatory foresight enables diverse stakeholders to collaboratively envision future scenarios, fostering inclusivity and proactive decision-making in public policy. Its strengths lie in generating rich qualitative insights and enhancing collective ownership of outcomes, though it can be limited by potential biases, resource intensiveness, and challenges in representing marginalized voices. Unlike traditional public consultation, participatory foresight emphasizes forward-looking engagement rather than reactive feedback, making it more suitable for complex, long-term strategic planning.
Choosing the Right Approach: Contextual Considerations
Public consultation involves gathering input from a broad audience to inform decision-making, while participatory foresight engages stakeholders in collaboratively envisioning future scenarios and shaping strategic plans. Choosing the right approach depends on contextual considerations such as the complexity of the issue, the desired level of stakeholder involvement, and the timeframe for outcomes. Effective decision-making integrates the scale of participation, clarity of objectives, and resource availability to select between consultative feedback and forward-looking, co-creative processes.
Related Important Terms
Deliberative Co-creation
Deliberative co-creation in public consultation involves stakeholders collaboratively engaging in structured dialogue to shape policy outcomes, emphasizing inclusivity and informed decision-making. Participatory foresight extends this by integrating future-oriented scenarios through collective intelligence, enabling communities to anticipate and co-design sustainable solutions.
Citizen Assemblies 2.0
Citizen Assemblies 2.0 exemplify participatory foresight by actively engaging diverse stakeholders in co-creating future scenarios, moving beyond traditional public consultations that often limit input to feedback and opinions. This advanced model integrates real-time data analysis and digital platforms to foster inclusive, deliberative democracy, enhancing the quality and impact of foresight processes.
Digital Consensus Platforms
Digital consensus platforms enhance public consultation by enabling interactive dialogue and real-time feedback, while participatory foresight leverages these platforms to collaboratively envision future scenarios and policy outcomes. This integration fosters inclusive decision-making processes by combining immediate public input with strategic long-term planning.
Anticipatory Stakeholder Mapping
Public consultation involves gathering feedback from community members through surveys or forums, while participatory foresight engages stakeholders in envisioning future scenarios to guide decision-making. Anticipatory Stakeholder Mapping identifies key actors and their potential influence on future developments, enhancing strategic planning in both approaches.
Visionary Scenario Hacking
Public consultation gathers broad-based feedback on policy proposals, while participatory foresight engages stakeholders in co-creating future scenarios to drive innovation and strategic planning. Visionary Scenario Hacking leverages collaborative foresight techniques to challenge assumptions and explore transformative pathways, enhancing adaptive governance and long-term resilience.
Micro-consultation Sprints
Micro-consultation Sprints enhance public engagement by enabling rapid, focused feedback cycles within participatory foresight frameworks, contrasting with traditional public consultations that often rely on broader, less frequent input. This agile approach accelerates iterative dialogue, harnessing diverse stakeholder insights to shape future-oriented policies with higher precision and inclusivity.
Futurist Engagement Labs
Futurist Engagement Labs specialize in blending public consultation with participatory foresight by actively involving diverse stakeholders in scenario planning and future-oriented decision-making processes. Their approach leverages interactive workshops and real-time feedback tools to create inclusive strategies that anticipate societal changes effectively.
AI-facilitated Collective Intelligence
Public consultation gathers individual opinions to inform decisions, while participatory foresight leverages AI-facilitated collective intelligence to predict future scenarios through collaborative problem-solving and trend analysis. AI-enhanced platforms synthesize diverse stakeholder inputs, enabling dynamic interaction and deeper insights for proactive policy and innovation strategies.
Sentiment Mining Feedback Loops
Public consultation primarily gathers opinions through sentiment mining feedback loops to gauge immediate public reactions, while participatory foresight employs these loops to iteratively refine future scenarios by integrating diverse stakeholder insights. Sentiment mining enables real-time analysis of emotions and attitudes, enhancing adaptive decision-making and fostering proactive community engagement in both processes.
Immersive Policy Prototyping
Immersive Policy Prototyping enables deeper citizen engagement by simulating future policy impacts in realistic virtual environments, surpassing traditional public consultation methods that often rely on passive feedback collection. This participatory foresight approach fosters collaborative decision-making and adaptive policy design by integrating diverse stakeholder insights through interactive, scenario-based experiences.
public consultation vs participatory foresight Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com