Public pet initiatives highlight the contrast between public education and experiential learning by emphasizing hands-on interaction with animals to enhance understanding and empathy. Experiential learning allows individuals to engage directly with pets, fostering deeper emotional connections and practical knowledge that traditional classroom settings often lack. This approach proves more effective in teaching responsible pet ownership, animal behavior, and welfare concepts through real-world experience rather than solely theoretical instruction.
Table of Comparison
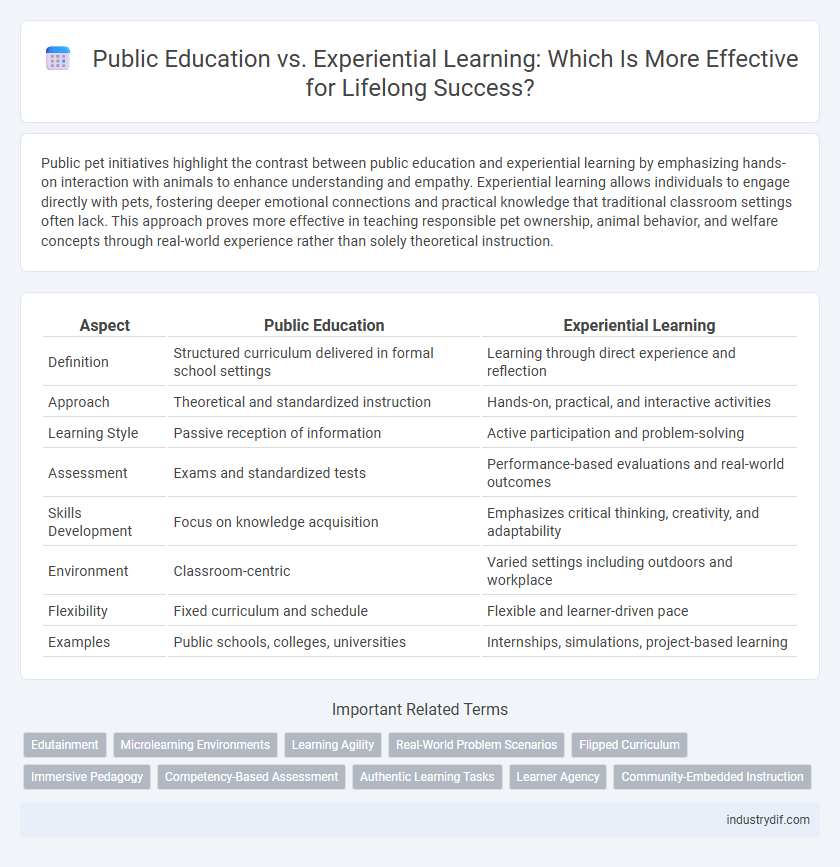
| Aspect | Public Education | Experiential Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured curriculum delivered in formal school settings | Learning through direct experience and reflection |
| Approach | Theoretical and standardized instruction | Hands-on, practical, and interactive activities |
| Learning Style | Passive reception of information | Active participation and problem-solving |
| Assessment | Exams and standardized tests | Performance-based evaluations and real-world outcomes |
| Skills Development | Focus on knowledge acquisition | Emphasizes critical thinking, creativity, and adaptability |
| Environment | Classroom-centric | Varied settings including outdoors and workplace |
| Flexibility | Fixed curriculum and schedule | Flexible and learner-driven pace |
| Examples | Public schools, colleges, universities | Internships, simulations, project-based learning |
Overview of Public Education Systems
Public education systems are structured to provide standardized curricula across diverse populations, emphasizing foundational knowledge in subjects such as math, science, and language arts. These systems rely on age-based grade levels, certified educators, and formal assessment methods to ensure consistent learning outcomes nationwide. Public education often prioritizes regulatory compliance and accessibility, which can limit flexibility compared to experiential learning approaches that emphasize practical, hands-on experience.
Defining Experiential Learning
Experiential learning is a hands-on educational approach emphasizing direct experience, critical reflection, and active experimentation to foster deeper understanding and skill development. Unlike traditional public education, which often relies on passive listening and rote memorization, experiential learning engages students through real-world challenges and collaborative problem-solving. This method enhances retention and adaptability by connecting theoretical knowledge with practical application.
Historical Evolution of Education Models
Public education systems have evolved from rigid, standardized models emphasizing rote memorization to more dynamic frameworks integrating experiential learning. Historically, education shifted from classical methods dominated by textbooks and lectures to approaches valuing hands-on activities, critical thinking, and real-world application. This evolution reflects societal demands for adaptable skills, fostering lifelong learning beyond traditional classroom boundaries.
Key Differences Between Public Education and Experiential Learning
Public education typically follows a structured curriculum with standardized assessments, emphasizing theoretical knowledge and classroom instruction. Experiential learning prioritizes hands-on activities, real-world experiences, and active participation, fostering critical thinking and practical skills development. Key differences include the learning environment, assessment methods, and the degree of student engagement, with experiential learning offering personalized and immersive opportunities beyond traditional academic settings.
Benefits of Traditional Public Education
Traditional public education provides a structured curriculum that ensures consistent learning standards and comprehensive coverage of core academic subjects such as math, science, and language arts. It offers access to certified teachers, standardized assessments, and resources that support student development and socialization in a diverse environment. Public schools also facilitate social equity by providing free education to all students regardless of socioeconomic background, promoting inclusivity and community engagement.
Advantages of Experiential Learning Approaches
Experiential learning approaches enhance student engagement by providing hands-on experiences that foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills beyond traditional public education methods. These approaches facilitate deeper understanding through real-world application, promoting retention and adaptability in diverse contexts. Evidence shows that experiential learning improves collaboration and motivation, leading to higher academic achievement and practical skill development.
Challenges Facing Public Education Today
Public education faces significant challenges including outdated curricula, limited resources, and standardized testing pressures that often fail to address diverse learning needs. Experiential learning offers dynamic alternatives by fostering critical thinking and real-world problem solving, but integrating such methods within rigid public school systems remains difficult. Budget constraints and insufficient teacher training exacerbate these obstacles, hindering the adoption of more interactive and student-centered educational models.
Integrating Experiential Learning in Public Schools
Integrating experiential learning in public schools enhances student engagement by providing hands-on activities that complement traditional academic curricula. This approach promotes critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and real-world application of knowledge, leading to improved academic outcomes and lifelong learning habits. Public education systems that incorporate project-based learning, internships, and community partnerships foster deeper understanding and prepare students for future workforce demands.
Case Studies: Success Stories in Experiential Learning
Case studies in experiential learning highlight transformative outcomes in public education, showcasing improved student engagement and retention. Programs like project-based learning at High Tech High and internships through Chicago's Youth Guidance demonstrate significant gains in critical thinking and real-world skills. These success stories underline the effectiveness of hands-on experiences in bridging theory and practice within public education settings.
Future Trends in Education: Blending Tradition with Experience
Future trends in education emphasize integrating public education systems with experiential learning to enhance student engagement and critical thinking skills. Incorporating real-world projects and hands-on activities within traditional curricula fosters deeper understanding and prepares students for dynamic work environments. This blended approach leverages technology and community partnerships to create adaptive, personalized learning experiences that reflect evolving societal and economic demands.
Related Important Terms
Edutainment
Edutainment leverages interactive and multimedia tools to blend public education with experiential learning, enhancing engagement and retention by making complex subjects accessible and enjoyable. This approach transforms traditional classroom content into dynamic experiences, promoting deeper understanding through hands-on activities and real-world simulations.
Microlearning Environments
Microlearning environments enhance public education by delivering concise, targeted lessons that improve retention and engagement through interactive, real-world scenarios. These platforms bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and experiential learning, enabling learners to apply concepts immediately in practical contexts.
Learning Agility
Learning agility, a critical skill in both public education and experiential learning, reflects a learner's ability to quickly adapt and apply knowledge in changing environments. Experiential learning significantly enhances learning agility by providing real-world challenges that encourage practical problem-solving and continuous feedback, fostering deeper understanding compared to traditional public education methods.
Real-World Problem Scenarios
Experiential learning immerses students in real-world problem scenarios, enhancing critical thinking and practical skills that traditional public education often lacks. This hands-on approach bridges theory and practice, preparing learners to tackle complex challenges with innovative solutions in dynamic environments.
Flipped Curriculum
Flipped Curriculum transforms public education by reversing traditional teaching methods, allowing students to engage with instructional content at home and apply knowledge through interactive, experiential learning in the classroom. This approach enhances student comprehension, critical thinking, and collaboration, aligning educational outcomes with real-world skills and modern workforce demands.
Immersive Pedagogy
Immersive pedagogy in public education emphasizes hands-on, experiential learning environments that enhance student engagement and critical thinking skills beyond traditional classroom methods. Integrating virtual reality, simulations, and real-world problem-solving activities fosters deeper understanding and retention compared to conventional lecture-based instruction.
Competency-Based Assessment
Competency-based assessment in public education emphasizes mastery of specific skills through measurable performance criteria, contrasting with experiential learning's focus on real-world experiences and practical application. This approach ensures students demonstrate concrete competencies before advancing, promoting personalized pathways and accountability in educational outcomes.
Authentic Learning Tasks
Authentic learning tasks in public education emphasize real-world problem-solving that connects curriculum to practical experiences, fostering deeper understanding and retention. Experiential learning integrates hands-on activities and community engagement, enhancing critical thinking and collaboration skills beyond traditional classroom instruction.
Learner Agency
Learner agency in public education often emphasizes standardized curricula, limiting student autonomy and personalized learning paths. Experiential learning fosters stronger learner agency by encouraging students to engage actively, make decisions, and reflect on real-world experiences, promoting deeper understanding and self-directed growth.
Community-Embedded Instruction
Community-Embedded Instruction enhances public education by integrating real-world experiences within local settings, fostering practical skills and social responsibility. This approach bridges classroom learning with community engagement, promoting deeper understanding and active citizenship.
public education vs experiential learning Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com