Community feedback fosters direct user input, enabling businesses to understand public needs and preferences effectively. Co-creation platforms engage users as active partners in developing products or services, driving innovation through collaborative creativity. Combining these approaches empowers organizations to build solutions that resonate deeply with their communities and enhance customer satisfaction.
Table of Comparison
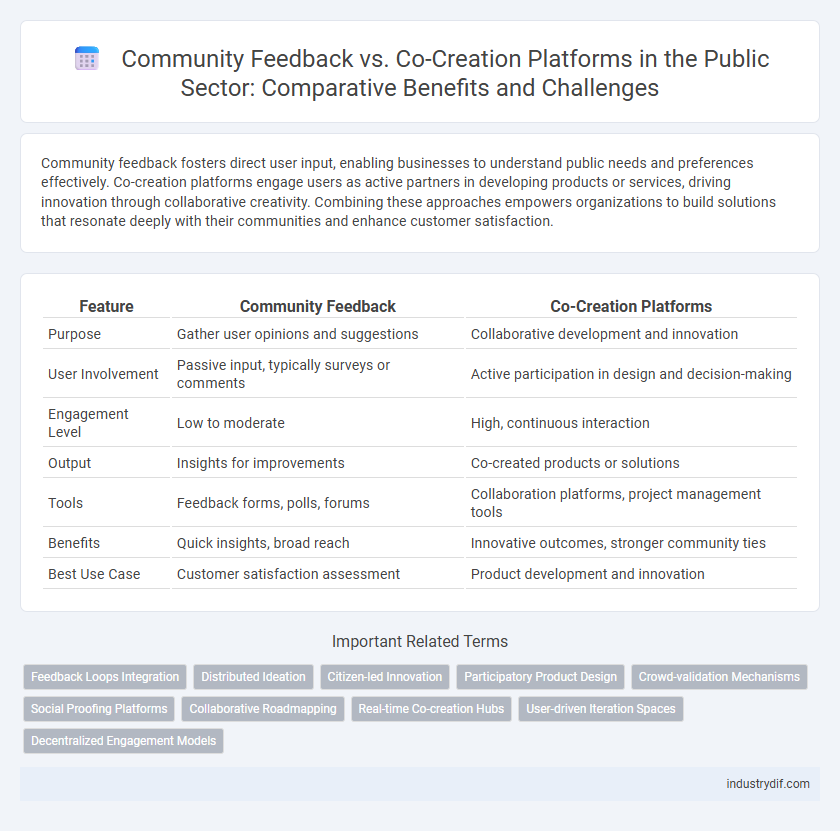
| Feature | Community Feedback | Co-Creation Platforms |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Gather user opinions and suggestions | Collaborative development and innovation |
| User Involvement | Passive input, typically surveys or comments | Active participation in design and decision-making |
| Engagement Level | Low to moderate | High, continuous interaction |
| Output | Insights for improvements | Co-created products or solutions |
| Tools | Feedback forms, polls, forums | Collaboration platforms, project management tools |
| Benefits | Quick insights, broad reach | Innovative outcomes, stronger community ties |
| Best Use Case | Customer satisfaction assessment | Product development and innovation |
Understanding Community Feedback in Public Industries
Community feedback in public industries involves collecting opinions, concerns, and suggestions from citizens to improve public services and policies effectively. Unlike co-creation platforms that actively engage community members in design and decision-making processes, community feedback primarily serves as an input for authorities to assess public needs and satisfaction levels. Analyzing this feedback through data-driven methods helps public institutions identify priority areas, enhance transparency, and foster trust between government bodies and the communities they serve.
Defining Co-Creation Platforms for Public Engagement
Co-creation platforms for public engagement enable direct collaboration between communities and organizations to jointly develop solutions, policies, or services, fostering deeper involvement than traditional community feedback mechanisms. These platforms facilitate interactive dialogues, idea sharing, and real-time input, allowing participants to contribute actively throughout the development process. By integrating diverse perspectives and expertise, co-creation platforms enhance transparency, trust, and innovation in public decision-making.
Key Differences Between Community Feedback and Co-Creation
Community feedback platforms primarily gather user opinions and insights through surveys, polls, and comment sections, enabling organizations to understand customer sentiments efficiently. Co-creation platforms involve stakeholders actively in the innovation process, facilitating collaborative development of products or services through workshops, brainstorming sessions, and prototype testing. The key difference lies in feedback being primarily reactive and evaluative, while co-creation is proactive and participatory, driving joint value creation and deeper engagement.
Benefits of Community Feedback for Public Sector Innovation
Community feedback fosters inclusive decision-making by directly incorporating residents' insights into public sector projects, enhancing transparency and trust. It enables government agencies to identify real-time issues and tailor solutions more effectively, leading to improved service delivery and resource allocation. Engaging the community through feedback mechanisms drives innovation by aligning initiatives with public needs, resulting in higher satisfaction and stronger civic engagement.
Advantages of Co-Creation Platforms in Policy Development
Co-creation platforms enhance policy development by fostering active collaboration between policymakers and community members, ensuring diverse perspectives are integrated into decision-making. These platforms facilitate real-time input, iterative feedback, and joint problem-solving, leading to more innovative and inclusive policy outcomes. The transparent and interactive nature of co-creation tools also builds trust and accountability, improving public engagement and satisfaction.
Challenges in Implementing Community Feedback Mechanisms
Community feedback mechanisms often encounter challenges including low engagement rates, difficulty in capturing diverse perspectives, and lack of transparency in how feedback is utilized. Unlike co-creation platforms, which foster collaborative development and shared ownership, feedback systems may suffer from one-way communication and limited participant influence. Ensuring effective moderation, real-time responsiveness, and integration of feedback into decision-making processes remain critical obstacles for meaningful community involvement.
Overcoming Barriers in Co-Creation Platform Adoption
Overcoming barriers in co-creation platform adoption involves addressing user engagement challenges and ensuring transparent communication channels to foster trust. Integrating community feedback mechanisms enhances platform relevance and encourages active participation by aligning features with user needs and expectations. Streamlined onboarding processes and continuous support reduce technical friction, promoting wider acceptance and sustained collaboration within diverse stakeholder groups.
Case Studies: Public Projects Leveraging Community Feedback
Public projects utilizing community feedback demonstrate higher engagement rates and improved project outcomes, as seen in initiatives like the New York City Participatory Budgeting process, which empowered residents to directly influence budget allocation. Co-creation platforms such as Iceland's Better Reykjavik combine feedback with collaborative decision-making, resulting in innovative urban solutions tailored to local needs. These case studies highlight the effectiveness of integrating community input through digital tools to enhance transparency and responsiveness in public sector projects.
Success Stories: Co-Creation Platforms in Public Services
Co-creation platforms in public services have demonstrated significant success by actively involving citizens in decision-making processes, leading to more tailored and effective policies. Platforms like Helsinki's Open Ministry enable residents to propose and refine legislative ideas, resulting in increased transparency and higher civic engagement rates. This participatory approach fosters trust between government and communities, enhancing service delivery and driving innovative public solutions.
Future Trends: Integrating Feedback and Co-Creation in the Public Sphere
Public sector innovation increasingly leverages community feedback and co-creation platforms to enhance civic engagement and service delivery. Emerging trends emphasize real-time data integration, AI-driven sentiment analysis, and collaborative digital environments that empower citizens to shape policies and projects actively. Future public platforms will prioritize transparency, inclusivity, and adaptive feedback loops to foster sustainable community-driven governance.
Related Important Terms
Feedback Loops Integration
Community feedback platforms collect user opinions and preferences, enabling organizations to identify key issues and opportunities for improvement. Co-creation platforms integrate continuous feedback loops by involving users directly in the design and development process, fostering collaborative innovation and more effective solutions.
Distributed Ideation
Community feedback platforms primarily collect and aggregate user opinions and suggestions for decision-making, whereas co-creation platforms enable active collaboration among diverse stakeholders to jointly develop innovative solutions. Distributed ideation thrives in co-creation environments by leveraging collective intelligence through interactive tools that facilitate real-time idea generation and refinement across geographically dispersed participants.
Citizen-led Innovation
Community feedback platforms primarily collect citizen opinions and insights to inform policy decisions, while co-creation platforms engage citizens as active collaborators in designing and implementing innovative solutions. Citizen-led innovation thrives in co-creation environments by leveraging collective expertise to address local challenges and enhance civic services.
Participatory Product Design
Participatory product design benefits from co-creation platforms by enabling direct collaboration between designers and end-users, fostering innovation through shared creativity and diverse perspectives. Community feedback platforms primarily gather user opinions post-development, limiting real-time influence on design decisions compared to the interactive, iterative processes facilitated by co-creation tools.
Crowd-validation Mechanisms
Community feedback platforms primarily gather opinions and preferences from a broad audience to validate ideas quickly, while co-creation platforms engage users collaboratively in developing solutions, enhancing depth and innovation through iterative crowd-validation mechanisms. Crowd-validation in co-creation leverages real-time user input and adaptive design processes to refine concepts, fostering higher engagement and more accurate alignment with community needs.
Social Proofing Platforms
Social proofing platforms enhance community feedback by enabling real-time validation and trust-building through user ratings, reviews, and endorsements, driving higher engagement and credibility. These platforms transform passive feedback into active co-creation by allowing users to contribute ideas, shape products, and influence decisions collaboratively.
Collaborative Roadmapping
Collaborative roadmapping leverages co-creation platforms to engage stakeholders directly in shaping project objectives and timelines, enabling iterative input and shared ownership beyond traditional community feedback mechanisms. These platforms facilitate real-time collaboration, ensuring diverse insights are integrated into strategic planning and enhancing transparency throughout the development process.
Real-time Co-creation Hubs
Real-time co-creation hubs enable dynamic collaboration by integrating community feedback directly into the development process, fostering innovation through immediate input and iterative design. These platforms create an interactive ecosystem where stakeholders collectively contribute, accelerating solutions tailored to community needs.
User-driven Iteration Spaces
User-driven iteration spaces in community feedback platforms facilitate continuous improvement by harnessing diverse user insights, while co-creation platforms enable deeper collaboration through real-time contribution and shared decision-making. Both approaches empower users to shape outcomes, but co-creation platforms offer structured environments for collective innovation beyond passive feedback.
Decentralized Engagement Models
Decentralized engagement models leverage community feedback and co-creation platforms to enhance participation by distributing decision-making power across multiple stakeholders. These models foster transparent collaboration and empower diverse contributors, driving innovation and ensuring that outcomes reflect collective input rather than top-down directives.
Community feedback vs Co-creation platforms Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com