Public notice serves as an official announcement to inform the community about important updates or regulations, ensuring transparency and compliance. An open data portal offers structured, accessible datasets for public use, promoting data-driven decision-making and innovation. Both tools enhance civic engagement but operate through different methods: direct communication versus interactive data access.
Table of Comparison
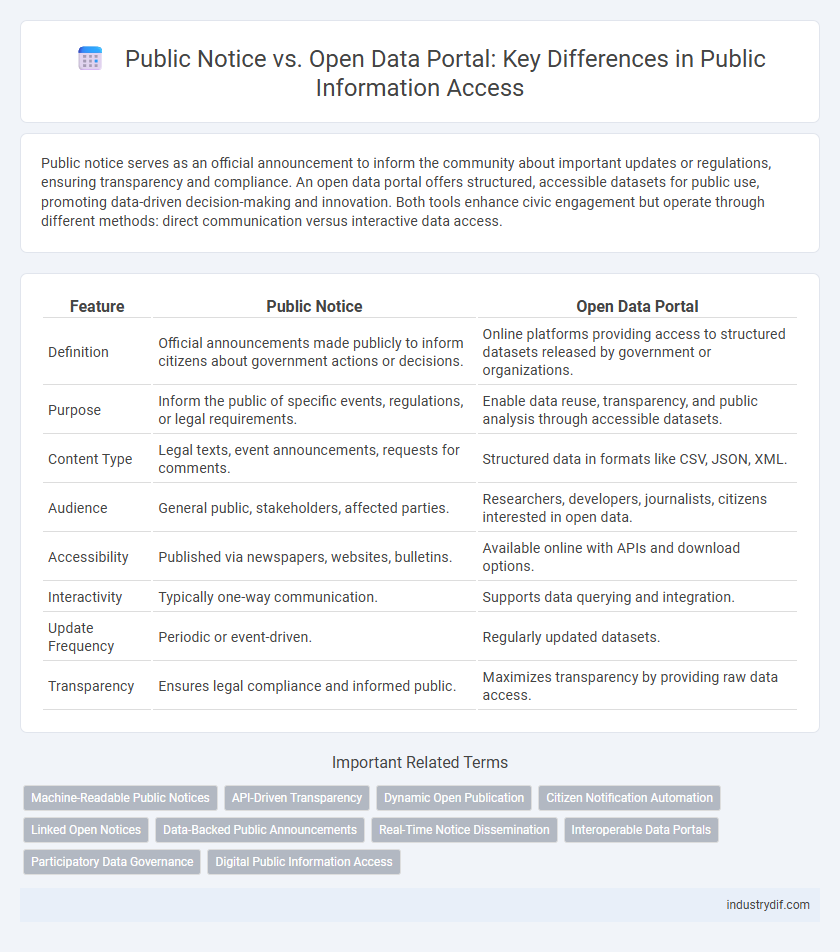
| Feature | Public Notice | Open Data Portal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official announcements made publicly to inform citizens about government actions or decisions. | Online platforms providing access to structured datasets released by government or organizations. |
| Purpose | Inform the public of specific events, regulations, or legal requirements. | Enable data reuse, transparency, and public analysis through accessible datasets. |
| Content Type | Legal texts, event announcements, requests for comments. | Structured data in formats like CSV, JSON, XML. |
| Audience | General public, stakeholders, affected parties. | Researchers, developers, journalists, citizens interested in open data. |
| Accessibility | Published via newspapers, websites, bulletins. | Available online with APIs and download options. |
| Interactivity | Typically one-way communication. | Supports data querying and integration. |
| Update Frequency | Periodic or event-driven. | Regularly updated datasets. |
| Transparency | Ensures legal compliance and informed public. | Maximizes transparency by providing raw data access. |
Definition of Public Notice
A public notice is an official announcement issued by government agencies or organizations to inform citizens about legal, regulatory, or administrative actions. It serves as a formal communication tool that ensures transparency and compliance with public notification requirements. Unlike an open data portal, which provides free access to datasets for public use and analysis, a public notice specifically targets informing the public about specific events, decisions, or policy changes.
Definition of Open Data Portal
An Open Data Portal is a centralized online platform that provides public access to datasets published by government agencies, organizations, or institutions in machine-readable formats. Unlike public notices, which serve as official announcements or legal disclosures intended for immediate informational purposes, Open Data Portals enable transparency, data-driven decision-making, and innovative applications by offering extensive, regularly updated datasets. These portals support interoperability through standardized metadata and APIs, facilitating easy data discovery, reuse, and integration across various sectors.
Historical Evolution: Public Notices and Open Data
Public notices originated as official announcements in newspapers to inform citizens about government actions and legal requirements, establishing a foundational method for public transparency. Open data portals, emerging in the 21st century, represent a digital evolution, enabling governments to share vast datasets online for public access, analysis, and reuse. This shift reflects advancements in technology and public demand for greater accountability through accessible, machine-readable information platforms.
Key Functions: Public Notice vs. Open Data Portal
Public notices serve as formal communications to inform the public about legal or regulatory matters, facilitating transparency and compliance with governmental procedures. Open data portals provide extensive access to datasets released by government agencies, enabling data-driven decision-making, research, and civic engagement. While public notices focus on specific announcements and legal requirements, open data portals encompass a broader range of data resources for analysis and innovation.
Accessibility and Transparency Comparison
Public notices provide targeted information in specific legal or regulatory contexts, often limited in scope and format, which may restrict broad accessibility. Open data portals offer comprehensive access to structured datasets, enabling greater transparency through machine-readable formats and user-friendly interfaces that support data analysis. The inherent design of open data portals fosters continuous public engagement and accountability beyond the static nature of traditional public notices.
Regulatory Frameworks Governing Each
Public notices are regulated by local government transparency laws mandating timely publication to inform citizens about legal actions, zoning changes, and public hearings. Open data portals operate under broader data governance frameworks such as the Open Data Charter or national policies promoting accessibility, privacy standards, and interoperability of datasets. Regulatory frameworks for public notices emphasize legal compliance and public participation, whereas open data portals focus on data quality, reusability, and open access principles.
Stakeholder Engagement: Impact and Reach
Public notices serve as formal communications targeting specific stakeholders, ensuring compliance and transparency in regulatory matters. Open data portals expand stakeholder engagement by providing broad access to datasets, enabling community analysis, innovation, and informed decision-making. The reach of open data portals surpasses traditional public notices by fostering ongoing interaction and participation from diverse audiences.
Technology Integration in Public Communication
Public notices serve as official announcements targeted to specific audiences, while open data portals provide comprehensive access to government datasets promoting transparency and civic engagement. Technology integration in public communication enhances real-time dissemination of information, enabling interactive platforms that support data accessibility and user empowerment. Leveraging APIs and mobile-friendly interfaces, governments improve public trust by facilitating seamless data retrieval and dynamic updates beyond traditional notice formats.
Challenges in Implementation and Adoption
Public notices often face challenges in implementation due to inconsistent dissemination methods and limited accessibility for diverse audiences, hindering widespread engagement. Open data portals encounter adoption barriers related to data standardization, quality assurance, and user-friendliness, which affect the ability of stakeholders to effectively utilize the information. Both systems require robust technological infrastructure and clear governance policies to overcome these obstacles and promote transparency.
Future Trends: Bridging Public Notices and Open Data Portals
Public notices are evolving from static announcements to dynamic datasets accessible through open data portals, enhancing transparency and citizen engagement. Future trends emphasize integrating real-time updates and interactive features within open data platforms, allowing users to analyze, visualize, and share public information seamlessly. Bridging public notices with open data portals enables governments to foster data-driven decision-making and promote greater accountability in public administration.
Related Important Terms
Machine-Readable Public Notices
Machine-readable public notices enhance transparency by enabling automated data extraction and analysis, unlike traditional public notices that are often unstructured and difficult to process. Open data portals provide centralized access to these machine-readable formats, facilitating efficient public engagement and data-driven decision-making.
API-Driven Transparency
Public notice provides static information for civic awareness, while open data portals enable dynamic access through API-driven transparency, allowing developers and citizens to query real-time government datasets efficiently. APIs in open data portals promote interactive engagement and foster innovation by delivering timely, machine-readable data that enhances accountability and public participation.
Dynamic Open Publication
Dynamic Open Publication enhances transparency by continuously updating public notices on open data portals, enabling real-time access to essential government information. This approach surpasses static public notices by integrating interactive data sets, fostering greater civic engagement and informed decision-making.
Citizen Notification Automation
Citizen Notification Automation streamlines public notice dissemination by integrating real-time updates directly from open data portals, enhancing transparency and timely communication. Leveraging automated alerts based on structured datasets ensures citizens receive precise information without manual intervention, improving civic engagement and responsiveness.
Linked Open Notices
Linked Open Notices enhance transparency by structuring public notices with semantic metadata, enabling seamless integration and querying within open data portals. This approach facilitates better accessibility and interoperability of government information compared to traditional public notice systems.
Data-Backed Public Announcements
Data-backed public announcements leverage verified datasets to enhance transparency and trust, providing citizens with accurate, actionable information compared to traditional public notices that often rely on static, unstructured text. Open data portals offer comprehensive access to raw datasets, enabling deeper analysis and community engagement beyond the summarized insights presented in public announcements.
Real-Time Notice Dissemination
Public notices provide official announcements that must be legally published and are often static, whereas open data portals offer dynamic, real-time access to updated datasets, enabling immediate dissemination and broader public engagement. Real-time notice dissemination through open data portals enhances transparency by allowing users to access, analyze, and share information instantly compared to traditional publication methods.
Interoperable Data Portals
Interoperable data portals enable seamless integration and standardized access to diverse government datasets, enhancing transparency beyond traditional public notices. These portals support machine-readable formats and API interfaces, facilitating data reuse and cross-agency collaboration for improved public service delivery.
Participatory Data Governance
Public notices provide official information directly from authorities, ensuring transparency and accountability, while open data portals offer accessible, machine-readable datasets that enable citizens to analyze and reuse information critically. Participatory data governance leverages both by fostering community engagement in data decision-making processes, enhancing data quality, inclusivity, and trust in public administration.
Digital Public Information Access
Public notices provide official announcements and legal information to citizens, ensuring transparency and compliance with regulatory requirements, while open data portals offer extensive, machine-readable datasets that enable broader public analysis and innovation through enhanced digital public information access. Digital public information access integrates both methods to maximize civic engagement, promoting accountability and data-driven decision-making across government services.
public notice vs open data portal Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com