Public policy involves decision-making by government authorities to address societal issues, often relying on top-down approaches. Participatory governance emphasizes inclusive collaboration, allowing stakeholders and community members to actively engage in the formulation and implementation of policies. Integrating participatory governance into public policy enhances transparency, accountability, and responsiveness to public needs.
Table of Comparison
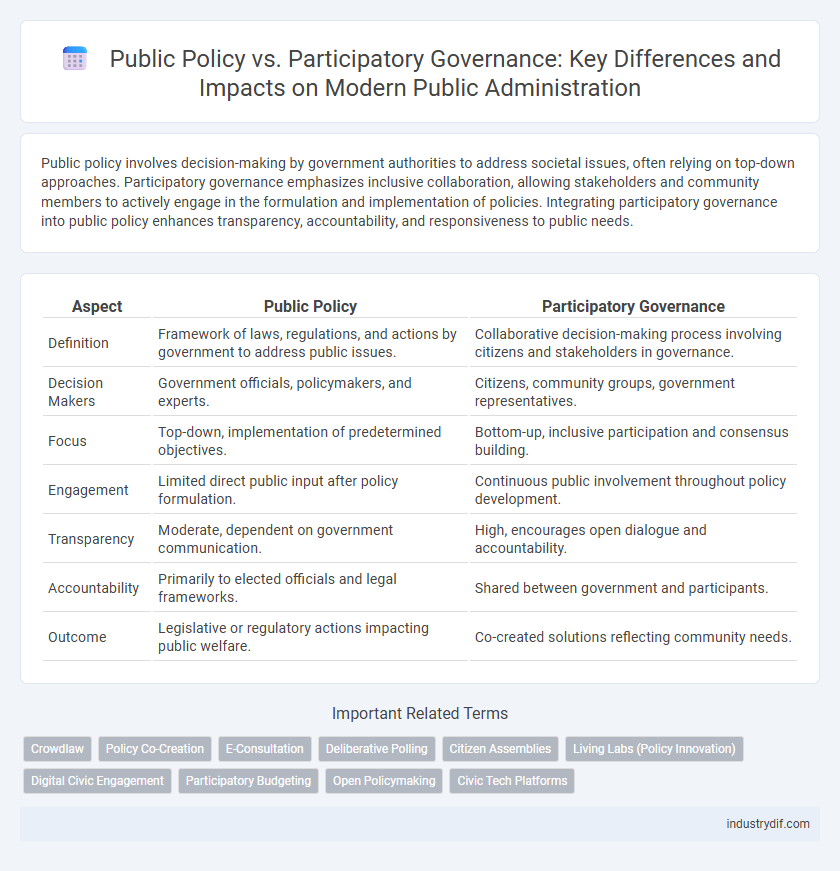
| Aspect | Public Policy | Participatory Governance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Framework of laws, regulations, and actions by government to address public issues. | Collaborative decision-making process involving citizens and stakeholders in governance. |
| Decision Makers | Government officials, policymakers, and experts. | Citizens, community groups, government representatives. |
| Focus | Top-down, implementation of predetermined objectives. | Bottom-up, inclusive participation and consensus building. |
| Engagement | Limited direct public input after policy formulation. | Continuous public involvement throughout policy development. |
| Transparency | Moderate, dependent on government communication. | High, encourages open dialogue and accountability. |
| Accountability | Primarily to elected officials and legal frameworks. | Shared between government and participants. |
| Outcome | Legislative or regulatory actions impacting public welfare. | Co-created solutions reflecting community needs. |
Defining Public Policy and Participatory Governance
Public policy refers to the system of laws, regulatory measures, courses of action, and funding priorities enacted by governmental institutions to address societal issues and promote the public good. Participatory governance is a democratic process that actively involves citizens, stakeholders, and community members in decision-making and policy formulation to enhance transparency, accountability, and inclusivity. Defining these concepts highlights public policy as the official framework for societal regulation, whereas participatory governance emphasizes collaborative engagement and shared authority in governance processes.
Historical Evolution of Public Policy
The historical evolution of public policy traces back to centralized decision-making processes within early governance structures, emphasizing top-down approaches to lawmaking and enforcement. Over time, shifts toward democratization and increased civic engagement led to participatory governance models that integrate citizen input in policy formulation and implementation. This transformation reflects broader societal changes prioritizing transparency, accountability, and inclusiveness in the governance framework.
The Rise of Participatory Governance Models
Participatory governance models have surged as a transformative approach in public policy, emphasizing direct citizen involvement in decision-making processes to enhance transparency and accountability. These models leverage digital platforms and community forums to facilitate inclusive dialogue, enabling diverse stakeholders to co-create policy solutions tailored to local needs. The shift from traditional top-down public policy frameworks to participatory governance reflects a growing demand for democratic legitimacy and more responsive public institutions.
Core Principles: Authority vs. Engagement
Public policy centers on authority, emphasizing top-down decision-making by government institutions to implement laws and regulations. Participatory governance prioritizes engagement, encouraging inclusive involvement of citizens in shaping policies through collaboration and dialogue. This fundamental difference highlights authority as centralized control versus engagement as decentralized participation in democratic processes.
Policy Formulation: Top-Down vs. Bottom-Up Approaches
Policy formulation in public policy often follows a top-down approach where decisions are made by centralized authorities and imposed on stakeholders, ensuring coherence and efficiency in implementation. Participatory governance embraces a bottom-up approach, engaging citizens and community groups in the decision-making process to enhance inclusivity, transparency, and local relevance. Both approaches shape policy outcomes by balancing expert-driven directives with grassroots inputs for more responsive governance.
Stakeholder Involvement in Decision-Making
Stakeholder involvement in decision-making within public policy ensures diverse perspectives from citizens, businesses, and interest groups are integrated into government actions, enhancing transparency and accountability. Participatory governance institutionalizes this engagement through mechanisms such as public consultations, advisory committees, and collaborative platforms, promoting inclusive and democratic processes. Effective stakeholder collaboration leads to more responsive policies that address community needs and build public trust.
Transparency and Accountability Mechanisms
Transparency in public policy ensures open access to information and decision-making processes, enabling citizens to scrutinize government actions. Participatory governance incorporates mechanisms such as public hearings and citizen advisory boards to enhance accountability by involving stakeholders directly in policy formulation and implementation. Both approaches foster a culture of responsibility by promoting continuous public oversight and feedback loops that hold officials accountable for their performance.
Impact on Policy Outcomes and Effectiveness
Public policy driven by traditional top-down approaches often results in limited stakeholder engagement, which can restrict policy effectiveness and adaptability. Participatory governance enhances policy outcomes by incorporating diverse community inputs, increasing transparency, and fostering accountability, leading to more responsive and sustainable solutions. Empirical studies show that participatory frameworks improve policy implementation success rates and public satisfaction compared to non-inclusive policy processes.
Case Studies: Comparative Applications
Case studies highlight distinct approaches in public policy and participatory governance, revealing variations in citizen engagement and decision-making processes. In Brazil's participatory budgeting model, increased transparency and local input improved policy outcomes compared to traditional top-down public policy frameworks in Mexico. Comparative analysis of these applications demonstrates the critical role of grassroots involvement in enhancing accountability and responsiveness in governance.
Future Trends in Public Administration
Future trends in public administration emphasize the integration of participatory governance with traditional public policy frameworks to enhance transparency, accountability, and citizen engagement. Digital platforms and data analytics are increasingly utilized to facilitate real-time stakeholder input and evidence-based decision-making processes. Advancements in AI and smart city technologies further enable adaptive, inclusive governance models that respond swiftly to complex societal challenges.
Related Important Terms
Crowdlaw
Crowdlaw enhances public policy by integrating participatory governance, enabling real-time citizen input to craft more inclusive regulations through digital platforms. This approach democratizes decision-making, leverages collective intelligence, and increases transparency, thereby improving policy effectiveness and public trust.
Policy Co-Creation
Policy co-creation in public policy leverages participatory governance by actively involving citizens, stakeholders, and government entities in collaborative decision-making processes that enhance transparency, inclusiveness, and accountability. This approach improves the relevance and effectiveness of policies by integrating diverse perspectives and fostering collective ownership.
E-Consultation
E-Consultation enhances public policy development by integrating citizen input through digital platforms, improving transparency, and fostering collaborative decision-making. This participatory governance tool enables real-time feedback and wider stakeholder engagement, resulting in more inclusive and democratic policy outcomes.
Deliberative Polling
Deliberative Polling integrates public policy development with participatory governance by randomly selecting diverse citizens to discuss policy issues in-depth, leading to more informed and representative policy outcomes. This method enhances democratic legitimacy and improves policy effectiveness by bridging expert knowledge and public preferences through structured deliberation.
Citizen Assemblies
Citizen assemblies serve as a foundational element in participatory governance by enabling diverse groups of citizens to deliberate on public policies, thereby enhancing democratic legitimacy and inclusivity. These assemblies contrast with traditional public policy processes by prioritizing direct citizen involvement and collective decision-making over top-down governmental directives.
Living Labs (Policy Innovation)
Living Labs serve as dynamic platforms fostering Public Policy innovation by integrating real-world user feedback into the governance process, enhancing policy responsiveness and effectiveness. Unlike traditional top-down policy frameworks, Participatory Governance through Living Labs promotes collaborative problem-solving among stakeholders, facilitating experimental approaches and iterative refinement in public service delivery.
Digital Civic Engagement
Digital civic engagement enhances participatory governance by leveraging interactive platforms that enable citizens to contribute directly to policy discussions and decision-making processes. Public policy increasingly integrates digital tools to facilitate transparency, inclusivity, and real-time feedback, transforming traditional top-down approaches into collaborative governance models.
Participatory Budgeting
Participatory budgeting empowers citizens to directly influence public spending decisions, enhancing transparency and accountability in public policy implementation. This democratic process fosters inclusive community engagement, leading to more equitable and effective allocation of resources based on local needs and priorities.
Open Policymaking
Open policymaking integrates public policy frameworks with participatory governance principles by actively involving citizens, stakeholders, and experts in decision-making processes to enhance transparency, accountability, and inclusiveness. This approach fosters collaborative problem-solving and democratic legitimacy, resulting in policies that better reflect community needs and improve public trust.
Civic Tech Platforms
Civic tech platforms empower participatory governance by enabling direct citizen engagement in policymaking processes, enhancing transparency and accountability in public policy formulation. These platforms utilize digital tools to facilitate real-time feedback, collaborative decision-making, and data-driven insights, bridging the gap between governments and communities for more inclusive and effective governance.
Public Policy vs Participatory Governance Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com