Public health campaigns target specific audiences with clear, factual messaging to promote healthy behaviors and prevent disease spread. Infodemic management involves monitoring, addressing, and correcting misinformation that can undermine public trust and effectiveness of health interventions. Coordinated efforts in both areas are essential to safeguard community health and enhance the impact of public safety initiatives.
Table of Comparison
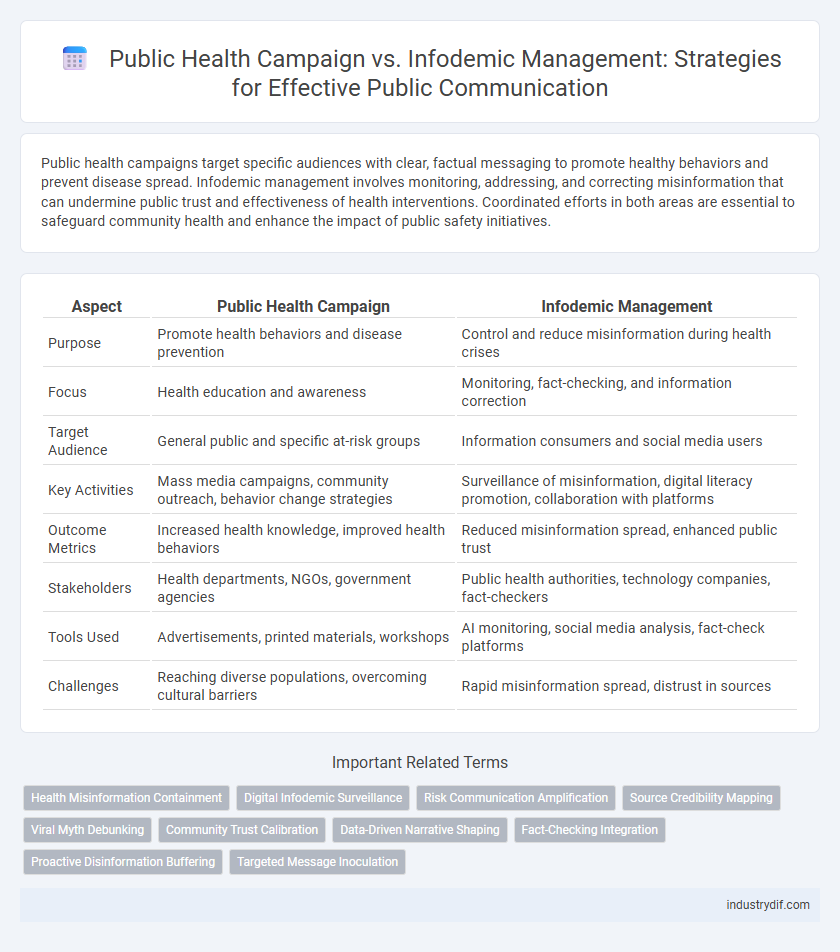
| Aspect | Public Health Campaign | Infodemic Management |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Promote health behaviors and disease prevention | Control and reduce misinformation during health crises |
| Focus | Health education and awareness | Monitoring, fact-checking, and information correction |
| Target Audience | General public and specific at-risk groups | Information consumers and social media users |
| Key Activities | Mass media campaigns, community outreach, behavior change strategies | Surveillance of misinformation, digital literacy promotion, collaboration with platforms |
| Outcome Metrics | Increased health knowledge, improved health behaviors | Reduced misinformation spread, enhanced public trust |
| Stakeholders | Health departments, NGOs, government agencies | Public health authorities, technology companies, fact-checkers |
| Tools Used | Advertisements, printed materials, workshops | AI monitoring, social media analysis, fact-check platforms |
| Challenges | Reaching diverse populations, overcoming cultural barriers | Rapid misinformation spread, distrust in sources |
Understanding Public Health Campaigns
Public health campaigns leverage targeted messaging, evidence-based strategies, and community engagement to effectively promote healthy behaviors and prevent disease outbreaks. These campaigns utilize multimedia platforms and data-driven insights to tailor communication, ensuring messages resonate with diverse populations and address specific health challenges. Understanding the dynamics of public health campaigns is crucial for contrasting their proactive goals with infodemic management, which focuses on combating misinformation to safeguard public trust and health outcomes.
Defining Infodemic Management
Infodemic management involves the strategic control and mitigation of misinformation and disinformation that spread rapidly during public health crises, complicating effective response efforts. Public health campaigns use evidence-based communication to promote accurate information and guide population behavior, directly counteracting the harmful effects of infodemics. Effective infodemic management integrates real-time monitoring, community engagement, and tailored messaging to safeguard public trust and enhance health outcomes.
Key Objectives: Public Health vs. Infodemic Response
Public health campaigns aim to promote healthy behaviors and prevent disease outbreaks by disseminating accurate, evidence-based information to broad populations, enhancing community resilience and healthcare access. Infodemic management focuses on identifying, monitoring, and countering misinformation and disinformation related to health topics, particularly during crises, to ensure the public receives trustworthy data. Both strategies emphasize improving public trust and timely communication but differ in their key objectives: health promotion versus controlling false information spread.
Communication Strategies in Public Health Initiatives
Effective communication strategies in public health initiatives prioritize clarity, cultural relevance, and timely dissemination of accurate information to combat misinformation and enhance public trust. Public health campaigns employ targeted messaging through multiple media platforms to increase awareness, promote healthy behaviors, and counteract the negative effects of infodemics. Integrating real-time monitoring tools and community engagement ensures adaptive communication efforts that address evolving public concerns during health crises.
Mechanisms of Misinformation Spread
Misinformation spreads rapidly through social media algorithms prioritizing sensational content, creating echo chambers that reinforce false beliefs. Public health campaigns combat this by deploying targeted messaging and real-time fact-checking to disrupt misinformation cycles. Effective infodemic management requires integrating behavioral insights and digital literacy to reduce susceptibility and promote reliable information sources.
Stakeholder Roles: Health Authorities and Public
Health authorities play a critical role in public health campaigns by designing evidence-based strategies, disseminating accurate information, and coordinating with healthcare providers to boost vaccination and preventive measures. The public's responsibility involves actively seeking verified information, participating in health programs, and adhering to recommended guidelines to curb disease spread. Collaboration between health authorities and the public enhances trust, mitigates misinformation, and strengthens infodemic management during health crises.
Metrics for Success: Campaigns vs. Infodemic Control
Public health campaigns measure success through engagement rates, behavior change metrics, and health outcome improvements, while infodemic management relies on metrics such as misinformation prevalence reduction, correction uptake, and trust restoration in credible sources. Campaign effectiveness is often quantified by vaccination rates, screening uptake, or awareness levels, whereas infodemic control focuses on digital analytics like share of accurate information, response times to false claims, and audience reach of verified content. Combining epidemiological data with social media monitoring offers a comprehensive metric approach to evaluate both public health campaigns and infodemic management efforts.
Challenges and Barriers in Implementation
Public health campaigns face significant challenges in implementing effective strategies due to widespread misinformation and the rapid spread of false information during infodemics. Barriers include limited health literacy, lack of trust in authorities, and resource constraints in reaching diverse populations through multiple communication channels. Overcoming these obstacles requires evidence-based messaging, real-time monitoring, and collaboration between public health agencies, technology platforms, and community leaders to enhance credible information dissemination.
Case Studies: Lessons from Recent Crises
Recent public health campaigns, such as those during the COVID-19 pandemic, highlighted the critical need for effective infodemic management to combat misinformation and enhance public trust. Case studies from countries like South Korea and New Zealand demonstrate that integrating real-time data monitoring with transparent communication strategies can significantly reduce misinformation spread and improve vaccination rates. These lessons emphasize the importance of coordinated multisectoral responses and digital literacy initiatives in managing health crises.
Future Directions in Public Health Communication
Future directions in public health communication emphasize integrating advanced infodemic management tools to enhance message accuracy and reach. Leveraging artificial intelligence and real-time data analytics enables targeted interventions that counter misinformation rapidly. Strengthening community engagement and multi-platform dissemination will increase trust and the effectiveness of public health campaigns.
Related Important Terms
Health Misinformation Containment
Health misinformation containment is critical for public health campaigns, as inaccurate information can undermine vaccination efforts, promote harmful behaviors, and fuel outbreaks of preventable diseases. Effective strategies include real-time monitoring of misinformation, collaboration with trusted community leaders, and dissemination of accurate, evidence-based information through multiple channels to restore public trust and protect population health.
Digital Infodemic Surveillance
Digital Infodemic Surveillance enhances public health campaigns by systematically monitoring and analyzing misinformation trends across social media and online platforms to enable timely, targeted interventions. Leveraging real-time data analytics and AI-driven tools improves the accuracy of infodemic management, reducing the spread of false information and supporting evidence-based public health messaging.
Risk Communication Amplification
Risk Communication Amplification in public health campaigns enhances message clarity and reach, combatting misinformation by leveraging trusted community channels and real-time feedback mechanisms. Effective infodemic management relies on this amplification to ensure accurate health information rapidly counters false narratives, increasing public compliance and resilience.
Source Credibility Mapping
Source Credibility Mapping is essential in public health campaigns to identify trustworthy information channels and counteract misinformation during infodemics. Accurate mapping of credible sources enhances the effectiveness of communication strategies, ensuring reliable dissemination of health data to the public.
Viral Myth Debunking
Viral myth debunking plays a crucial role in public health campaigns by counteracting misinformation that fuels infodemics, thereby improving public trust and compliance with health guidelines. Effective myth debunking relies on real-time monitoring of false claims and deploying evidence-based communication strategies to correct misconceptions swiftly.
Community Trust Calibration
Community trust calibration is essential for effective public health campaigns, as it shapes the public's acceptance and adherence to health guidelines. Infodemic management strategies that prioritize transparency, credible information sources, and active community engagement significantly strengthen trust, reducing misinformation's impact on population health outcomes.
Data-Driven Narrative Shaping
Data-driven narrative shaping in public health campaigns leverages real-time analytics and social media monitoring to counter misinformation and enhance message credibility, directly addressing the challenges posed by the infodemic. Integrating epidemiological data with targeted communication strategies optimizes public engagement and supports informed decision-making during health crises.
Fact-Checking Integration
Fact-checking integration enhances public health campaigns by ensuring accurate information dissemination, which helps counter widespread misinformation during infodemics. Leveraging real-time verification tools within communication strategies improves public trust and promotes informed decision-making in health crises.
Proactive Disinformation Buffering
Proactive disinformation buffering in public health campaigns involves strategically disseminating verified information to preemptively counteract false narratives and reduce misinformation spread. Leveraging real-time data analytics and community engagement enhances the effectiveness of these campaigns by building trust and resilience against infodemics.
Targeted Message Inoculation
Targeted message inoculation enhances public health campaigns by preemptively exposing individuals to weakened misinformation, strengthening their ability to resist infodemics effectively. This strategic approach reduces the spread of false information, improving overall community health outcomes through increased trust and informed decision-making.
public health campaign vs infodemic management Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com