Public records often face challenges such as limited accessibility, data tampering, and delays in updates, which compromise transparency and trust. Blockchain technology offers an immutable, decentralized ledger that ensures real-time, verifiable access to information, significantly enhancing transparency for public records. This shift reduces fraud risks and promotes accountability by enabling secure, transparent data sharing across multiple stakeholders.
Table of Comparison
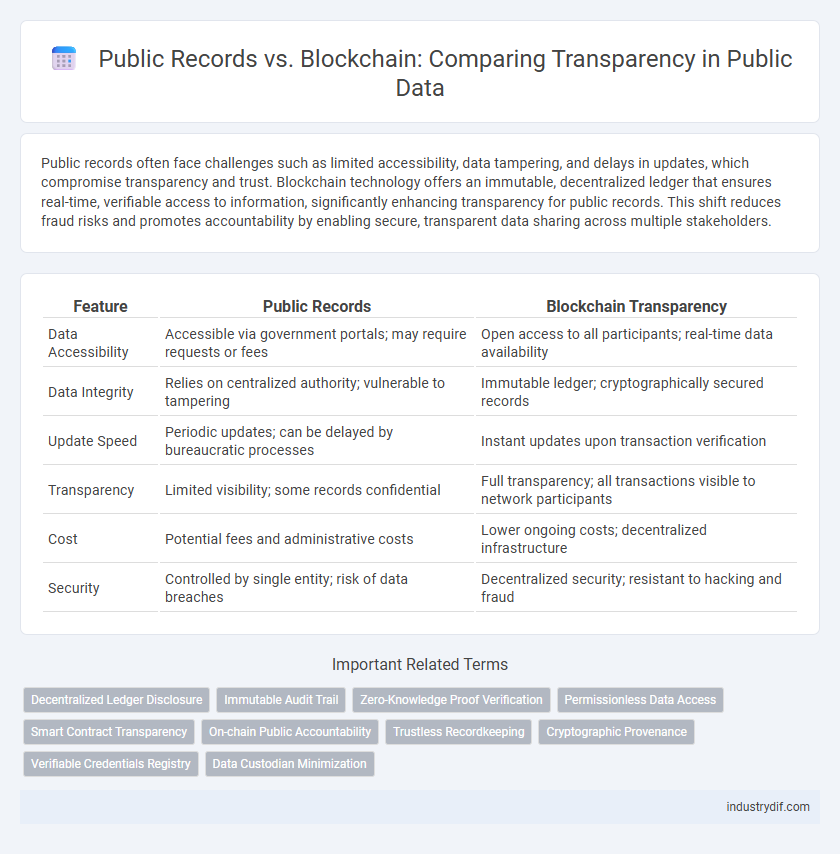
| Feature | Public Records | Blockchain Transparency |
|---|---|---|
| Data Accessibility | Accessible via government portals; may require requests or fees | Open access to all participants; real-time data availability |
| Data Integrity | Relies on centralized authority; vulnerable to tampering | Immutable ledger; cryptographically secured records |
| Update Speed | Periodic updates; can be delayed by bureaucratic processes | Instant updates upon transaction verification |
| Transparency | Limited visibility; some records confidential | Full transparency; all transactions visible to network participants |
| Cost | Potential fees and administrative costs | Lower ongoing costs; decentralized infrastructure |
| Security | Controlled by single entity; risk of data breaches | Decentralized security; resistant to hacking and fraud |
Defining Public Records: Traditional Concepts
Public records refer to documented information maintained by government agencies that are accessible to the public, including birth certificates, court records, and property deeds. These records are traditionally stored in centralized databases or physical archives, which can be subject to manipulation, loss, or limited accessibility. Unlike blockchain transparency, public records rely on established legal frameworks and institutional oversight to ensure authenticity and accountability.
Understanding Blockchain Transparency
Blockchain transparency ensures every transaction is recorded on a decentralized ledger accessible to all network participants, enhancing trust and verifiability compared to traditional public records. Unlike static and sometimes opaque public records, blockchain provides a real-time, tamper-resistant audit trail that can be independently verified without relying on a central authority. This immutable transparency reduces fraud risks while preserving data integrity, making blockchain a superior tool for public accountability and record-keeping.
Key Differences Between Public Records and Blockchain
Public records are officially maintained documents by government agencies, providing legally recognized information accessible to the public, while blockchain offers a decentralized and immutable ledger where data transparency is ensured through cryptographic methods. Unlike public records, blockchain transactions are time-stamped and recorded in a distributed manner, enhancing security and reducing the risk of tampering or fraud. Accessibility to public records often involves bureaucratic processes, whereas blockchain data is accessible in real-time to anyone with network access, promoting openness and accountability.
Data Integrity: Blockchain vs. Conventional Records
Blockchain technology ensures superior data integrity by providing immutable and time-stamped records that cannot be altered or deleted, unlike conventional public records which are susceptible to tampering and human error. Decentralized validation within blockchain networks guarantees consistent verification across all nodes, enhancing trustworthiness beyond centralized recordkeeping systems. Persistent cryptographic proofs in blockchain create an auditable trail that significantly reduces fraud risks compared to traditional record management.
Accessibility: Who Can View the Information?
Public records are accessible to anyone through government databases, allowing broad access to information such as property deeds, court records, and business licenses. Blockchain transparency provides a decentralized ledger viewable by all network participants, ensuring that transaction histories are openly accessible without centralized control. While public records require navigating bureaucratic systems, blockchain offers real-time, tamper-proof data visibility for anyone with internet access.
Privacy Concerns in Public Records and Blockchain
Public records often expose sensitive personal information, raising significant privacy concerns due to their accessibility by anyone. Blockchain transparency, while enhancing accountability through immutable transaction records, presents challenges in protecting individual privacy since data is permanently visible on a decentralized ledger. Advanced cryptographic techniques like zero-knowledge proofs are increasingly employed to balance transparency with privacy protections in blockchain platforms.
Security Measures: Centralized vs. Decentralized Systems
Public records rely on centralized systems with controlled access points, which create vulnerabilities to unauthorized tampering and data breaches. Blockchain transparency leverages decentralized security measures, distributing data across multiple nodes to prevent single points of failure and ensure immutability. This decentralized architecture enhances data integrity and provides stronger resistance against hacking compared to traditional public record databases.
Trust and Verification: Human Oversight vs. Smart Contracts
Public records rely on human oversight for trust and verification, where officials manually review and authenticate data, which can introduce errors or delays. Blockchain transparency leverages smart contracts to automate verification processes, ensuring immutable and real-time validation without intermediaries. This shift from human to algorithmic trust enhances accuracy but requires robust code auditing to prevent vulnerabilities.
Legal and Regulatory Implications
Public records provide a legally recognized source of verified information subject to established regulatory frameworks and privacy laws, ensuring accountability and legal compliance. Blockchain transparency offers immutable and decentralized data access, posing challenges for regulators in enforcing data protection, jurisdictional authority, and verifying the authenticity of off-chain legal documents. Balancing the legal recognition of public records with blockchain's transparency requires evolving regulations to address issues like data privacy, authenticity verification, and cross-border legal enforceability.
Future of Record-Keeping: Blockchain Adoption in Public Sectors
Blockchain technology promises to revolutionize public record-keeping by offering enhanced transparency, immutability, and security compared to traditional public records. Governments and public sectors increasingly explore blockchain adoption to ensure tamper-proof documentation, real-time accessibility, and improved trust in data integrity. This shift towards decentralized ledger systems optimizes record management and streamlines verification processes, marking the future of transparent and accountable public administration.
Related Important Terms
Decentralized Ledger Disclosure
Decentralized ledger disclosure enhances transparency by providing immutable, timestamped public records that reduce fraud and increase accountability. Unlike traditional public records, blockchain technology enables real-time access to verified data without centralized control, ensuring greater security and trust in information sharing.
Immutable Audit Trail
Public records provide a centralized and accessible source of information, but they are vulnerable to alteration and tampering over time. Blockchain technology offers an immutable audit trail by securely recording transactions in a decentralized ledger, ensuring transparency and preventing unauthorized modifications.
Zero-Knowledge Proof Verification
Zero-Knowledge Proof Verification enhances blockchain transparency by enabling users to validate transactions without exposing private data, offering a privacy-preserving alternative to traditional public records. This cryptographic method ensures data integrity and trust while maintaining confidentiality, addressing limitations inherent in conventional public record systems.
Permissionless Data Access
Permissionless data access in blockchain enables real-time transparency by allowing anyone to verify and audit transactions without intermediaries, unlike traditional public records which often require formal requests or fees for access. This decentralized, immutable ledger enhances trust and accountability by providing open, tamper-proof records accessible to all participants globally.
Smart Contract Transparency
Smart contract transparency on blockchain ensures real-time, immutable public records that enhance trust and verification processes beyond traditional public record systems. Unlike static public records, blockchain smart contracts provide automated, auditable transaction histories, increasing accountability and reducing fraud in digital agreements.
On-chain Public Accountability
On-chain public accountability leverages blockchain technology to create immutable, transparent records accessible to anyone, contrasting with traditional public records which often suffer from limited accessibility and potential manipulation. This decentralized ledger enhances trust by enabling real-time verification and tamper-proof documentation, ensuring greater transparency in governance and financial disclosures.
Trustless Recordkeeping
Public records traditionally rely on centralized authorities to verify and maintain data, which introduces risks of manipulation and errors, while blockchain transparency ensures immutable, trustless recordkeeping through decentralized consensus protocols. This trustless system enhances data integrity by enabling verifiable and tamper-proof entries accessible to all stakeholders without needing a centralized intermediary.
Cryptographic Provenance
Public records provide official documentation maintained by government entities, whereas blockchain transparency relies on cryptographic provenance to verify the authenticity and immutability of transaction histories. Cryptographic provenance in blockchain ensures tamper-proof, traceable data through cryptographic hashing and digital signatures, enhancing trust without centralized oversight.
Verifiable Credentials Registry
Verifiable Credentials Registry enhances transparency by enabling public records to be securely verified on blockchain platforms, reducing fraud and ensuring authenticity. This decentralized approach to public records increases trust through immutable verification while maintaining user privacy and control over shared information.
Data Custodian Minimization
Public records rely heavily on centralized data custodians, increasing risks of data breaches and manipulation, whereas blockchain transparency enables decentralized data access and verification, minimizing the need for trusted intermediaries. This reduction in data custodian roles enhances security, accountability, and public trust by empowering users with direct control over their information.
public records vs blockchain transparency Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com