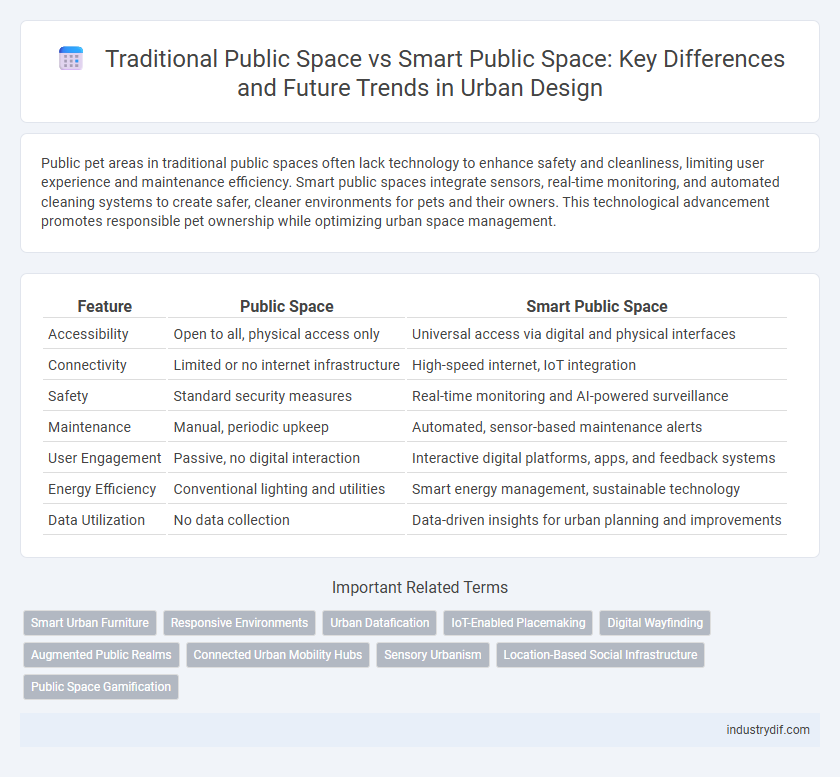
Public pet areas in traditional public spaces often lack technology to enhance safety and cleanliness, limiting user experience and maintenance efficiency. Smart public spaces integrate sensors, real-time monitoring, and automated cleaning systems to create safer, cleaner environments for pets and their owners. This technological advancement promotes responsible pet ownership while optimizing urban space management.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Public Space | Smart Public Space |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Open to all, physical access only | Universal access via digital and physical interfaces |
| Connectivity | Limited or no internet infrastructure | High-speed internet, IoT integration |
| Safety | Standard security measures | Real-time monitoring and AI-powered surveillance |
| Maintenance | Manual, periodic upkeep | Automated, sensor-based maintenance alerts |
| User Engagement | Passive, no digital interaction | Interactive digital platforms, apps, and feedback systems |
| Energy Efficiency | Conventional lighting and utilities | Smart energy management, sustainable technology |
| Data Utilization | No data collection | Data-driven insights for urban planning and improvements |
Definition of Traditional Public Space
Traditional public spaces are open areas such as parks, plazas, and streets that facilitate social interaction, cultural activities, and community engagement without advanced technological integration. These spaces are characterized by physical accessibility, natural elements, and communal infrastructure supporting informal gatherings and public events. The absence of digital connectivity and smart sensors distinguishes traditional public spaces from smart public spaces optimized through technology.
Evolution Toward Smart Public Spaces
Public spaces have evolved from traditional open areas serving basic social functions to smart public spaces integrated with advanced technologies such as IoT sensors, AI analytics, and real-time data systems. These innovations optimize urban management by enhancing safety, accessibility, and environmental sustainability while enabling interactive experiences for citizens. The transition toward smart public spaces reflects a shift in urban planning priorities, emphasizing connectivity, data-driven decision-making, and user-centric design.
Key Features of Public Spaces
Public spaces provide open areas for community interaction, socializing, and cultural events, featuring accessibility, safety, and inclusivity as key elements. Smart public spaces integrate digital technologies such as sensors, Wi-Fi, and IoT devices to enhance user experience, optimize resource management, and improve security. These spaces offer real-time data collection, adaptive lighting, and interactive information systems that promote sustainability and citizen engagement.
Essential Technologies in Smart Public Spaces
Smart public spaces integrate essential technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, advanced data analytics, and AI-driven automation to enhance urban efficiency, safety, and user experience. These technologies allow real-time monitoring of air quality, traffic flow, and energy consumption, enabling dynamic management and responsive services. Compared to traditional public spaces, smart public spaces leverage connectivity and digital infrastructure to create adaptive environments that promote sustainability and inclusivity.
Benefits of Smart Public Space Implementation
Smart public spaces enhance urban living by integrating IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and adaptive infrastructure to improve safety, efficiency, and environmental sustainability. These spaces offer benefits such as optimized traffic flow, energy savings through intelligent lighting systems, and increased citizen engagement via interactive platforms. Implementing smart public spaces fosters inclusivity, promotes economic growth, and supports resilient urban development aligned with smart city initiatives.
Challenges in Transitioning to Smart Public Spaces
Transitioning to smart public spaces involves overcoming challenges such as integrating advanced sensor networks with existing infrastructure and ensuring data privacy for users. Addressing interoperability between diverse technologies and managing the high costs of deployment require strategic planning and investment. Urban planners must also tackle public resistance to surveillance and navigate regulatory frameworks that govern digital innovations in public environments.
User Experience: Public vs. Smart Public Spaces
Public spaces offer basic accessibility and social interaction, but smart public spaces enhance user experience through integrated IoT devices, real-time data analytics, and adaptive environmental controls. Smart spaces provide personalized services such as dynamic lighting, navigation assistance via mobile apps, and responsive safety measures, elevating comfort and engagement. These advancements lead to increased user satisfaction, improved accessibility, and more efficient resource management in urban environments.
Sustainability in Smart Public Spaces
Smart public spaces leverage IoT sensors and data analytics to optimize resource consumption, significantly reducing water and energy waste compared to conventional public areas. Integrating renewable energy sources such as solar panels enhances sustainability by lowering carbon footprints and promoting environmental resilience. Advanced waste management systems and green infrastructure in smart public spaces contribute to improved air quality and biodiversity, fostering healthier urban ecosystems.
Privacy and Security in Smart Urban Spaces
Smart public spaces integrate advanced sensors and data-driven technologies to enhance urban security while maintaining privacy through encryption and anonymization techniques. Real-time monitoring and AI-driven analytics improve threat detection without compromising individual anonymity, balancing safety with privacy rights. Robust cybersecurity frameworks are critical to prevent data breaches, ensuring public trust in smart urban environments.
Future Trends in Public and Smart Public Spaces
Future trends in public and smart public spaces emphasize the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, enabling real-time data collection for enhanced safety, accessibility, and environmental sustainability. Smart public spaces leverage advanced sensors, AI-driven analytics, and adaptive infrastructure to optimize user experiences and resource management. Emphasis on augmented reality (AR) and 5G connectivity further transforms traditional public areas into interactive, responsive environments promoting community engagement and urban resilience.
Related Important Terms
Smart Urban Furniture
Smart urban furniture integrates advanced technologies such as IoT sensors, Wi-Fi connectivity, and interactive displays to transform traditional public spaces into intelligent, responsive environments that enhance user experience and safety. These innovations enable efficient energy use, real-time data collection, and improved urban management, positioning smart public spaces as vital components of modern, sustainable cities.
Responsive Environments
Responsive environments in smart public spaces integrate advanced sensor networks and IoT technology to dynamically adapt lighting, temperature, and sound based on real-time human presence and activity patterns. Unlike traditional public spaces, these responsive systems enhance user comfort, safety, and engagement by providing personalized interactions and efficient resource management.
Urban Datafication
Urban datafication transforms traditional public spaces into smart public spaces by integrating sensors, IoT devices, and real-time data analytics to enhance urban management and citizen engagement. This digital infrastructure enables efficient resource allocation, improved safety, and personalized services, reshaping how people interact with and experience their environment.
IoT-Enabled Placemaking
IoT-enabled placemaking transforms traditional public spaces by integrating sensor networks, real-time data analytics, and connected devices to enhance user engagement, safety, and environmental sustainability. This smart public space leverages Internet of Things technologies to optimize lighting, traffic flow, and maintenance operations, creating adaptive and responsive urban environments that improve quality of life.
Digital Wayfinding
Digital wayfinding in smart public spaces enhances navigation by integrating real-time data, interactive maps, and location-based services, improving accessibility and user experience. Unlike traditional public spaces, smart environments leverage IoT devices and mobile connectivity to provide dynamic route guidance and personalized information.
Augmented Public Realms
Augmented Public Realms transform traditional public spaces through the integration of interactive digital technologies, enhancing user engagement and accessibility while promoting social connectivity. These smart public spaces leverage augmented reality, IoT sensors, and data analytics to create adaptive environments that respond dynamically to community needs and urban activities.
Connected Urban Mobility Hubs
Connected Urban Mobility Hubs transform traditional public spaces into smart public spaces by integrating multiple transportation modes, real-time data, and IoT technologies to enhance commuter experience and urban efficiency. These hubs promote sustainable mobility, reduce congestion, and provide seamless connectivity, making cities more adaptive and user-centric.
Sensory Urbanism
Public spaces serve as crucial environments for social interaction and community engagement, but smart public spaces enhanced with sensory urbanism integrate advanced technologies such as IoT sensors and real-time data analytics to create adaptive, responsive environments that enhance user experience and urban functionality. Sensory urbanism leverages multi-sensory stimuli including sound, light, and motion detection to foster deeper emotional connections and improve accessibility, safety, and environmental monitoring within these smart urban landscapes.
Location-Based Social Infrastructure
Public spaces serve as essential hubs for social interaction and community engagement, while smart public spaces leverage Location-Based Social Infrastructure (LBSI) to enhance connectivity, real-time data sharing, and personalized user experiences. Integrating LBSI in smart public spaces enables dynamic crowd management, improves public safety, and fosters inclusive community participation through location-aware technologies.
Public Space Gamification
Public space gamification transforms traditional urban areas by integrating interactive digital technologies that encourage community engagement and social interaction. Smart public spaces utilize sensors, augmented reality, and game mechanics to create dynamic environments that promote physical activity, cultural participation, and real-time feedback.
public space vs smart public space Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com