Hiking offers an active outdoor experience that combines physical exercise with exploration of natural trails, promoting cardiovascular health and endurance. Forest bathing, or shinrin-yoku, provides a mindful immersion in the forest atmosphere that reduces stress and enhances mental well-being through sensory engagement with the environment. Both activities foster a deep connection with nature but differ in intensity and focus, catering to diverse preferences for recreation and relaxation.
Table of Comparison
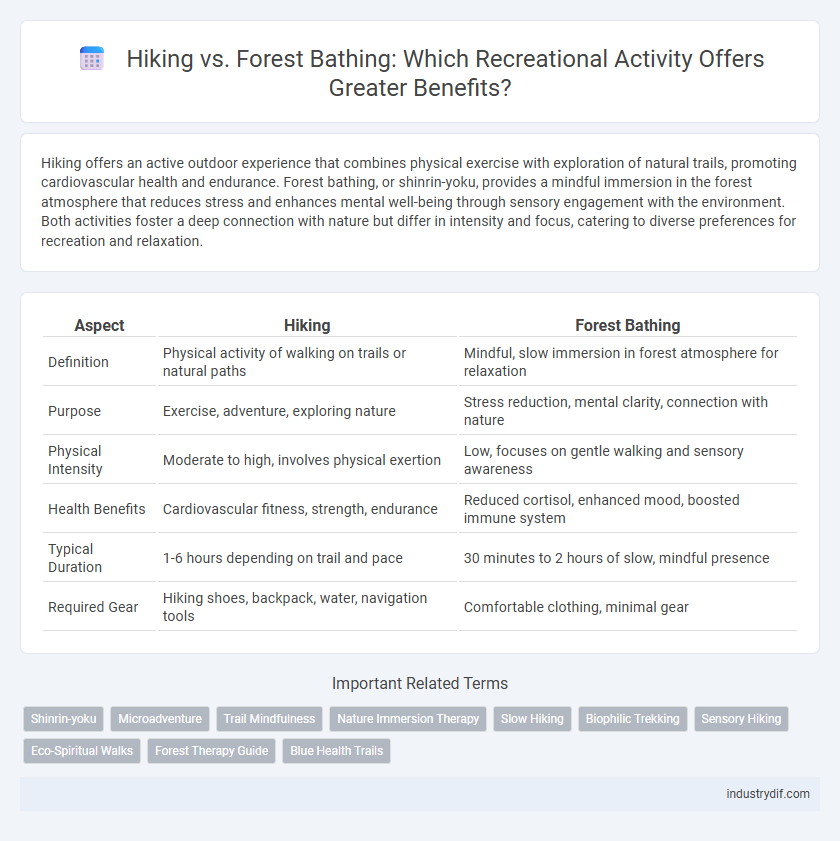
| Aspect | Hiking | Forest Bathing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical activity of walking on trails or natural paths | Mindful, slow immersion in forest atmosphere for relaxation |
| Purpose | Exercise, adventure, exploring nature | Stress reduction, mental clarity, connection with nature |
| Physical Intensity | Moderate to high, involves physical exertion | Low, focuses on gentle walking and sensory awareness |
| Health Benefits | Cardiovascular fitness, strength, endurance | Reduced cortisol, enhanced mood, boosted immune system |
| Typical Duration | 1-6 hours depending on trail and pace | 30 minutes to 2 hours of slow, mindful presence |
| Required Gear | Hiking shoes, backpack, water, navigation tools | Comfortable clothing, minimal gear |
Introduction to Hiking and Forest Bathing
Hiking involves walking through diverse natural landscapes, offering physical exercise and exploration of trails, mountains, and forests. Forest bathing, or Shinrin-yoku, is a mindful practice originating in Japan that encourages immersing oneself in the forest atmosphere to promote mental relaxation and stress reduction. Both activities provide unique connections to nature, enhancing overall well-being through different sensory and physical experiences.
Origins and History of Each Practice
Hiking traces its origins to ancient human migration and exploration, evolving into a recreational activity with roots in 19th-century Europe, particularly the Romantic movement that celebrated nature. Forest bathing, known as Shinrin-yoku, originated in Japan during the 1980s as a nature therapy practice designed to improve health and well-being by immersing individuals in forest environments. While hiking emphasizes physical endurance and adventure, forest bathing focuses on mindful sensory experiences and stress reduction linked to traditional Japanese and East Asian cultural practices.
Core Principles: Hiking vs Forest Bathing
Hiking centers on physical exertion, endurance, and exploring diverse terrains to achieve fitness and adventure, emphasizing active movement and goal-oriented trails. Forest bathing, or shinrin-yoku, prioritizes sensory immersion and mindful connection with nature, focusing on slowing down, deep breathing, and appreciating the natural environment for mental and emotional restoration. The core principles of hiking engage the body through exercise, while forest bathing cultivates mindfulness and stress reduction by fostering a tranquil presence in the forest.
Physical and Mental Health Benefits
Hiking improves cardiovascular fitness, muscle strength, and endurance through sustained physical activity, while boosting mental health by reducing stress and enhancing mood via exposure to nature's dynamic environments. Forest bathing, or shinrin-yoku, offers restorative effects by lowering cortisol levels, improving immune function, and promoting relaxation through mindful immersion in tranquil forest settings. Both activities complement each other by combining physical exertion with sensory relaxation, fostering holistic well-being.
Typical Activities Involved
Hiking typically involves walking along marked trails, navigating varying terrains, and reaching scenic viewpoints or summits, often carrying gear like backpacks, water, and navigation tools. Forest bathing, or shinrin-yoku, centers on immersive sensory experiences such as mindful breathing, listening to natural sounds, and gently observing the environment to reduce stress and promote mental well-being. Both activities foster a connection with nature but emphasize different physical and contemplative interactions within forested settings.
Ideal Locations and Environments
Mountain trails with varied elevation and panoramic views offer ideal locations for hiking, providing physical challenges and immersive natural scenery. Forest bathing thrives in dense, old-growth forests with rich biodiversity, where calm, shaded environments enhance mental relaxation and sensory connection. Coastal woodlands and tranquil parks also serve as preferred environments for forest bathing, promoting mindfulness and stress reduction.
Required Gear and Preparation
Hiking demands sturdy boots, weather-appropriate clothing, a navigation tool such as a map or GPS, and sufficient water and snacks to ensure safety and endurance on varied terrains. Forest bathing requires minimal gear, often just comfortable clothing and footwear suitable for walking slowly and quietly through natural environments, emphasizing sensory immersion over physical exertion. Preparation for hiking involves route planning and physical conditioning, while forest bathing prioritizes mental readiness to fully engage with the natural surroundings for relaxation and mindfulness.
Social vs Solitary Experiences
Hiking often involves group participation, fostering social interaction and shared experiences along diverse trails and scenic routes, enhancing camaraderie and motivation among participants. Forest bathing, or shinrin-yoku, emphasizes solitary immersion in nature to promote mindfulness, stress reduction, and emotional healing through quiet observation of natural surroundings. Both activities offer unique benefits, with hiking supporting social bonds and forest bathing encouraging introspective solitude.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Hiking trails, when heavily frequented, can lead to soil erosion, vegetation damage, and wildlife disturbance, impacting ecosystem sustainability. Forest bathing emphasizes minimal physical impact by promoting quiet observation and mindful presence, supporting conservation efforts and biodiversity. Both activities encourage environmental awareness, but forest bathing aligns more closely with low-impact recreation and sustainable interaction with nature.
Choosing the Right Activity for You
Hiking offers a dynamic way to explore diverse terrains, build endurance, and enjoy scenic vistas, making it ideal for those seeking physical challenge and adventure. Forest bathing emphasizes mindfulness and sensory immersion in nature, promoting relaxation and stress reduction through gentle, unstructured walks in wooded areas. Selecting the right activity depends on your personal goals--whether you prioritize fitness and exploration or tranquility and mental well-being.
Related Important Terms
Shinrin-yoku
Shinrin-yoku, or forest bathing, involves immersing oneself in a forest environment to enhance mental clarity, reduce stress hormones, and boost immune function through sensory engagement, differing from hiking which emphasizes physical exertion and endurance. Scientific studies reveal that Shinrin-yoku promotes parasympathetic nervous system activation, improving mood and cardiovascular health without requiring strenuous activity.
Microadventure
Microadventures combine elements of hiking and forest bathing by offering short, accessible outdoor experiences that immerse participants in nature while promoting mental well-being and physical activity. Unlike traditional long hikes, microadventures prioritize mindful engagement with the environment, enhancing sensory awareness and reducing stress through deliberate interaction with forest ecosystems.
Trail Mindfulness
Hiking enhances physical endurance and cardiovascular health while promoting mental clarity through active movement on diverse trails. Forest bathing, rooted in Japanese Shinrin-yoku, fosters deep sensory awareness and stress reduction by immersing individuals in the natural environment with mindful attention to sights, sounds, and scents.
Nature Immersion Therapy
Hiking and forest bathing both offer immersive nature therapy benefits, with hiking providing physical exercise and cardiovascular health improvements while forest bathing emphasizes sensory mindfulness that reduces stress and enhances emotional well-being. Studies show forest bathing increases parasympathetic nervous system activity, promoting relaxation, whereas hiking's aerobic demands improve endurance and muscle strength within natural environments.
Slow Hiking
Slow hiking emphasizes mindful walking at a deliberate pace, enhancing sensory connection with nature and promoting mental well-being, while forest bathing involves immersive, meditative experiences in woodland environments to reduce stress and improve immune function. Both practices prioritize slowing down, but slow hiking integrates gentle physical activity with nature awareness for holistic recreation benefits.
Biophilic Trekking
Biophilic trekking blends the physical challenge of hiking with immersive forest bathing, promoting mental well-being through sensory connection with nature. Unlike traditional hiking focused on distance and speed, biophilic trekking emphasizes mindful engagement with natural environments, enhancing emotional resilience and reducing stress.
Sensory Hiking
Sensory hiking engages all five senses by encouraging mindful awareness of the sights, sounds, smells, textures, and even tastes encountered along forest trails, enhancing the immersive experience beyond physical activity. Unlike traditional hiking focused on distance or speed, sensory hiking emphasizes deep connection with nature's subtle cues, promoting mental well-being and stress reduction through mindful observation and presence.
Eco-Spiritual Walks
Eco-spiritual walks blend the immersive mindfulness of forest bathing with the physical engagement of hiking, fostering deep ecological awareness and spiritual connection to nature. This practice encourages participants to attune to natural rhythms, promoting mental clarity and environmental stewardship through meditative movement and sensory exploration.
Forest Therapy Guide
Forest therapy guides lead immersive nature sessions that enhance mental clarity and reduce stress by engaging all senses in a purposeful forest environment. Unlike traditional hiking, forest bathing emphasizes mindfulness and slow, deliberate interaction with nature to promote holistic well-being.
Blue Health Trails
Blue Health Trails enhance both hiking and forest bathing experiences by integrating natural water elements known to reduce stress and improve mental well-being. Prioritizing access to streams, lakes, and coastal environments, these trails amplify the restorative effects of outdoor activities, making them ideal for physical exercise and immersive nature therapy.
Hiking vs Forest bathing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com