Landlords primarily generate income through property ownership and leasing, focusing on long-term rental agreements with minimal day-to-day involvement. Rentalpreneurs actively manage their rental properties as a business, leveraging strategies like short-term rentals, dynamic pricing, and marketing to maximize profitability. Embracing technology and market trends, rentalpreneurs often achieve higher returns by continuously optimizing rental experiences for tenants.
Table of Comparison
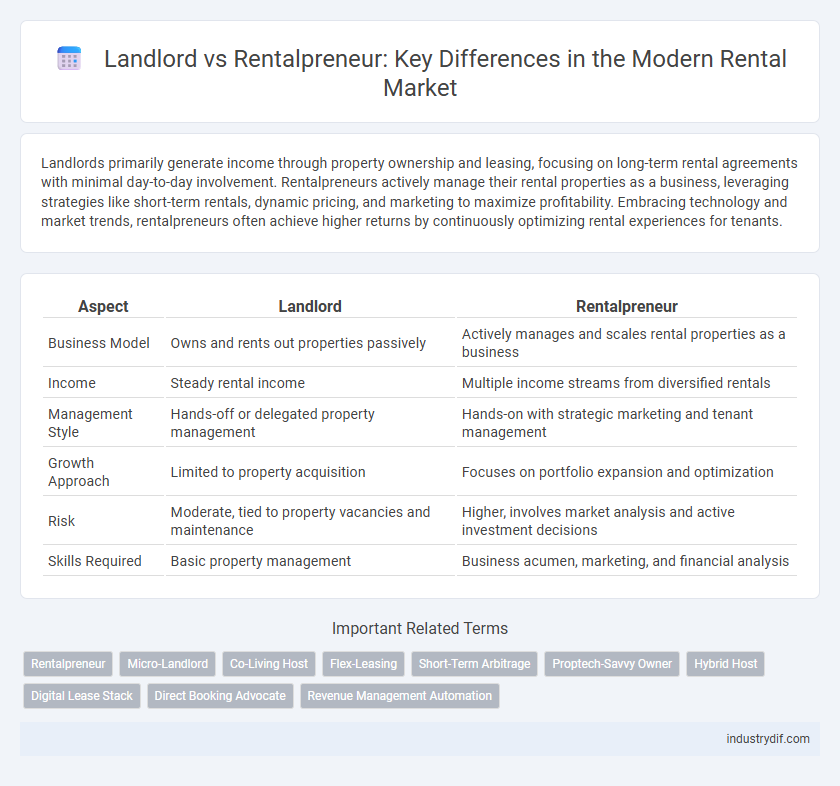
| Aspect | Landlord | Rentalpreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Owns and rents out properties passively | Actively manages and scales rental properties as a business |
| Income | Steady rental income | Multiple income streams from diversified rentals |
| Management Style | Hands-off or delegated property management | Hands-on with strategic marketing and tenant management |
| Growth Approach | Limited to property acquisition | Focuses on portfolio expansion and optimization |
| Risk | Moderate, tied to property vacancies and maintenance | Higher, involves market analysis and active investment decisions |
| Skills Required | Basic property management | Business acumen, marketing, and financial analysis |
Understanding the Roles: Landlord vs Rentalpreneur
A landlord primarily manages property ownership, tenant relations, and maintenance responsibilities to generate rental income with a long-term, hands-on approach. A rentalpreneur, however, adopts a strategic, entrepreneurial mindset, actively scaling rental portfolios, leveraging market trends, and optimizing profitability through innovative property management techniques. Understanding these distinctions helps investors align their goals with the appropriate operational style in the rental market.
Key Differences in Business Approach
Landlords primarily generate income through property ownership and long-term lease agreements, emphasizing asset appreciation and steady rental cash flow. Rentalpreneurs adopt a proactive business model that includes property acquisition, renovation, and strategic marketing to maximize short-term rental profits and diversify income streams. While landlords focus on passive income and property management, rentalpreneurs actively engage in market analysis, dynamic pricing, and guest experience to scale their rental business.
Investment Strategies Compared
Landlords typically focus on steady rental income through long-term tenant leases, prioritizing property maintenance and market appreciation for passive income growth. Rentalpreneurs adopt diverse investment strategies, including short-term rentals, property flipping, and leveraging technology to maximize cash flow and capitalize on market trends. Both approaches require strategic risk assessment, but rentalpreneurs often pursue higher returns through active property management and innovative marketing techniques.
Legal Responsibilities and Compliance
Landlords must adhere to local housing laws, ensuring property safety, tenant rights, and fair lease terms, with strict compliance to eviction procedures and security deposit regulations. Rentalpreneurs, managing multiple properties or units as a business, face enhanced legal responsibilities, including commercial licensing, rigorous record-keeping, and compliance with broader tenant protection statutes. Both roles require ongoing awareness of changing legislation to avoid penalties and secure lawful rental operations.
Income Streams and Profitability
Landlords primarily generate income through rental payments on owned properties, creating stable but often limited cash flow tied directly to occupancy rates. Rentalpreneurs diversify income streams by leveraging multiple properties, incorporating short-term rentals, and adding value through property management services or renovations, enhancing overall profitability. This multifaceted approach typically results in higher revenue potential and greater financial resilience in the rental market.
Property Management Styles
Landlords typically adopt a hands-on property management style, directly handling tenant issues, maintenance, and rent collection, often limiting scalability. Rentalpreneurs employ strategic, systematized management approaches, utilizing property managers, automated software, and outsourcing to optimize efficiency and maximize portfolio growth. This professionalized management style reduces day-to-day involvement while enhancing income stability and tenant satisfaction.
Risk Management Techniques
Landlords minimize financial risk by conducting thorough tenant screenings and maintaining consistent property inspections to prevent damage and ensure timely rent payments. Rentalpreneurs employ diversified real estate portfolios and leverage technology-driven analytics for market trend forecasting, allowing proactive adjustments to rent pricing and property investments. Both utilize legal agreements and insurance policies to safeguard against liabilities, but rentalpreneurs often integrate passive income strategies to balance risk across multiple sources.
Marketing and Tenant Acquisition Tactics
Landlords often rely on traditional marketing methods such as local listings and word-of-mouth referrals, while rentalpreneurs leverage digital marketing strategies, including social media advertising, SEO-optimized listings, and targeted email campaigns to attract a broader tenant base. Rentalpreneurs use data analytics and tenant screening software to streamline acquisition processes and enhance tenant quality, contrasting with landlords who may use manual vetting methods. These innovative marketing approaches enable rentalpreneurs to reduce vacancy rates and maximize rental income more effectively than traditional landlords.
Scaling Up: Portfolio Growth Strategies
Landlords primarily focus on managing individual or a few rental properties, optimizing cash flow through steady rental income, while rentalpreneurs actively pursue portfolio expansion using strategies like property flipping, leveraging financing, and diversifying property types. Scaling up requires rentalpreneurs to implement advanced systems for tenant screening, property management automation, and market analysis to maximize returns and minimize risks. Strategic acquisitions, refinancing existing assets, and reinvesting rental income drive rapid portfolio growth and increased equity for rentalpreneurs.
Future Trends in the Rental Industry
Landlords are increasingly adapting to future trends by incorporating smart home technology and sustainable practices to attract eco-conscious tenants. Rentalpreneurs emphasize data-driven property management and diversified rental portfolios to maximize income and mitigate risks in evolving markets. The rental industry's future hinges on automation, flexible leasing options, and tech-enabled tenant experiences to meet shifting consumer demands.
Related Important Terms
Rentalpreneur
Rentalpreneurs leverage innovative strategies and technology to maximize rental property income and streamline tenant management, distinguishing themselves from traditional landlords. This entrepreneurial approach emphasizes scaling portfolios, optimizing cash flow, and enhancing tenant experiences for sustainable long-term success.
Micro-Landlord
Micro-landlords, typically owning fewer than five rental units, differ from rentalpreneurs who actively scale and manage extensive property portfolios for profit maximization. While micro-landlords prioritize steady cash flow and manageable responsibilities, rentalpreneurs focus on leveraging market trends and strategic acquisitions to build substantial real estate empires.
Co-Living Host
Landlords typically manage individual rental units, while Rentalpreneurs approach property leasing as a business, often optimizing multiple units for co-living spaces to maximize occupancy and revenue. Co-Living Hosts specialize in curating shared living environments that foster community and convenience, blending hospitality with rental management for enhanced tenant experiences.
Flex-Leasing
Flex-Leasing offers a dynamic rental model where Rentalpreneurs maximize short-term profitability through flexible tenant agreements, contrasting traditional landlords who typically prioritize long-term leases for steady income. This approach leverages market demand fluctuations, enabling Rentalpreneurs to optimize property utilization and revenue streams effectively.
Short-Term Arbitrage
Short-term arbitrage leverages rentalpreneurs who strategically lease properties to sublet them at higher rates for short durations, maximizing cash flow compared to traditional landlords who rely on long-term tenants and steady rental income. Rentalpreneurs optimize occupancy rates and dynamic pricing through platforms like Airbnb, achieving greater profit margins and flexibility in managing rental assets.
Proptech-Savvy Owner
A proptech-savvy landlord leverages digital tools and platforms to streamline property management, optimize tenant engagement, and maximize rental income, distinguishing themselves from traditional rentalpreneurs who rely on conventional methods. This tech-driven approach enables real-time data analytics, automated maintenance scheduling, and efficient communication, transforming rental property ownership into a scalable, tech-enabled business model.
Hybrid Host
A hybrid host blends the roles of a traditional landlord and a rentalpreneur by managing long-term leases while actively optimizing short-term rental income through platforms like Airbnb, maximizing property ROI with flexible strategies. This approach leverages professional hosting skills and property management to enhance guest experience and financial performance simultaneously.
Digital Lease Stack
Landlords primarily manage rental properties using traditional methods, while rentalpreneurs leverage a digital lease stack to automate workflows, streamline tenant onboarding, and enhance property management efficiency. Utilizing cloud-based platforms with integrated e-signatures, payment processing, and maintenance tracking offers rentalpreneurs a competitive advantage in maximizing rental income and reducing operational costs.
Direct Booking Advocate
Landlord rental models often rely on traditional listing platforms, limiting direct engagement with tenants, while Rentalpreneurs prioritize direct bookings to maximize profit and control over tenant relationships. Advocating for direct booking enables Rentalpreneurs to reduce commission costs, enhance personalized communication, and build a loyal customer base, transforming rental management into a scalable business model.
Revenue Management Automation
Landlords traditionally manage rental income manually, often missing opportunities to optimize pricing and occupancy rates, while rentalpreneurs leverage revenue management automation tools that analyze market trends, adjust rental prices dynamically, and maximize cash flow efficiently. Automated systems provide rentalpreneurs with real-time data insights and predictive analytics, resulting in increased profitability and reduced vacancy periods compared to conventional landlord methods.
Landlord vs Rentalpreneur Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com