Renting typically involves a fixed-term agreement with a single payment for the duration, offering straightforward access to property or equipment without ownership. Subscription-based rental provides continuous use with flexible payment schedules, often including maintenance and upgrade options for greater convenience. Both models cater to varying needs, where traditional renting suits short-term commitments, and subscription rentals appeal to users seeking adaptability and ongoing service.
Table of Comparison
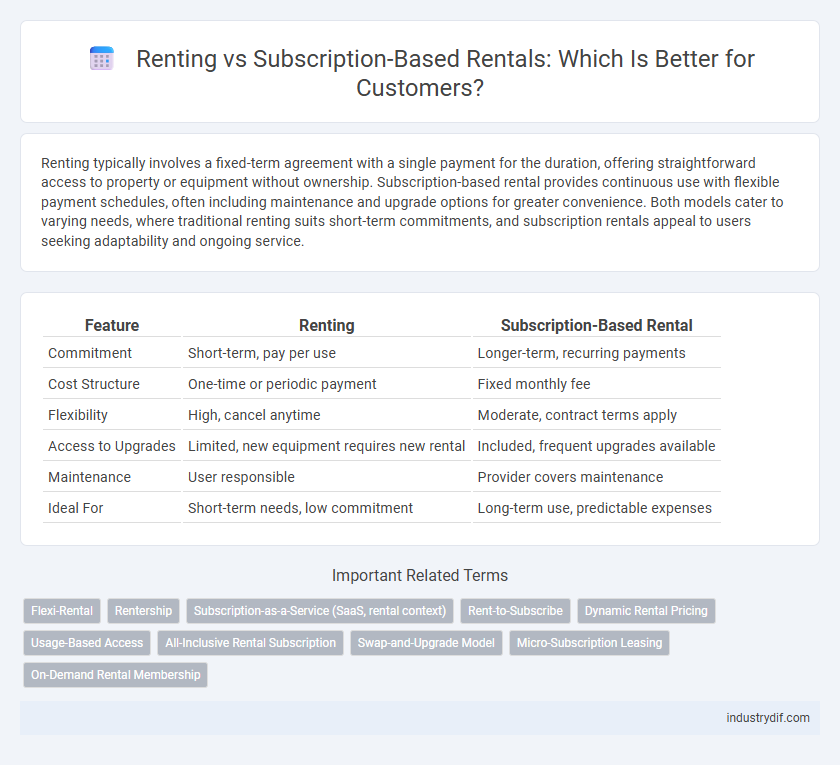
| Feature | Renting | Subscription-Based Rental |
|---|---|---|
| Commitment | Short-term, pay per use | Longer-term, recurring payments |
| Cost Structure | One-time or periodic payment | Fixed monthly fee |
| Flexibility | High, cancel anytime | Moderate, contract terms apply |
| Access to Upgrades | Limited, new equipment requires new rental | Included, frequent upgrades available |
| Maintenance | User responsible | Provider covers maintenance |
| Ideal For | Short-term needs, low commitment | Long-term use, predictable expenses |
Overview: Renting vs Subscription-Based Rental
Renting typically involves short-term use of an asset with fixed rental periods and payments, offering flexibility for occasional needs. Subscription-based rental models provide continuous access through recurring payments, often including maintenance and upgrades, ideal for long-term and consistent use. Both options cater to different user preferences, balancing cost, convenience, and commitment duration.
Key Definitions: Rent and Subscription Models
Renting involves paying a fixed amount for temporary use of an asset, typically with defined start and end dates, whereas subscription-based rental offers ongoing access to products or services for a recurring fee, often with added flexibility and included maintenance. Rent models emphasize short-term, usage-based agreements, while subscription models prioritize continuous access and convenience through periodic payments. Key metrics for renting include rental duration and total cost, whereas subscriptions focus on subscription period, renewal frequency, and value-added services.
Cost Structure Comparison
Renting typically involves a fixed upfront security deposit and monthly payments, offering predictable short-term costs but potentially higher overall expenses for long-term use. Subscription-based rentals feature a recurring fee that often includes maintenance and insurance, reducing unexpected costs and providing more flexibility for ongoing use. Evaluating total cost of ownership in each model highlights subscription plans as more cost-effective for frequent upgrades and extended durations.
Flexibility and Commitment Levels
Subscription-based rental services offer greater flexibility with shorter commitment periods and the option to switch or cancel plans easily, catering to evolving needs. Traditional renting typically involves longer lease agreements, requiring tenants to commit for fixed durations that may limit adaptability. Choosing between these models depends on balancing the need for flexibility against stability and long-term planning in rental arrangements.
User Experience and Convenience
Subscription-based rental offers enhanced user experience by providing flexible return options and seamless product swaps, eliminating the hassles of traditional renting processes. Users benefit from predictable monthly fees and continuous access to the latest products without long-term commitments. This model maximizes convenience through automated payments and personalized selections, fostering higher satisfaction and loyalty.
Access to Product Variety
Renting offers direct access to a specific product for a defined period, enabling users to choose exactly what they need without long-term commitment. Subscription-based rentals provide continuous access to a rotating selection of products, often allowing customers to experience a wider variety and regularly update their choices. This model enhances product variety by giving users flexibility and exposure to the latest items without multiple rental transactions.
Maintenance and Support Differences
Renting typically includes basic maintenance services covered by the rental agreement, ensuring operational functionality during the rental period. Subscription-based rental models often provide comprehensive support with regular maintenance, software updates, and priority customer service, enhancing equipment uptime and user experience. The subscription approach minimizes unexpected repair costs, offering predictable expenses and continuous technical assistance.
Ideal Use Cases for Each Model
Traditional renting suits long-term use cases such as housing or equipment where consistent access over months or years is needed, offering stability and cost-efficiency. Subscription-based rental models excel in scenarios requiring flexibility and frequent upgrades, like tech gadgets, fashion items, or vehicles, providing access to the latest products without large upfront costs. Businesses benefit from subscription rentals when aiming to reduce capital expenditure and adapt quickly to changing demands, while traditional rentals are ideal for users seeking predictable, extended usage.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Rental markets are increasingly shifting towards subscription-based rental models, driven by changing consumer preferences for flexibility, lower upfront costs, and access to a wider variety of products. Market trends indicate a surge in sectors like electronics, fashion, and automotive rentals adopting subscription services to enhance customer retention and predict recurring revenue streams. Data from industry reports show that 65% of renters prefer subscription-based options due to convenience and continuous product upgrades, signaling a paradigm shift in rental consumption behavior.
Choosing the Right Model: Factors to Consider
Choosing between renting and subscription-based rental depends on factors such as duration, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Renting typically suits short-term needs with upfront payments, while subscription models offer ongoing access with predictable monthly fees and added services. Evaluating usage frequency, budget constraints, and the importance of maintenance or upgrades helps determine the optimal rental approach.
Related Important Terms
Flexi-Rental
Flexi-Rental offers a hybrid model combining the cost-effectiveness of traditional renting with the adaptability of subscription-based rental, enabling users to switch items or services without long-term commitments. This model enhances user flexibility by providing customizable rental periods and easy upgrades, optimizing asset utilization and customer satisfaction in dynamic markets.
Rentership
Rentership offers flexible access to products without long-term commitment, contrasting with subscription-based rental models that typically require recurring payments for continuous use. This approach empowers renters with on-demand usage and often no upfront costs, enhancing convenience in today's dynamic rental market.
Subscription-as-a-Service (SaaS, rental context)
Subscription-as-a-Service (SaaS) rental models offer customers flexible, recurring access to products with lower upfront costs compared to traditional one-time rental agreements, enhancing cash flow management and customer retention. These SaaS rental platforms leverage data analytics to personalize offerings, optimize inventory utilization, and enable seamless scalability for both renters and providers.
Rent-to-Subscribe
Rent-to-subscribe models combine the flexibility of traditional renting with subscription benefits like regular upgrades and maintenance, offering consumers a cost-effective way to access high-value products without long-term commitment. This approach enhances user experience by providing seamless transitions between products and predictable monthly fees, appealing to tech-savvy and budget-conscious renters.
Dynamic Rental Pricing
Dynamic rental pricing leverages real-time market data and demand fluctuations to adjust rental rates, offering higher profitability compared to fixed subscription-based rental models. This pricing strategy maximizes occupancy and revenue by responding to seasonal trends, consumer behavior, and competitor rates.
Usage-Based Access
Usage-based access in rental models allows customers to pay only for the duration or extent of use, offering flexibility and cost-efficiency compared to traditional subscription-based rentals with fixed fees. This approach minimizes upfront costs and aligns expenses directly with actual consumption, making it ideal for irregular or short-term needs.
All-Inclusive Rental Subscription
All-inclusive rental subscriptions offer customers a comprehensive solution by bundling products, maintenance, and support into a single monthly fee, simplifying budget management and reducing unexpected costs. This model contrasts with traditional rentals that often charge separately for equipment, repairs, and upgrades, providing greater convenience and flexibility for long-term users.
Swap-and-Upgrade Model
The swap-and-upgrade model in rental services offers customers flexibility by allowing them to exchange rented items for newer or different versions within a subscription period, enhancing product access without long-term commitments. This model contrasts with traditional renting by emphasizing continuous product updates and personalized user experiences, driving higher customer retention and satisfaction.
Micro-Subscription Leasing
Micro-subscription leasing offers flexible, short-term rental options with lower upfront costs compared to traditional renting, catering to consumers seeking convenience and access to products without long-term commitments. This model enhances affordability and adaptability by allowing users to pay for usage periods as brief as weeks or days, making it ideal for rapidly changing needs and budget-conscious customers.
On-Demand Rental Membership
On-demand rental membership offers flexible access to products without long-term commitments, enabling users to rent items as needed while benefiting from curated selections and subscription perks. This model combines the convenience of traditional rental with the cost-effectiveness and variety of subscription services, optimizing user experience and resource utilization.
Renting vs Subscription-Based Rental Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com