Barcode scanning offers a cost-effective and widely adopted method for inventory management, relying on line-of-sight technology to quickly identify products during checkout or stocktaking. RFID inventory systems enhance efficiency by enabling wireless, simultaneous scanning of multiple items without direct visibility, significantly reducing human error and labor time. Retailers must weigh the upfront investment and operational benefits of RFID against the simplicity and lower cost of barcode scanning to optimize their inventory accuracy and supply chain management.
Table of Comparison
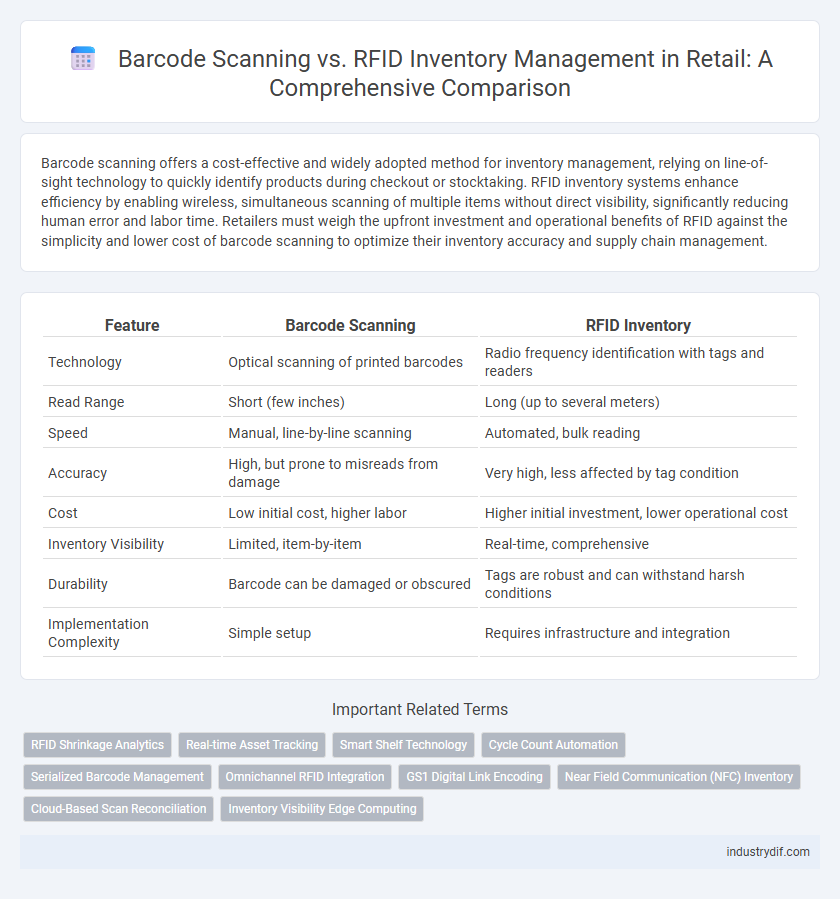
| Feature | Barcode Scanning | RFID Inventory |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Optical scanning of printed barcodes | Radio frequency identification with tags and readers |
| Read Range | Short (few inches) | Long (up to several meters) |
| Speed | Manual, line-by-line scanning | Automated, bulk reading |
| Accuracy | High, but prone to misreads from damage | Very high, less affected by tag condition |
| Cost | Low initial cost, higher labor | Higher initial investment, lower operational cost |
| Inventory Visibility | Limited, item-by-item | Real-time, comprehensive |
| Durability | Barcode can be damaged or obscured | Tags are robust and can withstand harsh conditions |
| Implementation Complexity | Simple setup | Requires infrastructure and integration |
Introduction to Barcode Scanning and RFID in Retail
Barcode scanning in retail utilizes printed barcodes to efficiently track products at checkout and during inventory management, offering cost-effective and reliable data capture. RFID technology employs radio frequency identification tags that enable real-time, contactless scanning of items, enhancing inventory accuracy and reducing manual labor. Both systems optimize supply chain visibility, with RFID providing faster item-level tracking and barcode scanning remaining widespread due to its simplicity and affordability.
How Barcode Scanning Works in Inventory Management
Barcode scanning in inventory management involves using optical technology to read printed barcode labels on products, capturing product information such as SKU, price, and batch number. Scanners emit laser beams or use imaging sensors to decode the barcode pattern, enabling quick and accurate data entry into inventory systems for real-time stock tracking and error reduction. This method supports efficient inventory audits, restocking, and sales transactions by providing precise product identification and seamless integration with point-of-sale software.
Understanding RFID Technology for Retail Inventory
RFID technology revolutionizes retail inventory management by using radio waves to automatically identify and track products, enabling real-time visibility and reducing human error compared to traditional barcode scanning. RFID tags store more data and can be read simultaneously without line-of-sight, increasing efficiency in stocktaking and loss prevention. Integrating RFID systems enhances inventory accuracy, streamlines supply chain operations, and supports dynamic demand forecasting.
Key Differences Between Barcode and RFID Systems
Barcode scanning relies on optical recognition of printed codes, requiring direct line-of-sight and manual scanning, while RFID systems use radio waves to automatically detect tags without visual contact. RFID offers faster inventory tracking and real-time data updates, enhancing accuracy and efficiency compared to barcode scanning's dependency on individual scans. Cost and implementation complexities vary, with barcodes being cheaper and easier to deploy, whereas RFID demands higher initial investment but provides superior automation and data richness.
Accuracy and Efficiency: Barcode Scanning vs RFID
RFID inventory systems significantly enhance accuracy by reducing human errors common in barcode scanning, which relies on direct line-of-sight scanning and manual handling. RFID technology enables rapid, bulk scanning of items, improving efficiency by drastically cutting down the time required for inventory counts compared to the single-item scanning process of barcodes. Retailers benefit from RFID's ability to provide real-time inventory data, improving stock management accuracy and operational productivity.
Cost Comparison: Barcode Scanning vs RFID Implementation
Barcode scanning offers a lower upfront cost, with scanners and labels generally priced between $200 and $500, making it a budget-friendly option for small to medium retailers. RFID implementation requires a higher initial investment, including RFID tags costing around $0.10 to $0.50 each and readers priced from $1,000 to $5,000, which suits larger operations needing real-time inventory tracking. Long-term savings may favor RFID due to reduced labor costs and improved accuracy, but barcode systems remain cost-effective for straightforward inventory management needs.
Integration and Scalability in Retail Environments
Barcode scanning offers straightforward integration with existing POS systems and inventory software, making it cost-effective for small to medium retail operations. RFID technology provides superior scalability and real-time inventory tracking across large retail environments, enabling automated stock management and enhanced accuracy. Retailers must evaluate their infrastructure and growth plans to determine the optimal balance between the ease of barcode system integration and the scalable benefits of RFID deployment.
Security and Data Management Considerations
Barcode scanning offers straightforward inventory tracking with limited data encryption, making it more vulnerable to theft and tampering compared to RFID systems. RFID inventory management enhances security through unique tag identification and encryption protocols, allowing real-time tracking and reducing unauthorized access risks. Effective data management is optimized in RFID systems by enabling automated updates and centralized databases, which improve accuracy and minimize human error during inventory audits.
Real-World Use Cases: Barcode vs RFID Success Stories
Retailers leverage barcode scanning for efficient stock management in small to medium-sized stores, as seen in grocery chains using handheld scanners to reduce checkout times and track inventory in real-time. RFID technology excels in large warehouses or high-value goods environments, with brands like Zara employing RFID for automatic stock replenishment and theft prevention, significantly improving inventory accuracy. Case studies highlight barcode systems' cost-effectiveness and RFID's advanced data capture capabilities, guiding retailers to blend both methods based on scale and complexity.
Choosing the Right Inventory Solution for Your Retail Business
Selecting the right inventory solution for your retail business depends on factors such as accuracy, cost, and operational efficiency. Barcode scanning offers a cost-effective and widely adopted method for tracking individual items, while RFID inventory systems provide faster, real-time tracking and bulk item management with enhanced accuracy. Evaluating store size, inventory turnover, and technology infrastructure helps determine whether barcode or RFID aligns better with your business goals and customer experience.
Related Important Terms
RFID Shrinkage Analytics
RFID shrinkage analytics in retail provide real-time, high-accuracy inventory tracking by detecting unauthorized product movements and discrepancies faster than traditional barcode scanning. Enhanced visibility through RFID enables retailers to reduce losses, optimize stock levels, and improve overall supply chain transparency.
Real-time Asset Tracking
Barcode scanning offers quick and accurate identification of individual items but requires line-of-sight and manual scanning, limiting real-time asset tracking capabilities in retail environments. RFID inventory systems enable continuous, non-line-of-sight monitoring of stock levels and asset movement, providing real-time data updates essential for efficient inventory management and reducing stockouts.
Smart Shelf Technology
Smart shelf technology integrates RFID inventory systems, enabling real-time, accurate stock monitoring without manual scanning, unlike traditional barcode scanning that requires direct line-of-sight and individual item interaction. RFID-enabled smart shelves enhance inventory accuracy, reduce labor costs, and improve customer experience by providing instant product availability updates and automated replenishment alerts.
Cycle Count Automation
Barcode scanning enables precise cycle count automation by quickly capturing product data with handheld devices, reducing human error and improving inventory accuracy. RFID inventory systems enhance this process further by allowing simultaneous scanning of multiple items without line-of-sight, accelerating cycle counts and providing real-time stock visibility in retail environments.
Serialized Barcode Management
Serialized barcode management ensures precise tracking of individual retail items by assigning unique identifiers to each product, enhancing inventory accuracy and reducing stock discrepancies. Unlike RFID inventory systems that rely on radio frequency signals, barcode scanning requires direct line-of-sight but offers cost-effective, scalable solutions for serialized product management in retail environments.
Omnichannel RFID Integration
Omnichannel RFID integration streamlines inventory accuracy and real-time visibility across retail channels by embedding RFID tags in merchandise, enabling seamless scanning and tracking compared to traditional barcode scanning which requires direct line-of-sight and manual updates. This technology enhances supply chain efficiency, reduces stockouts, and supports dynamic inventory management critical for consistent customer experience in omnichannel retail environments.
GS1 Digital Link Encoding
GS1 Digital Link Encoding enhances barcode scanning by embedding rich product data into a single scannable code, enabling seamless integration with RFID inventory systems for real-time stock tracking and improved accuracy. Retailers leveraging GS1 Digital Link benefit from streamlined supply chain operations and enriched customer experiences through unified product identification across both barcode and RFID technologies.
Near Field Communication (NFC) Inventory
Near Field Communication (NFC) inventory offers faster, contactless scanning capabilities compared to traditional barcode scanning, enabling real-time stock tracking and reducing human error in retail environments. Unlike RFID systems that may require specialized infrastructure, NFC leverages ubiquitous smartphone technology, facilitating seamless integration and improved inventory accuracy with minimal hardware investment.
Cloud-Based Scan Reconciliation
Cloud-based scan reconciliation enhances inventory accuracy by integrating barcode scanning data with real-time RFID tracking, enabling seamless synchronization across retail systems. This approach reduces discrepancies, accelerates stock audits, and improves supply chain visibility by leveraging cloud computing for scalable data management and analytics.
Inventory Visibility Edge Computing
Barcode scanning offers reliable, cost-effective inventory tracking but relies on line-of-sight and manual scanning, limiting real-time visibility in retail environments. RFID technology paired with edge computing enhances inventory visibility by enabling continuous, automated data processing at the source, improving accuracy and reducing stockouts.
Barcode Scanning vs RFID Inventory Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com