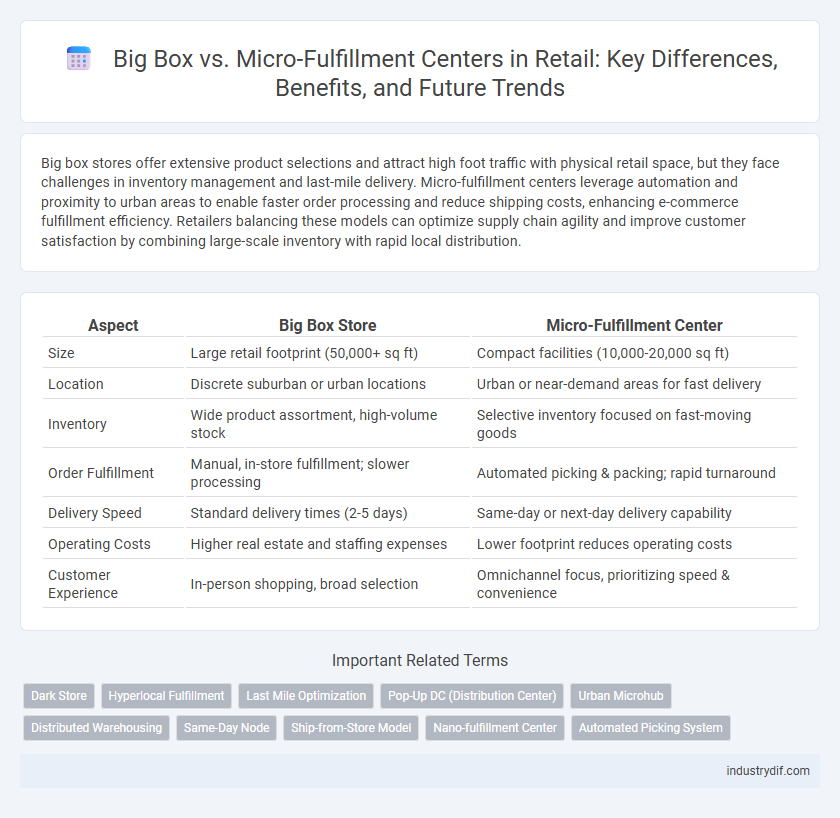
Big box stores offer extensive product selections and attract high foot traffic with physical retail space, but they face challenges in inventory management and last-mile delivery. Micro-fulfillment centers leverage automation and proximity to urban areas to enable faster order processing and reduce shipping costs, enhancing e-commerce fulfillment efficiency. Retailers balancing these models can optimize supply chain agility and improve customer satisfaction by combining large-scale inventory with rapid local distribution.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Big Box Store | Micro-Fulfillment Center |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Large retail footprint (50,000+ sq ft) | Compact facilities (10,000-20,000 sq ft) |
| Location | Discrete suburban or urban locations | Urban or near-demand areas for fast delivery |
| Inventory | Wide product assortment, high-volume stock | Selective inventory focused on fast-moving goods |
| Order Fulfillment | Manual, in-store fulfillment; slower processing | Automated picking & packing; rapid turnaround |
| Delivery Speed | Standard delivery times (2-5 days) | Same-day or next-day delivery capability |
| Operating Costs | Higher real estate and staffing expenses | Lower footprint reduces operating costs |
| Customer Experience | In-person shopping, broad selection | Omnichannel focus, prioritizing speed & convenience |
Defining Big Box Retail and Micro-Fulfillment Centers
Big box retail stores are large-scale retail establishments characterized by extensive physical footprints, offering a wide variety of products under one roof, often exceeding 50,000 square feet. Micro-fulfillment centers are compact, technology-driven warehouses located near urban populations that use automation to rapidly process and fulfill online orders within smaller spaces, typically under 15,000 square feet. The contrast between these two formats lies in their operational scale and proximity to consumers, impacting inventory management and delivery speed in the retail supply chain.
Operational Models: Scale vs. Agility
Big box stores leverage large-scale operational models with extensive inventory and space to optimize economies of scale, enabling high-volume sales and lower per-unit costs. Micro-fulfillment centers prioritize agility through smaller footprints and automated technologies, allowing rapid order processing and efficient last-mile delivery in urban markets. The trade-off between scale and agility defines their distinct roles in the retail supply chain, shaping fulfillment strategies to meet diverse consumer demands.
Inventory Management Strategies
Big box stores rely on extensive inventory holdings to ensure product availability and capitalize on bulk purchasing, but this often leads to higher holding costs and slower stock turnover. Micro-fulfillment centers leverage automation and data-driven inventory management, enabling rapid replenishment and precise demand forecasting within urban areas. Integrating micro-fulfillment with traditional big box supply chains optimizes stock levels, reduces delivery times, and enhances overall inventory efficiency.
Location and Customer Proximity
Big box stores are typically located in suburban areas with ample space, catering to a broad customer base but often requiring customers to travel longer distances. Micro-fulfillment centers are strategically placed in urban or densely populated locations, significantly reducing delivery times and enhancing customer proximity. This urban-centric approach allows retailers to meet rising consumer demands for fast, convenient order fulfillment.
Fulfillment Speed and Efficiency
Big box retail stores typically handle fulfillment with larger inventories and slower processing times due to their expansive layouts and manual handling processes. Micro-fulfillment centers leverage automation and proximity to urban areas, significantly increasing fulfillment speed and order accuracy. These centers reduce last-mile delivery times and operational costs, enhancing overall efficiency in the retail supply chain.
Technology Integration in Both Formats
Big box stores leverage advanced inventory management systems and automated checkout technologies to streamline operations and enhance customer experience. Micro-fulfillment centers utilize robotics, AI-driven order picking, and real-time data analytics to optimize space and accelerate delivery times in urban areas. Integration of IoT sensors and cloud computing enables both formats to maintain precise stock levels and improve supply chain responsiveness.
Cost Structures and Investment Requirements
Big box stores require significant upfront capital investment in large physical spaces and extensive inventory, leading to high fixed costs in rent, utilities, and labor. Micro-fulfillment centers demand lower initial investment due to smaller footprints and automated technology, resulting in reduced operational expenses and improved scalability. Cost structures in big box retail are dominated by overhead and inventory carrying costs, while micro-fulfillment centers emphasize technology integration and efficient last-mile delivery.
Impact on Last-Mile Delivery
Big box stores often face challenges with last-mile delivery due to their large footprints and centralized inventory, leading to longer delivery times and higher transportation costs. Micro-fulfillment centers, strategically located in urban areas, significantly reduce delivery distances, enabling faster and more cost-effective last-mile logistics. This shift enhances customer satisfaction through quicker order fulfillment and supports sustainable delivery practices by minimizing fuel consumption.
Sustainability Considerations
Big box retail stores typically have larger carbon footprints due to extensive space requirements and higher energy consumption, whereas micro-fulfillment centers optimize last-mile delivery, reducing transportation emissions and improving supply chain efficiency. Micro-fulfillment centers leverage automation and localized inventory, minimizing food waste and packaging needs, aligning with sustainability goals. Choosing micro-fulfillment solutions can significantly lower environmental impact compared to traditional big box retail models by enhancing resource efficiency and reducing logistics-related emissions.
Future Trends in Retail Fulfillment
Big box stores are evolving by integrating micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) within their footprint to boost same-day delivery efficiency and reduce last-mile shipping costs. Emerging retail fulfillment trends emphasize automation, robotics, and AI-driven inventory management in MFCs to accelerate order processing and improve accuracy. The future of retail fulfillment will prioritize urban micro-fulfillment to meet growing e-commerce demand while maintaining cost-effective scalability compared to traditional large warehouses.
Related Important Terms
Dark Store
Dark stores function as micro-fulfillment centers focused on optimizing order accuracy and delivery speed within urban retail environments, contrasting with traditional big box stores that emphasize vast physical inventory and in-store customer experience. Leveraging advanced automation and localized inventory, dark stores reduce last-mile delivery costs while supporting omni-channel retail strategies more efficiently than sprawling big box formats.
Hyperlocal Fulfillment
Big box stores typically offer vast inventories and one-stop shopping, but micro-fulfillment centers enable hyperlocal fulfillment by utilizing automated, compact spaces near urban areas to expedite last-mile delivery. This approach reduces delivery times and enhances inventory turnover by stocking products closer to consumer demand hotspots.
Last Mile Optimization
Big box stores leverage large-scale inventories and centralized locations to streamline last mile deliveries but often face challenges with speed and cost efficiency in urban areas. Micro-fulfillment centers utilize compact, automated facilities near dense consumer populations, enabling faster delivery times and reduced transportation expenses, thus optimizing last mile logistics in retail.
Pop-Up DC (Distribution Center)
Pop-Up Distribution Centers (DCs) offer agile, scalable solutions bridging the gap between traditional Big Box stores and Micro-fulfillment Centers by enabling rapid inventory deployment closer to consumers, reducing delivery times and last-mile costs. These flexible DCs optimize urban retail supply chains by supporting localized demand spikes without the substantial real estate investment required for large Big Box stores or permanent Micro-fulfillment facilities.
Urban Microhub
Urban micro-fulfillment centers optimize retail supply chains by enabling faster delivery and reducing last-mile costs compared to traditional big box stores, which require large footprints and extensive inventory. These microhubs leverage automation and proximity to dense urban populations to meet growing e-commerce demand while minimizing real estate and operational expenses.
Distributed Warehousing
Big box stores rely on centralized inventory within expansive spaces to serve large, regional markets, whereas micro-fulfillment centers prioritize distributed warehousing by positioning small, automated facilities closer to urban consumers, drastically reducing last-mile delivery times. Distributed warehousing enhances supply chain flexibility and responsiveness, enabling retailers to efficiently manage stock levels across multiple locations and meet growing demands for fast e-commerce fulfillment.
Same-Day Node
Big box stores serve as extensive same-day nodes by leveraging large physical footprints for vast inventory storage and immediate customer access, while micro-fulfillment centers optimize urban proximity and automation to accelerate last-mile delivery within dense retail markets. Emphasizing strategic location and technology, micro-fulfillment centers outperform big box stores in rapid order processing and reducing delivery times for same-day fulfillment.
Ship-from-Store Model
Ship-from-store models leverage existing big box retail locations to fulfill online orders quickly, reducing delivery times and shipping costs by utilizing in-store inventory. Micro-fulfillment centers, strategically placed near urban areas, complement this by handling high volumes of e-commerce orders with automated systems, enhancing efficiency in last-mile logistics.
Nano-fulfillment Center
Nano-fulfillment centers, significantly smaller than big box stores and traditional micro-fulfillment centers, optimize last-mile delivery by automating order picking within urban or highly localized areas, reducing delivery times and operational costs. These compact facilities leverage advanced robotics and AI to enhance inventory management, making them ideal for retailers seeking to provide rapid e-commerce fulfillment in dense metropolitan markets.
Automated Picking System
Automated picking systems in micro-fulfillment centers enhance order accuracy and speed by utilizing robotics and AI, optimizing space within urban retail environments compared to traditional big box stores. This technology reduces labor costs and improves inventory management, enabling faster delivery times and meeting rising consumer demand for convenience in e-commerce.
Big box vs Micro-fulfillment center Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com