Brick-and-mortar stores offer customers a tactile shopping experience with immediate product access and personalized service, fostering brand loyalty through physical presence. Dark stores prioritize efficiency and speed by operating as local fulfillment centers for online orders, reducing delivery times and costs. Retailers often balance both models to meet diverse consumer preferences and optimize supply chain logistics.
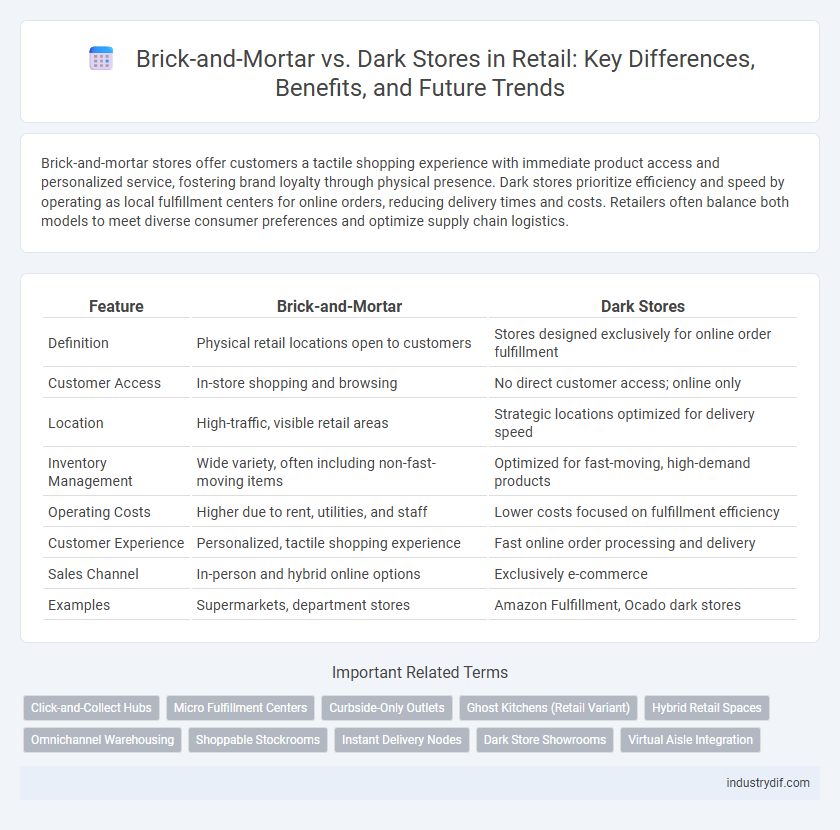
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Brick-and-Mortar | Dark Stores |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical retail locations open to customers | Stores designed exclusively for online order fulfillment |
| Customer Access | In-store shopping and browsing | No direct customer access; online only |
| Location | High-traffic, visible retail areas | Strategic locations optimized for delivery speed |
| Inventory Management | Wide variety, often including non-fast-moving items | Optimized for fast-moving, high-demand products |
| Operating Costs | Higher due to rent, utilities, and staff | Lower costs focused on fulfillment efficiency |
| Customer Experience | Personalized, tactile shopping experience | Fast online order processing and delivery |
| Sales Channel | In-person and hybrid online options | Exclusively e-commerce |
| Examples | Supermarkets, department stores | Amazon Fulfillment, Ocado dark stores |
Introduction to Brick-and-Mortar and Dark Stores
Brick-and-mortar stores are physical retail locations where customers can browse products and make purchases in person, fostering direct human interaction and immediate product access. Dark stores operate as fulfillment centers exclusively for online orders, optimized for efficient picking, packing, and delivery without customer foot traffic. The contrasting models highlight the evolving retail landscape, balancing traditional shopping experiences with growing e-commerce demands.
Defining Brick-and-Mortar Retail
Brick-and-mortar retail refers to physical stores where customers can browse, interact with products, and make purchases in person, offering tangible shopping experiences and immediate product access. This traditional retail model supports direct customer service, product trials, and instant fulfillment, which foster consumer trust and brand loyalty. Unlike dark stores, which operate as fulfillment centers without direct customer access, brick-and-mortar stores are integral to local economies and provide critical touchpoints for omnichannel retail strategies.
What Are Dark Stores?
Dark stores are physical retail spaces that operate exclusively for online order fulfillment without customer access, optimizing inventory management and delivery speed. Unlike traditional brick-and-mortar stores, dark stores are designed to streamline picking and packing processes for faster last-mile delivery. Retailers leverage dark stores to reduce operational costs, enhance product availability, and improve customer experience in e-commerce.
Key Differences Between Brick-and-Mortar and Dark Stores
Brick-and-mortar stores are physical retail locations offering in-person shopping experiences and immediate product availability, while dark stores function exclusively as fulfillment centers for online orders, lacking customer-facing areas. Brick-and-mortar stores prioritize customer engagement and brand experience, whereas dark stores optimize inventory management and rapid delivery logistics. The fundamental difference lies in their operational design: brick-and-mortar serves walk-in shoppers, while dark stores streamline e-commerce fulfillment to enhance delivery efficiency.
Customer Experience: Physical vs Digital Fulfillment
Brick-and-mortar stores provide customers with tangible sensory experiences, immediate product access, and personalized in-person service, fostering stronger brand loyalty through physical interactions. Dark stores enhance digital fulfillment efficiency by optimizing inventory management and enabling faster, contactless order processing tailored for online shopping convenience. Balancing the immediacy of physical retail with the streamlined convenience of dark store logistics significantly shapes customer satisfaction in the evolving retail landscape.
Inventory Management Strategies
Brick-and-mortar stores utilize on-site inventory management systems to ensure immediate product availability for walk-in customers, emphasizing real-time stock tracking and shelf replenishment. Dark stores, optimized for online order fulfillment, deploy advanced warehouse management systems (WMS) that enhance picking accuracy, reduce lead times, and integrate with e-commerce platforms for dynamic inventory allocation. Effective inventory management in both formats relies on data analytics and demand forecasting to balance stock levels, minimize holding costs, and prevent stockouts or overstock situations.
Operational Costs and Profit Margins
Brick-and-mortar stores incur higher operational costs due to expenses like rent, utilities, and in-store staff wages, which can compress profit margins significantly. Dark stores operate with lower overhead by eliminating customer-facing infrastructure, enabling more efficient inventory management and faster order fulfillment, thus enhancing profitability. The streamlined logistics and reduced fixed costs in dark stores often result in higher profit margins compared to traditional retail outlets.
Impact on Supply Chain and Logistics
Brick-and-mortar stores demand a complex supply chain with frequent restocking and in-store inventory management, often requiring larger distribution centers and robust last-mile delivery systems. Dark stores optimize supply chains by serving exclusively as fulfillment centers for online orders, reducing the need for customer-facing operations and enabling faster, more efficient order processing and local delivery. This shift streamlines logistics, lowers overhead costs, and enhances inventory accuracy, fundamentally transforming retail supply chain dynamics.
Emerging Trends in Retail Store Formats
Emerging trends in retail store formats highlight the rising importance of dark stores, which serve as localized fulfillment centers optimized for rapid online order processing, contrasting traditional brick-and-mortar stores focused on in-person shopping experiences. Retailers are increasingly adopting hybrid models that integrate physical stores with digital inventory management to enhance convenience and reduce delivery times. This shift reflects consumer demand for seamless omnichannel experiences, leveraging data analytics and automation to streamline inventory, fulfill orders efficiently, and drive operational agility.
Future Outlook: Brick-and-Mortar vs Dark Stores
Brick-and-mortar stores will continue evolving by integrating digital technologies and offering experiential shopping to compete with dark stores' efficiency in online order fulfillment. Dark stores, optimized for speed and inventory management, are expected to expand in urban areas, driven by rising e-commerce demand and last-mile delivery improvements. Retailers investing in hybrid models that combine physical presence with dark store backend capabilities are positioned to capture future market growth and consumer convenience preferences.
Related Important Terms
Click-and-Collect Hubs
Click-and-collect hubs in brick-and-mortar stores enhance customer convenience by allowing seamless in-person pickup, reducing delivery times and operational costs associated with dark stores. These hybrid retail models optimize inventory management and boost foot traffic while leveraging omnichannel strategies to meet evolving consumer preferences.
Micro Fulfillment Centers
Micro fulfillment centers (MFCs) strategically replace traditional brick-and-mortar retail spaces by maximizing automation and robotics to fulfill online orders quickly within urban areas. These dark stores, designed exclusively for e-commerce, optimize inventory management and reduce delivery times, enhancing customer satisfaction while lowering operational costs.
Curbside-Only Outlets
Curbside-only outlets bridge the gap between brick-and-mortar stores and dark stores by offering consumers immediate product pickup without entering a physical location, enhancing convenience and safety. These outlets optimize inventory management and reduce operational costs by leveraging localized fulfillment while meeting growing demand for contactless retail experiences.
Ghost Kitchens (Retail Variant)
Ghost kitchens, a retail variant of dark stores, operate without a storefront and are designed exclusively for online order fulfillment, enabling retailers to optimize delivery efficiency and reduce overhead costs compared to traditional brick-and-mortar outlets. These facilities leverage real-time inventory management and advanced logistics, providing rapid, contactless service that caters to the growing demand for convenience in urban retail markets.
Hybrid Retail Spaces
Hybrid retail spaces combine brick-and-mortar stores with dark store functionality, enabling retailers to optimize inventory management and fulfill online orders efficiently while maintaining in-person customer experiences. This integrated approach boosts sales by leveraging physical locations for quick delivery and localized stock, reducing last-mile logistics costs and enhancing overall operational agility.
Omnichannel Warehousing
Brick-and-mortar stores and dark stores serve complementary roles in omnichannel warehousing by optimizing inventory distribution and fulfillment speed, enhancing customer satisfaction through seamless online and offline integration. Utilizing dark stores as localized fulfillment centers reduces delivery times and operational costs, while physical stores provide immediate pickup options and experiential shopping, collectively driving efficient retail supply chain execution.
Shoppable Stockrooms
Shoppable stockrooms in brick-and-mortar stores enhance customer experience by providing real-time inventory visibility and immediate product access, merging physical retail benefits with e-commerce efficiency. Dark stores optimize last-mile delivery by functioning exclusively as local fulfillment centers, reducing delivery times and operational costs while supporting omnichannel retail strategies.
Instant Delivery Nodes
Brick-and-mortar stores serve as traditional instant delivery nodes enabling immediate customer access and in-person shopping experiences, while dark stores function exclusively as localized fulfillment centers optimized for rapid order processing and delivery, reducing last-mile transit times. Retailers leveraging dark stores enhance operational efficiency and meet growing consumer demand for instant delivery by strategically positioning these nodes closer to high-density urban areas.
Dark Store Showrooms
Dark store showrooms revolutionize retail by combining physical product displays with online order fulfillment, enabling retailers to optimize inventory management and reduce last-mile delivery times. These hybrid spaces enhance customer experience by offering tactile interaction with products while streamlining e-commerce logistics in dense urban markets.
Virtual Aisle Integration
Virtual aisle integration bridges brick-and-mortar stores and dark stores by enabling real-time inventory visibility and seamless order fulfillment across both channels. This technology enhances customer experience through faster delivery options and optimized stock management, driving efficiency in the retail supply chain.
Brick-and-mortar vs Dark stores Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com