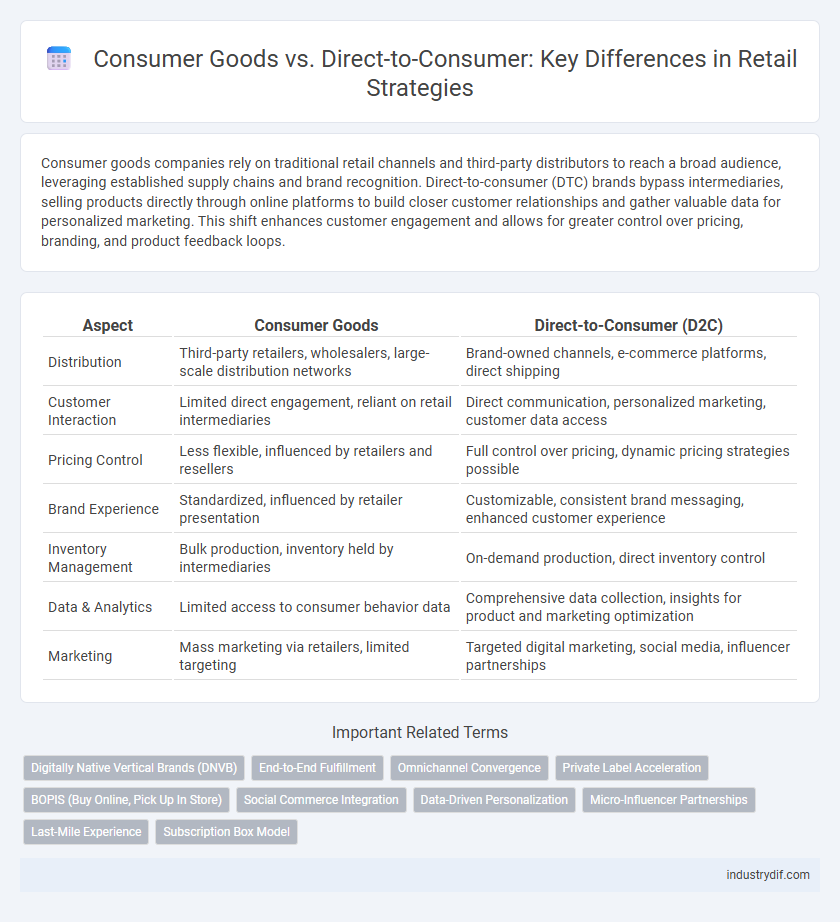
Consumer goods companies rely on traditional retail channels and third-party distributors to reach a broad audience, leveraging established supply chains and brand recognition. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands bypass intermediaries, selling products directly through online platforms to build closer customer relationships and gather valuable data for personalized marketing. This shift enhances customer engagement and allows for greater control over pricing, branding, and product feedback loops.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Consumer Goods | Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) |
|---|---|---|
| Distribution | Third-party retailers, wholesalers, large-scale distribution networks | Brand-owned channels, e-commerce platforms, direct shipping |
| Customer Interaction | Limited direct engagement, reliant on retail intermediaries | Direct communication, personalized marketing, customer data access |
| Pricing Control | Less flexible, influenced by retailers and resellers | Full control over pricing, dynamic pricing strategies possible |
| Brand Experience | Standardized, influenced by retailer presentation | Customizable, consistent brand messaging, enhanced customer experience |
| Inventory Management | Bulk production, inventory held by intermediaries | On-demand production, direct inventory control |
| Data & Analytics | Limited access to consumer behavior data | Comprehensive data collection, insights for product and marketing optimization |
| Marketing | Mass marketing via retailers, limited targeting | Targeted digital marketing, social media, influencer partnerships |
Definition of Consumer Goods and Direct-to-Consumer
Consumer goods refer to tangible products purchased by end-users for personal use, encompassing categories such as food, clothing, electronics, and household items. Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) is a retail model where brands sell products directly to customers, bypassing traditional intermediaries like wholesalers and retailers to enhance customer engagement and control over brand experience. Understanding the distinction highlights how consumer goods represent the product category, while DTC defines the distribution channel optimizing sales and consumer relationships.
Key Differences Between Consumer Goods and DTC
Consumer goods companies primarily distribute products through third-party retailers, while direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands sell products directly to customers via online platforms or branded stores. Consumer goods firms rely heavily on large-scale retail partnerships, often limiting control over customer data and brand experience, whereas DTC businesses leverage personalized marketing and direct consumer insights to build stronger relationships. Inventory management and supply chain dynamics differ significantly, with consumer goods focusing on mass production and widespread availability, contrasting with DTC's emphasis on agility and tailored product offerings.
Evolution of Retail: Traditional vs DTC Models
Consumer goods brands traditionally relied on wholesale distribution channels, retail partnerships, and extensive supply chains to reach mass markets, emphasizing broad product availability and brand visibility. DTC models disrupt this norm by leveraging e-commerce platforms and direct customer relationships, enabling personalized marketing, data-driven insights, and higher profit margins through cutting out intermediaries. The retail evolution reflects a shift from passive consumer engagement to proactive brand-consumer interaction, fostering brand loyalty and agility in responding to consumer trends.
Supply Chain Impacts in Consumer Goods vs DTC
Consumer goods companies rely on complex, multi-tiered supply chains involving wholesalers, distributors, and retailers, which can lead to longer lead times and higher inventory costs. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) models streamline the supply chain by eliminating intermediaries, enabling faster order fulfillment and enhanced control over inventory management. This streamlined approach reduces overhead expenses and improves responsiveness to consumer demand fluctuations, ultimately driving greater supply chain agility.
Branding Strategies: Consumer Goods vs DTC
Consumer goods companies rely heavily on mass branding strategies that emphasize broad market appeal through consistent messaging across diverse retail channels, utilizing established brand equity to drive consumer trust. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands focus on personalized, agile branding strategies powered by direct customer interactions, digital engagement, and data-driven insights to create tailored experiences and foster community loyalty. The strategic shift from traditional mass marketing to targeted, authentic storytelling enables DTC brands to differentiate themselves and rapidly adapt to evolving consumer preferences.
Customer Experience and Engagement
Consumer goods brands traditionally rely on retailers for distribution, which limits direct interaction with customers and reduces opportunities for personalized experiences. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) models empower brands to collect rich customer data, enabling tailored marketing, seamless engagement, and improved customer loyalty. Enhanced customer experience in DTC channels drives higher satisfaction and lifetime value by offering customized products, fast shipping, and responsive support.
Marketing Channels for Consumer Goods and DTC
Marketing channels for Consumer Goods typically involve multiple intermediaries such as wholesalers, distributors, and retailers, creating a wide-reaching supply chain that leverages traditional outlets like supermarkets, department stores, and mass merchandisers. Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) brands primarily use digital platforms, including branded e-commerce websites, social media, and mobile apps, enabling personalized marketing and direct customer engagement. The DTC model emphasizes data-driven strategies and real-time customer feedback to optimize marketing campaigns, reducing reliance on third-party retailers and enhancing brand control.
Profit Margins and Revenue Models
Consumer goods companies typically rely on wholesale distribution channels, resulting in lower profit margins due to retailer markups, but benefit from larger volume sales and established brand recognition. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) models bypass intermediaries, enabling higher profit margins by controlling pricing and customer experience while generating revenue primarily through online sales platforms. The DTC approach also leverages data-driven marketing and personalized customer engagement, which can increase lifetime value and reduce customer acquisition costs compared to traditional consumer goods strategies.
Data Analytics and Consumer Insights
Consumer goods companies leverage data analytics to analyze broad market trends and aggregate consumer insights from diverse retail channels, enabling optimized product distribution and inventory management. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands utilize real-time data analytics to gather detailed consumer behavior and preferences directly from their own platforms, facilitating personalized marketing strategies and enhanced customer experience. Advanced consumer insights derived from DTC models provide actionable feedback loops that drive product innovation and foster stronger brand loyalty.
Future Trends in Retail: The Shift Towards DTC
The future of retail is increasingly defined by the shift towards direct-to-consumer (DTC) models, which leverage digital platforms to foster personalized shopping experiences and enhance customer loyalty. Consumer goods brands adopting DTC strategies benefit from greater control over brand messaging, data-driven insights, and higher profit margins by bypassing traditional retail intermediaries. This transition is accelerated by advancements in e-commerce technology, social media integration, and changing consumer preferences favoring convenience and customization.
Related Important Terms
Digitally Native Vertical Brands (DNVB)
Consumer Goods companies typically rely on traditional retail distribution channels, while Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) brands, especially Digitally Native Vertical Brands (DNVB), leverage e-commerce platforms to control the entire customer experience and gather rich consumer data. DNVBs optimize digital marketing, personalized customer engagement, and agile supply chains to drive rapid growth and higher profit margins compared to conventional consumer goods companies.
End-to-End Fulfillment
Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) models streamline end-to-end fulfillment by eliminating intermediaries, enabling faster delivery, real-time inventory management, and personalized customer experiences. In contrast, traditional Consumer Goods companies rely on complex supply chains with wholesalers and retailers, often leading to longer fulfillment cycles and less direct customer engagement.
Omnichannel Convergence
Omnichannel convergence in retail merges Consumer Goods companies' extensive distribution networks with Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) brands' personalized customer interactions, creating seamless shopping experiences across physical stores, e-commerce, and mobile platforms. This integration leverages data analytics and supply chain agility to optimize inventory management, enhance customer engagement, and drive revenue growth in a competitive market.
Private Label Acceleration
Private label acceleration in retail is reshaping consumer goods by enabling brands to bypass traditional distribution channels and engage directly with customers through direct-to-consumer strategies. This shift enhances profit margins, fosters brand loyalty, and leverages data analytics to tailor product offerings, driving rapid growth and competitive advantage in the evolving marketplace.
BOPIS (Buy Online, Pick Up In Store)
Consumer goods companies increasingly leverage BOPIS (Buy Online, Pick Up In Store) strategies to enhance customer convenience and reduce shipping costs, driving higher in-store foot traffic and impulse purchases. Direct-to-consumer brands utilize BOPIS to seamlessly integrate online and offline channels, improving last-mile fulfillment efficiency and delivering personalized shopping experiences that boost customer loyalty.
Social Commerce Integration
Consumer goods brands increasingly leverage social commerce integration to enhance direct-to-consumer (DTC) strategies by enabling seamless in-app purchases and personalized engagement through platforms like Instagram and TikTok. This approach boosts conversion rates and customer loyalty by combining product discovery with social interaction, driving higher sales compared to traditional retail channels.
Data-Driven Personalization
Consumer goods brands leverage broad market analytics to optimize product distribution and pricing, while direct-to-consumer (DTC) companies utilize data-driven personalization to tailor marketing campaigns and product recommendations based on real-time consumer behavior and preferences. Advanced machine learning algorithms and CRM platforms enable DTC brands to enhance customer engagement and increase lifetime value by delivering individualized shopping experiences.
Micro-Influencer Partnerships
Consumer goods brands leverage micro-influencer partnerships to boost authentic engagement and expand reach in niche markets, driving higher conversion rates than traditional advertising. Direct-to-consumer companies prioritize these collaborations to foster personalized connections and gather real-time consumer insights, enhancing product development and customer loyalty.
Last-Mile Experience
Consumer goods companies rely on third-party retailers and logistics providers for last-mile delivery, often resulting in less control over shipping speed and customer experience. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands prioritize streamlined last-mile strategies, leveraging data-driven logistics and personalized touchpoints to enhance delivery reliability and customer satisfaction.
Subscription Box Model
The subscription box model in retail enables consumer goods brands to bypass traditional distribution channels by selling directly to consumers, enhancing customer retention and personalized experiences. This direct-to-consumer approach leverages data-driven insights to curate tailored product selections, boosting customer lifetime value and brand loyalty.
Consumer Goods vs Direct-to-Consumer Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com