Private label products enable retailers to offer exclusive items that boost profit margins by cutting out intermediaries, while DTC brands build strong consumer relationships through personalized marketing and direct feedback. Private label often leverages existing retail infrastructure for immediate shelf presence, whereas DTC brands rely heavily on digital platforms for customer acquisition and brand storytelling. Both strategies optimize supply chain control but differ in customer engagement and brand loyalty dynamics.
Table of Comparison
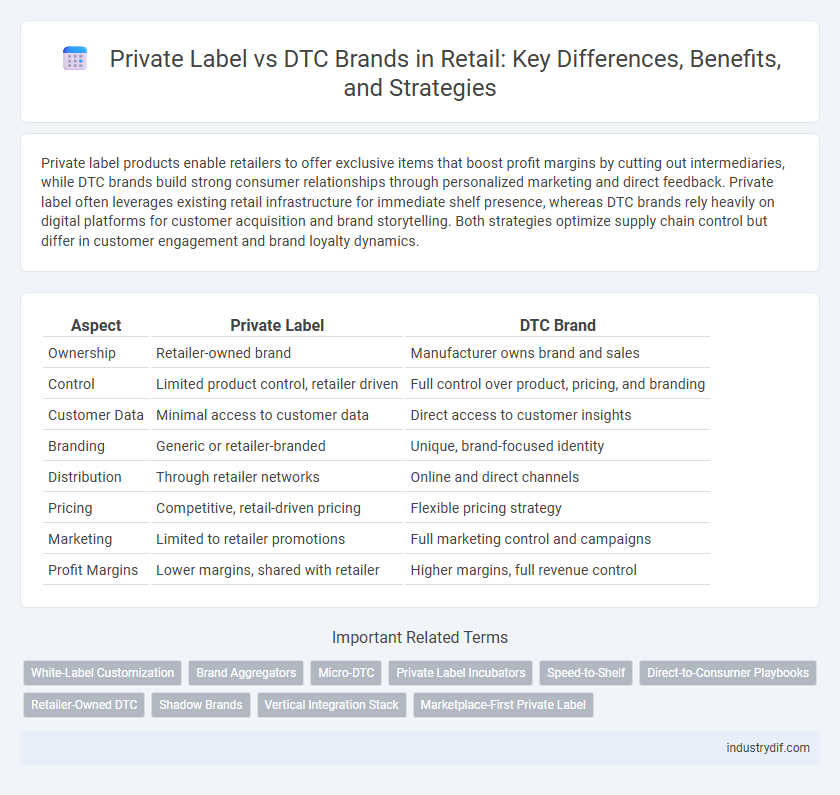
| Aspect | Private Label | DTC Brand |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Retailer-owned brand | Manufacturer owns brand and sales |
| Control | Limited product control, retailer driven | Full control over product, pricing, and branding |
| Customer Data | Minimal access to customer data | Direct access to customer insights |
| Branding | Generic or retailer-branded | Unique, brand-focused identity |
| Distribution | Through retailer networks | Online and direct channels |
| Pricing | Competitive, retail-driven pricing | Flexible pricing strategy |
| Marketing | Limited to retailer promotions | Full marketing control and campaigns |
| Profit Margins | Lower margins, shared with retailer | Higher margins, full revenue control |
Definition of Private Label and DTC Brands
Private label products are manufactured by one company and sold under another company's brand, often found in retail stores offering exclusive items that enhance brand loyalty and control over pricing. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands bypass traditional retail channels, selling products directly to customers via online platforms, enabling personalized marketing and higher profit margins. Both models cater to different business strategies, with private labels focusing on retail partnerships and DTC brands emphasizing customer engagement and brand experience.
Key Differences Between Private Label and DTC
Private label products are manufactured by third-party companies and sold under a retailer's brand, enabling retailers to control pricing and shelf placement without managing production. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands maintain full control over product development, marketing, and customer experience by selling directly through owned channels like e-commerce websites. The key differences lie in ownership of manufacturing, customer relationship management, and brand equity development, where private label relies on retailer branding while DTC cultivates a direct consumer connection.
Advantages of Private Label for Retailers
Private label products offer retailers higher profit margins by cutting out intermediaries and allowing control over production costs. Retailers can tailor private labels to customer preferences, enhancing brand loyalty and competitive differentiation. Exclusive private label offerings also enable better shelf space management and inventory control, driving overall sales growth.
Benefits of DTC Brands for Consumers
DTC brands offer consumers enhanced transparency and direct communication, enabling personalized shopping experiences and faster access to product innovations. By cutting out intermediaries, DTC brands often provide higher-quality products at more competitive prices. This direct relationship fosters greater trust, loyalty, and customer satisfaction compared to traditional private label offerings.
Supply Chain and Manufacturing Considerations
Private label brands leverage established manufacturers and streamlined supply chains to reduce production costs and enhance scalability, while DTC brands often maintain greater control over manufacturing processes, enabling faster innovation and customization. Supply chain agility is crucial for DTC brands to meet direct consumer demand, whereas private labels rely on retailer-driven inventory management and bulk ordering efficiencies. Both models require strategic coordination between sourcing, production, and logistics to optimize lead times and maintain product quality.
Brand Ownership and Control
Private Label brands are typically owned and controlled by retailers, allowing them to manage product development, pricing, and marketing strategies directly. In contrast, Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) brands maintain full ownership and control over their products and brand identity, enabling them to build stronger customer relationships and agilely respond to market trends. This ownership difference influences supply chain management, brand differentiation, and customer loyalty within the retail sector.
Marketing Strategies: Private Label vs DTC
Private Label brands leverage retailer loyalty and shelf placement to optimize in-store marketing while utilizing targeted promotions and loyalty programs to boost repeat purchases. DTC brands prioritize direct consumer engagement through personalized digital marketing, social media campaigns, and data-driven customer insights for tailored product offerings. Both strategies focus on maximizing customer acquisition and retention, but DTC emphasizes brand storytelling and community building to differentiate from traditional retail Private Labels.
Customer Experience and Engagement
Private label products often benefit from established retail trust and widespread availability, enhancing customer convenience and immediate engagement through familiar store environments. DTC brands prioritize personalized customer experiences by leveraging direct feedback channels and data analytics to tailor marketing and product development, fostering deeper emotional connections and loyalty. Enhanced engagement in DTC models drives repeat purchases and brand advocacy, while private labels excel in price competitiveness and in-store discovery.
Profit Margins and Cost Structures
Private label products typically offer higher profit margins due to lower production costs and established retailer distribution, while DTC brands incur greater expenses in marketing, customer acquisition, and fulfillment but can command premium pricing through brand control. Cost structures for private labels favor economies of scale and bulk purchasing, reducing manufacturing and logistics expenses. DTC brands often face variable costs linked to digital advertising and customer service, impacting overall profitability despite stronger brand loyalty.
Future Trends in Private Label and DTC Retail
Private Label and DTC brands are shaping the future of retail by prioritizing personalized customer experiences and leveraging advanced data analytics for targeted marketing. Private Label products are increasingly integrating sustainable practices and premium quality to compete with established DTC brands that excel in nimble supply chain management and digital-first engagement. Retailers investing in omnichannel strategies and AI-powered demand forecasting can expect enhanced customer loyalty and accelerated growth in both Private Label and DTC segments.
Related Important Terms
White-Label Customization
Private label retail products offer retailers the advantage of white-label customization, enabling tailored branding and packaging to meet specific market demands, which enhances customer loyalty and increases profit margins. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands, while owning the entire customer experience, often invest more heavily in developing unique product innovation but may face higher costs compared to scalable white-label solutions.
Brand Aggregators
Brand aggregators increasingly prioritize acquiring private label products due to lower production costs and established retailer distribution channels, enabling rapid market penetration and scalable growth. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands attract aggregators by offering strong customer loyalty and data-driven insights, which enhance personalized marketing and long-term brand equity.
Micro-DTC
Micro-DTC brands leverage direct consumer relationships and data analytics to offer highly personalized products, differentiating themselves from traditional private label goods often manufactured for large retailers with less brand control. By bypassing intermediaries, Micro-DTC enables agile inventory management and targeted marketing strategies, fostering stronger customer loyalty and higher profit margins in the competitive retail landscape.
Private Label Incubators
Private Label incubators accelerate product development by leveraging retail partnerships and streamlined supply chains, enabling faster market entry and higher profit margins compared to traditional Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) brands. These incubators specialize in data-driven consumer insights and operational efficiencies that optimize inventory management and reduce customer acquisition costs in the retail sector.
Speed-to-Shelf
Private label products benefit from established retailer relationships and streamlined supply chains, enabling faster speed-to-shelf compared to direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands that often face longer lead times due to building brand awareness and managing individual order fulfillment. Retailers leveraging private labels can quickly respond to market demand and seasonal trends, optimizing inventory turnover and shelf availability.
Direct-to-Consumer Playbooks
Private label strategies leverage retail partnerships to optimize shelf placement and consumer trust, while direct-to-consumer (DTC) playbooks prioritize owning the customer journey through personalized marketing, streamlined e-commerce platforms, and data-driven insights. DTC brands intensify customer engagement by controlling brand messaging, accelerating feedback loops, and maximizing lifetime value via subscription models and targeted loyalty programs.
Retailer-Owned DTC
Retailer-owned DTC brands offer greater control over customer data and brand experience compared to traditional private label products, enabling personalized marketing and enhanced loyalty programs. These brands leverage direct consumer relationships to optimize pricing strategies and product innovation, driving higher margins and improved shelf differentiation in competitive retail markets.
Shadow Brands
Shadow brands in retail emerge when private label products are marketed under different names to mimic direct-to-consumer (DTC) branding strategies, blurring lines between retailer exclusivity and brand identity. These shadow brands leverage the control of private labels while adopting DTC's personalized marketing and customer engagement tactics to enhance consumer trust and loyalty.
Vertical Integration Stack
Private label retailers achieve competitive advantage through vertical integration by controlling manufacturing, branding, and distribution under one streamlined supply chain, reducing costs and increasing market responsiveness. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands leverage vertical integration with advanced data analytics and digital marketing to enhance customer experience, optimize inventory management, and accelerate innovation cycles.
Marketplace-First Private Label
Marketplace-first private label brands leverage established e-commerce platforms to rapidly scale visibility and sales, bypassing traditional retail channels. These brands optimize product listings, utilize data-driven pricing strategies, and harness marketplace analytics to outperform direct-to-consumer (DTC) brands in customer acquisition and operational efficiency.
Private Label vs DTC Brand Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com