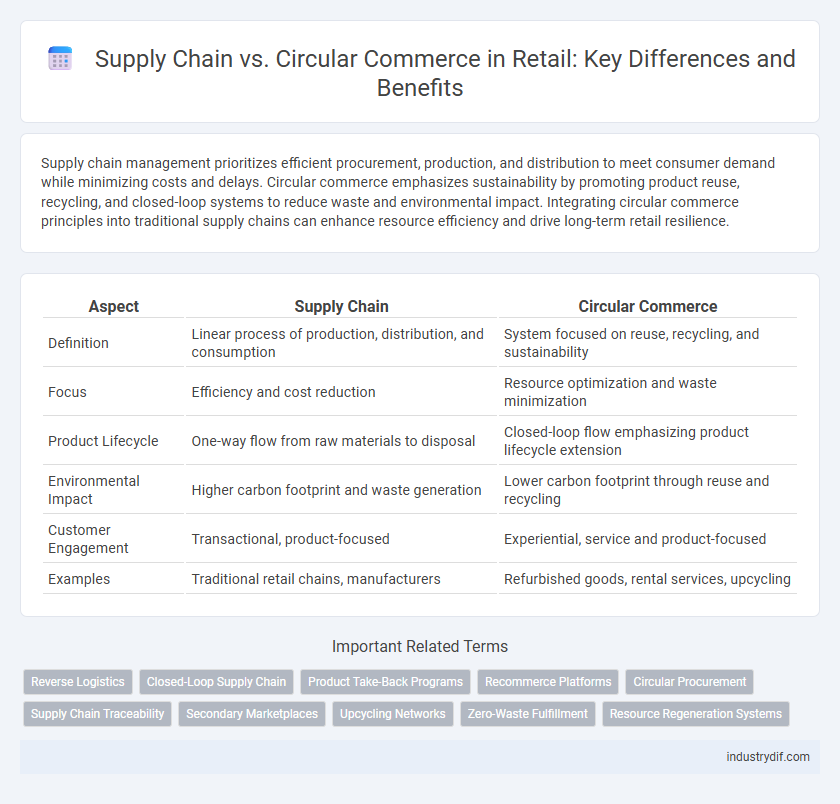
Supply chain management prioritizes efficient procurement, production, and distribution to meet consumer demand while minimizing costs and delays. Circular commerce emphasizes sustainability by promoting product reuse, recycling, and closed-loop systems to reduce waste and environmental impact. Integrating circular commerce principles into traditional supply chains can enhance resource efficiency and drive long-term retail resilience.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Supply Chain | Circular Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Linear process of production, distribution, and consumption | System focused on reuse, recycling, and sustainability |
| Focus | Efficiency and cost reduction | Resource optimization and waste minimization |
| Product Lifecycle | One-way flow from raw materials to disposal | Closed-loop flow emphasizing product lifecycle extension |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint and waste generation | Lower carbon footprint through reuse and recycling |
| Customer Engagement | Transactional, product-focused | Experiential, service and product-focused |
| Examples | Traditional retail chains, manufacturers | Refurbished goods, rental services, upcycling |
Understanding Supply Chain in Retail
Understanding supply chain in retail involves managing the flow of goods from suppliers to customers efficiently, ensuring product availability and minimizing costs. Key components include procurement, inventory management, logistics, and demand forecasting, which optimize operational performance and customer satisfaction. An effective retail supply chain integrates technology and data analytics to enhance transparency, reduce lead times, and adapt to market fluctuations.
What is Circular Commerce?
Circular commerce integrates sustainable practices into retail supply chains by prioritizing product lifecycle extension, resource efficiency, and waste reduction through reuse, refurbishment, and recycling. Unlike traditional linear supply chain models that follow a take-make-dispose approach, circular commerce emphasizes closed-loop systems that maintain the value of materials and products for as long as possible. This approach fosters eco-friendly consumer behavior, reduces environmental impact, and supports a resilient retail ecosystem driven by circular economy principles.
Key Differences: Supply Chain vs Circular Commerce
Supply chain management in retail focuses on the linear flow of products from suppliers to consumers, emphasizing efficiency and cost reduction through streamlined logistics and inventory control. Circular commerce prioritizes sustainability by designing processes that enable product reuse, recycling, and waste minimization, thereby extending product lifecycles and creating closed-loop systems. Key differences include the supply chain's emphasis on one-way product movement versus circular commerce's model of continuous resource circulation and value retention.
Traditional Supply Chain Models Explained
Traditional supply chain models in retail prioritize linear processes involving sourcing, manufacturing, distribution, and consumption with emphasis on efficiency and cost reduction. These models often generate significant waste due to single-use packaging and limited recycling efforts, contrasting with circular commerce that aims for resource reuse and sustainability. Inventory management, supplier relationships, and logistics are optimized through predictive analytics and just-in-time delivery to minimize lead times and stockouts within conventional supply chains.
Principles of Circular Commerce in Retail
Circular commerce in retail emphasizes designing products for longevity, promoting resource regeneration, and minimizing waste through reuse, repair, and recycling. Supply chain strategies integrate closed-loop systems that optimize material flows, reduce dependence on virgin resources, and enhance sustainability metrics. Retailers adopting circular principles drive value by extending product lifecycles, improving customer engagement, and supporting environmental stewardship.
Benefits of Circular Commerce for Retailers
Circular commerce enhances supply chain efficiency by minimizing waste and promoting resource reuse, leading to significant cost savings for retailers. It fosters stronger customer loyalty as eco-conscious consumers prefer sustainable brands that prioritize product lifecycle extension. Retailers benefit from improved brand reputation and competitive advantage by adopting circular business models that align with increasing environmental regulations and market demand for sustainability.
Challenges in Transitioning from Linear to Circular Models
Retail supply chains face significant challenges transitioning from linear to circular commerce models, including the complexity of redesigning product life cycles to enable reuse, refurbishing, and recycling processes. Managing reverse logistics and tracking returned or end-of-life products require advanced technologies and collaboration with multiple stakeholders, increasing operational costs and data management needs. Consumer behavior shifts and regulatory compliance further complicate the integration of circular practices within existing supply chain frameworks.
Impact on Inventory Management and Logistics
Supply chain management in retail emphasizes efficient inventory control and streamlined logistics to reduce costs and meet consumer demand. Circular commerce integrates product return, refurbishment, and recycling processes, requiring adaptive inventory systems to handle reverse logistics and extend product lifecycle value. Implementing circular strategies transforms traditional inventory management by prioritizing sustainability, reducing waste, and optimizing resource flow throughout the supply chain.
Sustainability and Environmental Implications
Supply chain management in retail focuses on optimizing logistics and inventory to reduce waste and carbon emissions, enhancing sustainability by streamlining sourcing and distribution processes. Circular commerce promotes environmental responsibility through product life extension, recycling, and reuse, minimizing resource extraction and landfill accumulation. Integrating circular commerce principles within supply chains fosters a closed-loop system that significantly mitigates environmental impacts and supports long-term ecological balance.
Future Trends: Integrating Circular Commerce in Retail Supply Chains
Future trends in retail will emphasize integrating circular commerce principles within supply chains to enhance sustainability and resource efficiency. Retailers are increasingly adopting closed-loop systems that prioritize product lifecycle extension, waste reduction, and material reuse. Advanced technologies like blockchain and IoT enable real-time tracking and transparency, facilitating a seamless transition from traditional linear supply chains to circular models.
Related Important Terms
Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics plays a critical role in both supply chain management and circular commerce by efficiently managing product returns, refurbishments, and recycling processes to minimize waste and optimize resource use. Integrating advanced tracking technologies and sustainable practices enhances reverse logistics, supporting circular commerce goals while reducing costs and environmental impact in traditional supply chains.
Closed-Loop Supply Chain
A Closed-Loop Supply Chain integrates product returns, recycling, and remanufacturing processes to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency in retail operations. This circular commerce model reduces reliance on virgin materials and lowers carbon footprint while enhancing supply chain resilience and cost savings.
Product Take-Back Programs
Product take-back programs in retail supply chains facilitate the return and recycling of used products, reducing waste and supporting sustainable circular commerce models. These initiatives enhance resource efficiency by reintegrating materials into production cycles, minimizing environmental impact while maintaining supply chain responsiveness.
Recommerce Platforms
Recommerce platforms drive circular commerce by enabling the resale and refurbishment of products, reducing waste and extending product lifecycles compared to traditional supply chain models that prioritize linear production and distribution. These platforms leverage real-time inventory data and consumer demand analytics to optimize returns processing and inventory turnover, enhancing sustainability and cost-efficiency in retail operations.
Circular Procurement
Circular procurement in retail prioritizes sourcing products and materials that are reusable, recyclable, or made from sustainable resources, reducing waste and environmental impact across the supply chain. Integrating circular commerce strategies enhances supply chain resilience by extending product lifecycles and promoting closed-loop systems that minimize resource dependency.
Supply Chain Traceability
Supply chain traceability in retail enhances transparency by tracking products from origin to consumer, ensuring authenticity and ethical sourcing. Circular commerce integrates traceability to optimize resource recovery and reduce waste, supporting sustainable retail ecosystems.
Secondary Marketplaces
Secondary marketplaces in retail drive circular commerce by extending product lifecycles through resale, refurbishment, and remanufacturing, reducing waste while optimizing supply chain efficiency. Integrating these marketplaces promotes sustainability and cost savings by diverting inventory from landfills and recapturing value from returned or excess merchandise.
Upcycling Networks
Upcycling networks in retail supply chains transform waste materials into valuable products, reducing environmental impact and enhancing resource efficiency. These networks support circular commerce by fostering collaboration between manufacturers, suppliers, and consumers to create sustainable value loops.
Zero-Waste Fulfillment
Zero-waste fulfillment in retail integrates supply chain efficiency with circular commerce principles to minimize waste through product lifecycle management and resource recovery. Implementing closed-loop systems in distribution and packaging reduces landfill contributions and enhances sustainability by reusing materials and optimizing inventory flow.
Resource Regeneration Systems
Resource regeneration systems in retail supply chains prioritize the restoration and reuse of materials to minimize waste and reduce environmental impact. Circular commerce integrates these systems by promoting closed-loop processes, enabling businesses to extend product lifecycles and enhance sustainability through efficient resource management.
Supply Chain vs Circular Commerce Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com