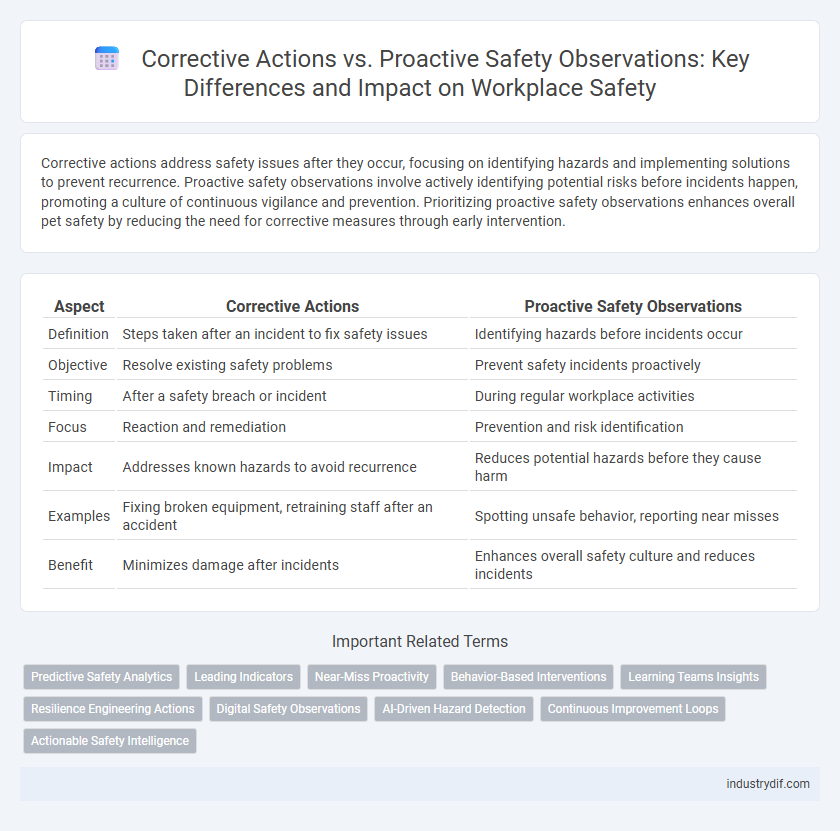
Corrective actions address safety issues after they occur, focusing on identifying hazards and implementing solutions to prevent recurrence. Proactive safety observations involve actively identifying potential risks before incidents happen, promoting a culture of continuous vigilance and prevention. Prioritizing proactive safety observations enhances overall pet safety by reducing the need for corrective measures through early intervention.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Corrective Actions | Proactive Safety Observations |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Steps taken after an incident to fix safety issues | Identifying hazards before incidents occur |
| Objective | Resolve existing safety problems | Prevent safety incidents proactively |
| Timing | After a safety breach or incident | During regular workplace activities |
| Focus | Reaction and remediation | Prevention and risk identification |
| Impact | Addresses known hazards to avoid recurrence | Reduces potential hazards before they cause harm |
| Examples | Fixing broken equipment, retraining staff after an accident | Spotting unsafe behavior, reporting near misses |
| Benefit | Minimizes damage after incidents | Enhances overall safety culture and reduces incidents |
Understanding Corrective Actions in Safety Management
Corrective actions in safety management address identified hazards by implementing changes to eliminate or control risks after an incident or near-miss occurs. These actions are essential for preventing recurrence and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, thereby enhancing workplace safety. Understanding the distinction between reactive corrective measures and proactive safety observations enables organizations to create a balanced safety program that reduces overall risk exposure.
Defining Proactive Safety Observations
Proactive safety observations involve identifying potential hazards and unsafe behaviors before incidents occur, enabling organizations to mitigate risks in advance. These observations focus on active monitoring and early intervention, promoting a culture of continuous improvement and hazard prevention. Implementing proactive safety measures reduces workplace accidents by addressing root causes rather than reacting to incidents.
Key Differences Between Corrective Actions and Proactive Safety Measures
Corrective actions address identified safety issues after incidents or near-misses, focusing on resolving existing risks to prevent recurrence. Proactive safety observations involve identifying potential hazards before incidents occur, enabling preventive measures to enhance overall workplace safety. Key differences include timing and approach: corrective actions are reactive, while proactive observations emphasize early detection and risk mitigation.
The Role of Corrective Actions in Incident Response
Corrective actions play a critical role in incident response by addressing root causes and preventing recurrence of safety incidents. They involve immediate measures to rectify hazards, improve processes, and ensure compliance with safety standards. Implementing corrective actions promptly reduces risk exposure and enhances overall workplace safety management systems.
Benefits of Proactive Safety Observations in the Workplace
Proactive safety observations identify potential hazards before incidents occur, significantly reducing workplace accidents and associated costs. These observations foster a safety culture by engaging employees in hazard recognition and encouraging continuous improvement. Implementing proactive measures enhances compliance with safety regulations and minimizes downtime caused by corrective actions.
Examples of Effective Corrective Actions
Effective corrective actions include conducting root cause analysis to address hazards, implementing engineering controls like machine guards to eliminate risks, and providing targeted employee training programs to prevent recurrence of safety incidents. Installing safety barriers in high-risk areas and regularly inspecting equipment for potential failures ensure compliance with safety regulations and demonstrate a commitment to workplace safety. These corrective measures significantly reduce workplace injuries and enhance overall safety culture by addressing both immediate and underlying safety concerns.
Strategies for Implementing Proactive Safety Programs
Implementing proactive safety programs requires strategic emphasis on regular hazard identification and real-time safety observations to prevent incidents before they occur. Integrating employee training focused on recognizing unsafe conditions empowers personnel to take immediate corrective measures, reducing workplace risks effectively. Leveraging data analytics from safety observations facilitates targeted interventions, enhancing overall organizational safety culture and compliance.
Measuring the Impact of Corrective Actions vs Proactive Observations
Measuring the impact of corrective actions centers on quantifiable reductions in incidents, compliance with safety regulations, and documented closure rates of identified hazards. Proactive safety observations emphasize early hazard identification and behavior-based safety improvements, tracking near-miss reports and employee engagement metrics. Comparing both approaches highlights that corrective actions provide reactive, outcome-based data, while proactive observations yield preventative insights critical for sustained safety culture enhancement.
Common Challenges in Applying Safety Corrections and Proactive Methods
Implementing corrective actions often faces challenges such as delayed hazard identification and reactive reporting, which limit their effectiveness in preventing incidents. Proactive safety observations require consistent engagement and training to overcome organizational resistance and ensure accurate, timely hazard detection. Balancing these approaches demands integrating real-time data analytics and fostering a safety culture committed to continuous improvement.
Best Practices for Integrating Both Approaches in Industrial Safety
Integrating corrective actions with proactive safety observations enhances industrial safety by addressing existing hazards and preventing potential incidents before they occur. Best practices include establishing clear communication channels for reporting observations, utilizing data analytics to identify patterns, and fostering a safety culture that encourages employee engagement and continuous improvement. Combining timely corrective measures with systematic proactive monitoring reduces workplace accidents and promotes sustainable operational safety.
Related Important Terms
Predictive Safety Analytics
Corrective actions address incidents after they occur, while proactive safety observations and predictive safety analytics identify potential hazards by analyzing patterns and trends to prevent accidents before they happen. Predictive safety analytics leverages data from proactive observations to forecast risks, enabling targeted interventions that enhance workplace safety and reduce incident rates.
Leading Indicators
Corrective actions address incidents after they occur, serving as lagging indicators that reflect past safety performance, while proactive safety observations function as leading indicators by identifying potential hazards before accidents happen. Emphasizing leading indicators through regular safety observations enhances risk mitigation and cultivates a safer work environment.
Near-Miss Proactivity
Near-miss proactivity emphasizes identifying and addressing potential hazards before incidents occur, enabling organizations to implement corrective actions that prevent future accidents. Proactive safety observations foster a culture of continuous improvement by capturing early warning signs and mitigating risks proactively rather than reacting to incidents after they happen.
Behavior-Based Interventions
Behavior-based interventions prioritize proactive safety observations to identify and modify unsafe behaviors before incidents occur, enhancing workplace safety culture. Corrective actions address incidents after they happen, focusing on rectifying specific safety violations rather than preventing behavioral risks.
Learning Teams Insights
Corrective actions address identified safety issues after incidents occur, while proactive safety observations enable teams to detect hazards before they result in harm, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Learning teams gain valuable insights by analyzing patterns in proactive observations, which helps implement targeted interventions that reduce incident rates and enhance workplace safety.
Resilience Engineering Actions
Resilience Engineering actions emphasize proactive safety observations to identify and mitigate potential hazards before incidents occur, enhancing system adaptability and reliability. Corrective actions, while reactive in nature, address specific failures but lack the anticipatory focus that strengthens an organization's overall resilience and safety culture.
Digital Safety Observations
Corrective actions address safety incidents after they occur, while proactive safety observations identify potential hazards in real-time to prevent accidents before they happen. Digital safety observations leverage mobile apps and cloud-based platforms to streamline data collection, enable immediate risk analysis, and enhance overall workplace safety culture through timely interventions.
AI-Driven Hazard Detection
AI-driven hazard detection enhances proactive safety observations by identifying potential risks before incidents occur, enabling timely interventions that reduce workplace accidents. Corrective actions address hazards after they manifest, but integrating AI technology shifts safety management towards prevention, optimizing hazard mitigation strategies and improving compliance tracking.
Continuous Improvement Loops
Corrective actions address specific safety incidents after they occur, closing the loop by resolving identified hazards and preventing recurrence; proactive safety observations identify potential risks before incidents happen, enabling earlier intervention and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Integrating both approaches creates dynamic feedback loops that enhance workplace safety performance through ongoing hazard identification, risk mitigation, and behavior modification.
Actionable Safety Intelligence
Corrective actions address identified hazards after incidents, providing reactive solutions to prevent recurrence, while proactive safety observations gather real-time data to identify potential risks before they result in harm. Actionable safety intelligence integrates both approaches, utilizing continuous feedback and data analytics to enhance overall workplace safety and minimize incidents effectively.
Corrective Actions vs Proactive Safety Observations Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com