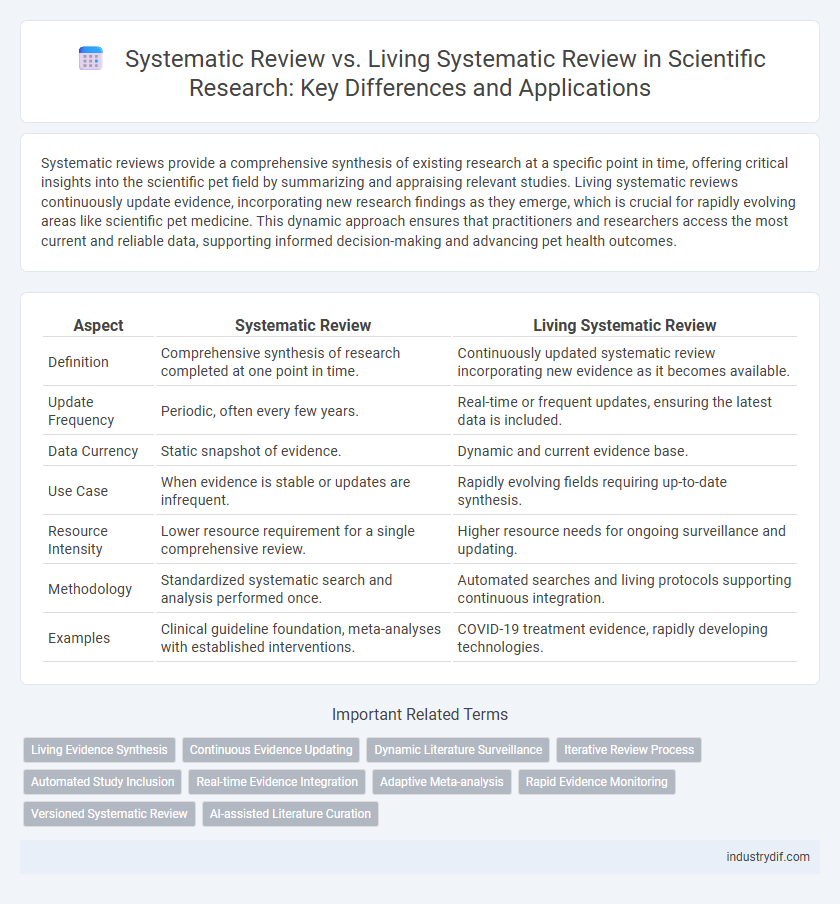
Systematic reviews provide a comprehensive synthesis of existing research at a specific point in time, offering critical insights into the scientific pet field by summarizing and appraising relevant studies. Living systematic reviews continuously update evidence, incorporating new research findings as they emerge, which is crucial for rapidly evolving areas like scientific pet medicine. This dynamic approach ensures that practitioners and researchers access the most current and reliable data, supporting informed decision-making and advancing pet health outcomes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Systematic Review | Living Systematic Review |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Comprehensive synthesis of research completed at one point in time. | Continuously updated systematic review incorporating new evidence as it becomes available. |
| Update Frequency | Periodic, often every few years. | Real-time or frequent updates, ensuring the latest data is included. |
| Data Currency | Static snapshot of evidence. | Dynamic and current evidence base. |
| Use Case | When evidence is stable or updates are infrequent. | Rapidly evolving fields requiring up-to-date synthesis. |
| Resource Intensity | Lower resource requirement for a single comprehensive review. | Higher resource needs for ongoing surveillance and updating. |
| Methodology | Standardized systematic search and analysis performed once. | Automated searches and living protocols supporting continuous integration. |
| Examples | Clinical guideline foundation, meta-analyses with established interventions. | COVID-19 treatment evidence, rapidly developing technologies. |
Definition of Systematic Review
A Systematic Review is a rigorous methodology that collects and critically analyzes multiple research studies addressing a specific clinical question, adhering to predefined criteria to minimize bias. It involves comprehensive literature searches, data extraction, and quality assessment of included studies to synthesize evidence systematically. The goal is to provide a high-level summary of existing research to inform evidence-based practice and guide future investigations.
Definition of Living Systematic Review
Living Systematic Review (LSR) is an evidence synthesis approach designed to incorporate new research findings continuously as they become available, ensuring the review remains current and relevant. Unlike traditional Systematic Reviews, which are static and updated periodically, LSRs use automated search strategies and frequent screening processes to integrate emerging data promptly. This real-time updating enhances decision-making in rapidly evolving scientific fields by providing the most up-to-date evidence base.
Key Differences Between Systematic and Living Systematic Reviews
Systematic reviews synthesize existing research data up to a predetermined cut-off date, offering a static overview of evidence, while living systematic reviews continuously update findings by incorporating new studies as they become available, ensuring the most current evidence base. Traditional systematic reviews follow a fixed protocol and update infrequently, whereas living systematic reviews use dynamic methodologies and real-time search strategies to provide ongoing evidence synthesis. This key difference impacts decision-making in clinical guidelines and policy development by delivering either a snapshot or a continuously evolving understanding of research outcomes.
Methodological Approaches in Both Review Types
Systematic reviews utilize predefined protocols that include comprehensive literature searches, rigid inclusion criteria, and critical appraisal to synthesize existing evidence at a fixed point in time. Living systematic reviews extend this approach by incorporating continuous, real-time updates with automated search strategies and dynamic evidence integration, enabling timely incorporation of new findings. Advanced methodological tools such as machine learning algorithms and interactive data visualization platforms support efficient data management and iterative analysis in living systematic reviews.
Update Frequency: Static vs Dynamic Evidence Synthesis
Systematic reviews provide a static synthesis of evidence, typically updated every few years, limiting their ability to reflect the most current research. Living systematic reviews employ a dynamic approach with continuous literature surveillance and frequent updates, ensuring real-time integration of emerging data. This ongoing update frequency enhances decision-making by maintaining current and relevant evidence throughout the review lifecycle.
Technological Tools Supporting Living Systematic Reviews
Technological tools such as machine learning algorithms, natural language processing, and automated data extraction systems significantly enhance Living Systematic Reviews (LSRs) by enabling continuous literature surveillance and rapid integration of new evidence. Platforms like Covidence and RobotReviewer facilitate real-time updates, reducing manual effort and improving accuracy in evidence synthesis. These advancements support dynamic decision-making processes in healthcare by maintaining up-to-date and reliable systematic reviews.
Challenges in Conducting Living Systematic Reviews
Living systematic reviews face significant challenges including the constant need for updating data as new studies emerge, requiring substantial time and resource investment. Maintaining methodological rigor while incorporating continuous evidence demands advanced data management systems and frequent expert involvement. Additionally, balancing rapid publication with thorough peer review processes poses ongoing difficulties in producing reliable and timely findings.
Applications in Evidence-Based Practice
Systematic reviews aggregate and critically appraise all relevant studies on a specific clinical question, serving as foundational tools in evidence-based practice for guideline development and healthcare decision-making. Living systematic reviews continuously update evidence synthesis as new studies emerge, enhancing the timeliness and accuracy of recommendations in rapidly evolving fields such as COVID-19 treatment and personalized medicine. The dynamic nature of living systematic reviews supports adaptive clinical protocols and policy adjustments by integrating real-time data, improving patient outcomes through evidence that reflects current research advancements.
Quality Assessment and Reporting Standards
Systematic reviews require rigorous quality assessment tools such as the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool to ensure methodological transparency and reproducibility. Living systematic reviews continuously update evidence synthesis with real-time data integration, necessitating adaptive reporting standards like the PRISMA 2020 extension for living systematic reviews. Both approaches emphasize robust quality assessment and adherence to evolving reporting frameworks to maintain validity and reliability in dynamic scientific landscapes.
Future Directions in Systematic Evidence Synthesis
Future directions in systematic evidence synthesis emphasize integrating real-time data updates and adaptive methodologies through Living Systematic Reviews (LSRs), enabling continuous incorporation of emerging research findings. Advanced computational tools and automated data extraction enhance the precision and efficiency of LSRs, addressing the limitations of traditional Systematic Reviews that rely on static, periodically updated evidence. This shift facilitates more dynamic, responsive, and relevant decision-making in clinical and policy settings by maintaining up-to-date syntheses of rapidly evolving scientific knowledge.
Related Important Terms
Living Evidence Synthesis
Living Systematic Reviews continuously update evidence synthesis by incorporating new research data in real-time, enhancing the accuracy and relevance of findings compared to traditional Systematic Reviews which provide static summaries at a fixed point. This dynamic approach in Living Evidence Synthesis supports timely decision-making in rapidly evolving scientific fields such as clinical trials and public health interventions.
Continuous Evidence Updating
Living systematic reviews continuously integrate new research findings through automated literature searches and real-time data synthesis, ensuring up-to-date evidence for clinical decision-making. Traditional systematic reviews provide comprehensive analyses at a single time point but lack mechanisms for ongoing evidence updates, resulting in potential obsolescence as new studies emerge.
Dynamic Literature Surveillance
Living Systematic Reviews (LSRs) incorporate dynamic literature surveillance by continuously updating evidence synthesis as new studies emerge, enhancing real-time decision-making accuracy. Traditional Systematic Reviews rely on static literature searches conducted at a single time point, which may limit their relevance over time due to rapidly evolving scientific data.
Iterative Review Process
A Systematic Review employs a fixed iterative review process with predefined intervals for literature updating, ensuring comprehensive evidence synthesis at a single point in time. In contrast, a Living Systematic Review utilizes a continuous iterative review process, incorporating new research findings in real-time to maintain up-to-date and dynamic evidence summaries.
Automated Study Inclusion
Automated study inclusion in living systematic reviews leverages machine learning algorithms to continuously update evidence synthesis by rapidly screening and incorporating new research, enhancing the timeliness and accuracy compared to traditional systematic reviews. This dynamic approach facilitates real-time data integration, enabling more responsive and up-to-date clinical decision-making and guideline development.
Real-time Evidence Integration
Living systematic reviews integrate real-time evidence by continuously updating with new data, enhancing the accuracy and relevance of findings compared to traditional systematic reviews, which provide static summaries based on a fixed set of studies. This dynamic approach enables faster translation of emerging research into clinical and policy decision-making, particularly in rapidly evolving scientific fields.
Adaptive Meta-analysis
Systematic reviews synthesize existing evidence at a single point, while living systematic reviews continuously incorporate new data, enabling adaptive meta-analysis to update conclusions dynamically. This adaptive approach enhances accuracy in evidence synthesis by integrating emerging studies in real-time, improving decision-making in scientific research.
Rapid Evidence Monitoring
Systematic reviews synthesize existing research comprehensively but may become outdated due to the time-intensive nature of data collection and analysis. Living systematic reviews employ continuous literature surveillance and rapid evidence monitoring to integrate new findings promptly, enhancing currency and decision-making accuracy in fast-evolving scientific fields.
Versioned Systematic Review
Systematic reviews provide a comprehensive synthesis of existing research up to a fixed point, while living systematic reviews (LSRs) offer continuously updated evidence by incorporating new studies as they emerge. Versioned systematic reviews integrate the systematic review framework with incremental updates organized by distinct version releases, enabling transparent tracking of evidence evolution over time.
AI-assisted Literature Curation
Systematic reviews provide comprehensive, static syntheses of existing research, while living systematic reviews continuously update evidence by integrating new studies as they are published, enhancing decision-making accuracy. AI-assisted literature curation accelerates data extraction and screening processes in both review types, improving efficiency and reducing human error in managing vast biomedical datasets.
Systematic Review vs Living Systematic Review Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com