API and GraphQL Federation both facilitate data retrieval across multiple services, but APIs typically expose fixed endpoints with defined structures, whereas GraphQL Federation enables a unified graph schema that dynamically composes data from multiple sources. GraphQL Federation improves flexibility by allowing clients to query only the data they need, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching common in traditional API calls. Developers prefer GraphQL Federation for its scalability and seamless integration of microservices without requiring multiple endpoint management.
Table of Comparison
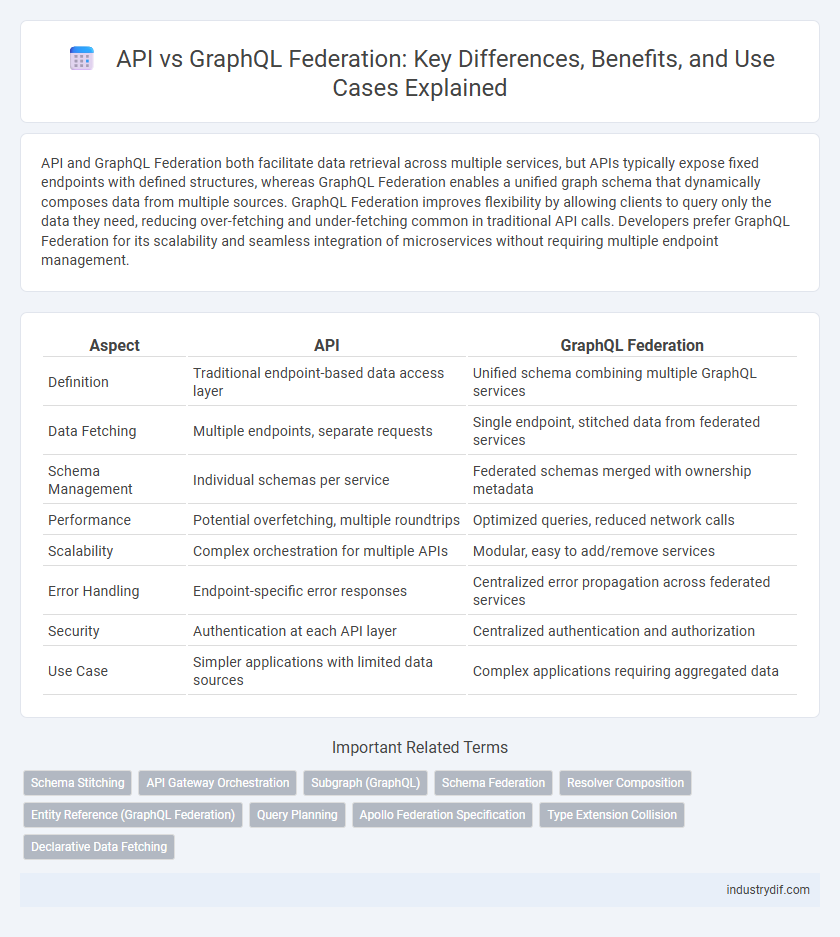
| Aspect | API | GraphQL Federation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional endpoint-based data access layer | Unified schema combining multiple GraphQL services |
| Data Fetching | Multiple endpoints, separate requests | Single endpoint, stitched data from federated services |
| Schema Management | Individual schemas per service | Federated schemas merged with ownership metadata |
| Performance | Potential overfetching, multiple roundtrips | Optimized queries, reduced network calls |
| Scalability | Complex orchestration for multiple APIs | Modular, easy to add/remove services |
| Error Handling | Endpoint-specific error responses | Centralized error propagation across federated services |
| Security | Authentication at each API layer | Centralized authentication and authorization |
| Use Case | Simpler applications with limited data sources | Complex applications requiring aggregated data |
Introduction to APIs and GraphQL Federation
APIs serve as standardized interfaces enabling communication between software applications, typically following REST or RPC protocols, while GraphQL Federation extends GraphQL by allowing multiple services to compose a single unified graph. This federated architecture empowers distributed teams to independently develop and maintain graph schemas, enhancing scalability and modularity of API consumption. By integrating diverse data sources under a cohesive GraphQL schema, federation streamlines client queries and optimizes data retrieval efficiency.
Core Principles of Traditional APIs
Traditional APIs rely on a fixed endpoint structure and predefined request-response patterns, focusing on a tightly controlled data schema and versioning to ensure stability. They emphasize straightforward client-server communication, often leading to over-fetching or under-fetching of data due to rigid resource boundaries. Security mechanisms like authentication and rate limiting are integral to maintain reliable and scalable access within these legacy API designs.
Understanding GraphQL Federation Architecture
GraphQL Federation architecture enables multiple GraphQL services to unify their schemas into a single graph, improving modularity and scalability for complex applications. By using a gateway that composes federated schemas, it resolves queries across different services efficiently, reducing the need for multiple REST API calls. This approach contrasts traditional API architectures by allowing more flexible data querying and minimizing over-fetching or under-fetching issues inherent in RESTful APIs.
Key Differences: REST APIs vs GraphQL Federation
REST APIs rely on multiple endpoints to fetch distinct data resources, often causing over-fetching or under-fetching of information. GraphQL Federation integrates multiple GraphQL services into a single unified graph, enabling precise queries that minimize data transfer and improve client efficiency. The key differences lie in REST's endpoint-specific access versus Federation's schema stitching, which enhances scalability and flexibility in complex systems.
Performance Considerations in API and Federation Models
API performance depends on the efficiency of endpoint design and data retrieval, where REST APIs may suffer from over-fetching or under-fetching data. GraphQL federation optimizes query execution by aggregating multiple services into a unified graph, reducing network requests and improving response times. However, federation introduces complexity in query planning and can increase latency if not properly orchestrated across distributed schemas.
Security Implications: API Gateway vs Federated GraphQL
API Gateways centralize security management by enforcing authentication, rate limiting, and data validation at a single entry point, reducing attack surfaces. Federated GraphQL distributes schema responsibilities, necessitating coordinated security policies and robust authorization mechanisms across multiple services to prevent data leakage. Security implications favor API Gateways for simplified monitoring, while Federated GraphQL demands granular, service-level security controls to maintain integrity and confidentiality.
Scalability and Microservices Integration
GraphQL Federation enables scalable microservices integration by allowing multiple GraphQL services to combine into a single unified graph, reducing network overhead and improving query efficiency. Unlike traditional REST APIs, which require managing multiple endpoints, Federation centralizes schema management, enhancing developer productivity and minimizing integration complexity. This approach supports independent service evolution and seamless collaboration across distributed teams, making it ideal for large-scale applications with diverse microservices.
Data Fetching Efficiency: REST Endpoints vs Federated Schema
REST endpoints often result in over-fetching or under-fetching data due to fixed response structures, leading to inefficient data transfer and increased network latency. In contrast, GraphQL Federation enables precise data fetching across multiple services with a unified schema, reducing redundant requests and optimizing payload size. This federated approach improves performance by aggregating only the necessary fields, minimizing round trips and bandwidth usage.
Use Cases: When to Choose API or GraphQL Federation
API architecture suits projects requiring simple, well-defined endpoints and minimal client flexibility, such as legacy systems or microservices with limited schema complexity. GraphQL Federation is ideal for complex, large-scale applications needing unified schema across multiple teams, enabling efficient data querying and minimizing over-fetching. Choose API for straightforward data retrieval scenarios, and GraphQL Federation when diverse data sources must be seamlessly integrated under a single query system.
Future Trends in API and GraphQL Federation Technologies
API development is increasingly shifting towards GraphQL Federation to enhance modularity and streamline data access in complex microservice architectures. Emerging trends highlight the integration of AI-driven schema stitching and automated query optimization, boosting performance and developer productivity. The future of API technologies emphasizes interoperability standards, decentralized governance models, and enhanced security protocols to support scalable, distributed data ecosystems.
Related Important Terms
Schema Stitching
Schema stitching in GraphQL Federation integrates multiple GraphQL schemas into a unified API by merging their types and resolvers, enabling seamless data retrieval across services. Unlike traditional REST APIs, this approach reduces network requests and improves client efficiency by providing a single endpoint that aggregates distributed data sources.
API Gateway Orchestration
API Gateway Orchestration centralizes API management by routing requests through a single entry point, enhancing security, rate limiting, and protocol translation. GraphQL Federation decentralizes schema management across services but relies on an orchestrator to unify GraphQL APIs, improving query efficiency and service modularity.
Subgraph (GraphQL)
Subgraphs in GraphQL Federation encapsulate distinct domains within a distributed graph architecture, enabling modular schema design and efficient query resolution across services. Unlike traditional APIs, subgraphs reduce network overhead by allowing clients to request precisely the data they need through a unified graph endpoint, enhancing performance and developer productivity.
Schema Federation
Schema Federation in GraphQL enables the composition of multiple service schemas into a single graph, allowing independent teams to manage distinct parts of the API while maintaining a unified data graph. Unlike traditional API gateways that aggregate REST endpoints, GraphQL Federation focuses on seamless schema stitching and entity resolution across federated services for more efficient and flexible data querying.
Resolver Composition
API architectures typically handle resolver composition through traditional REST endpoints managing discrete resources, whereas GraphQL Federation centralizes resolver logic by stitching multiple GraphQL services into a unified graph, enabling precise data fetching and efficient query resolution. Resolver composition in GraphQL Federation enhances modularity and scalability by delegating subgraph resolvers to collaborate seamlessly, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching compared to monolithic APIs.
Entity Reference (GraphQL Federation)
Entity Reference in GraphQL Federation enables seamless resolution of shared entities across multiple subgraphs by uniquely identifying and linking them via key fields, enhancing data consistency and query efficiency. Unlike traditional API integration, this approach allows federated services to collaboratively expose and resolve parts of a single unified graph without duplicating entity definitions or data retrieval logic.
Query Planning
API query planning typically relies on predefined endpoints and rigid schemas, resulting in slower response times and limited flexibility. GraphQL Federation optimizes query planning by dynamically composing subgraphs, enabling efficient data retrieval and minimizing over-fetching through precise query resolution.
Apollo Federation Specification
Apollo Federation Specification enables the composition of multiple GraphQL services into a single graph, allowing for decentralized schema ownership and extensibility while maintaining a unified API. Unlike traditional REST APIs that rely on fixed endpoints, Apollo Federation leverages service-specified schema directives and query planning to optimize data fetching and minimize over-fetching in complex distributed architectures.
Type Extension Collision
Type extension collision in API vs GraphQL Federation occurs when multiple services attempt to extend the same GraphQL type with conflicting fields or directives, causing schema ambiguity and runtime errors. Proper schema stitching and unique namespace conventions help mitigate these collisions by ensuring type extensions are clearly distinguished across federated services.
Declarative Data Fetching
GraphQL Federation enables declarative data fetching by allowing clients to specify exact data requirements across distributed services in a unified schema, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching common in traditional REST APIs. This approach optimizes network efficiency and simplifies client development by consolidating multiple data sources into a single, cohesive query interface.
API vs GraphQL Federation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com