Traditional API architectures rely on fixed endpoints and predefined data structures, often resulting in over-fetching or under-fetching of information. Graph Query Language (GraphQL) enables clients to request exactly the data they need, improving efficiency and reducing bandwidth usage. Its flexible schema allows for seamless integration and evolution of APIs without disrupting existing queries.
Table of Comparison
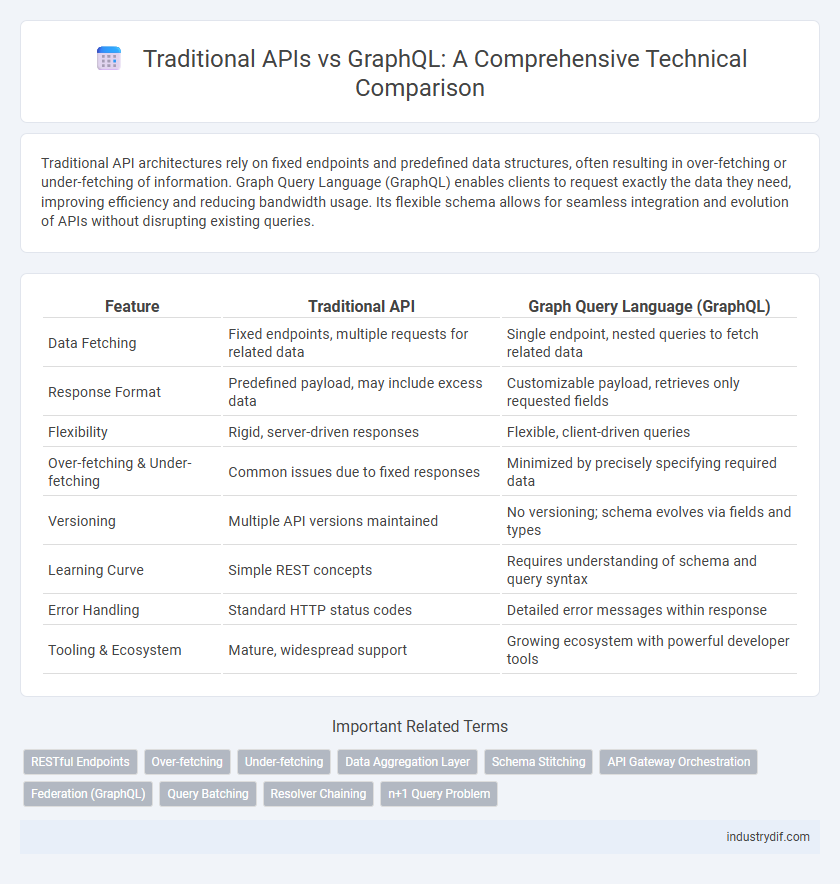
| Feature | Traditional API | Graph Query Language (GraphQL) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Fetching | Fixed endpoints, multiple requests for related data | Single endpoint, nested queries to fetch related data |
| Response Format | Predefined payload, may include excess data | Customizable payload, retrieves only requested fields |
| Flexibility | Rigid, server-driven responses | Flexible, client-driven queries |
| Over-fetching & Under-fetching | Common issues due to fixed responses | Minimized by precisely specifying required data |
| Versioning | Multiple API versions maintained | No versioning; schema evolves via fields and types |
| Learning Curve | Simple REST concepts | Requires understanding of schema and query syntax |
| Error Handling | Standard HTTP status codes | Detailed error messages within response |
| Tooling & Ecosystem | Mature, widespread support | Growing ecosystem with powerful developer tools |
Introduction to Traditional APIs and Graph Query Language
Traditional APIs typically operate through fixed endpoints using REST principles, where each endpoint returns a predefined data structure, often leading to over-fetching or under-fetching of information. Graph Query Language (GraphQL) offers a flexible approach by allowing clients to specify exactly what data they need through a single endpoint, improving efficiency and reducing payload sizes. This contrast highlights GraphQL's capability to optimize data retrieval, enhancing performance in complex applications compared to conventional REST APIs.
Core Principles: RESTful APIs vs GraphQL
RESTful APIs operate on fixed endpoints with defined resources and use standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE, emphasizing statelessness and resource representation. GraphQL, in contrast, offers a flexible query structure allowing clients to specify exactly which data fields they need, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching of data. Core principles of GraphQL include a single endpoint, schema introspection, and hierarchical queries, enabling efficient and precise data retrieval compared to the rigid RESTful design.
Data Fetching Approaches: Over-fetching and Under-fetching
Traditional APIs often lead to over-fetching or under-fetching data due to fixed endpoint responses, causing inefficiencies in network usage and application performance. Graph Query Language, such as GraphQL, enables precise data retrieval by allowing clients to specify exactly which fields are needed, minimizing both over-fetching and under-fetching problems. This selective data fetching approach optimizes payload size and reduces unnecessary data processing on both client and server sides.
Flexibility and Efficiency in Data Retrieval
Traditional APIs often require multiple endpoints to fetch related data, leading to over-fetching or under-fetching issues, whereas Graph Query Language allows clients to request exactly the data they need in a single query, enhancing efficiency. GraphQL's flexible schema enables dynamic queries that adapt to evolving client requirements without backend changes, significantly improving development agility. This granular control over data retrieval reduces network overhead and accelerates response times compared to rigid RESTful API structures.
Schema Design: Rigid Endpoints vs Dynamic Queries
Traditional APIs rely on rigid endpoints with predefined schemas, limiting flexibility and often requiring multiple requests to fetch complex data structures. Graph Query Language, such as GraphQL, enables dynamic queries by allowing clients to specify exactly what fields and relationships to retrieve, optimizing data transfer and reducing over-fetching. This dynamic approach simplifies schema design by treating the schema as a contract that evolves with client needs, enhancing both scalability and developer experience.
Response Structure: Fixed vs Customizable Outputs
Traditional APIs typically return fixed response structures defined by specific endpoints, limiting flexibility in data retrieval and often resulting in over-fetching or under-fetching of information. Graph Query Languages like GraphQL allow clients to customize response outputs by specifying exactly which fields and nested data to retrieve, optimizing network usage and improving performance. This customizable response structure enhances efficiency in complex data interactions by tailoring responses to precise client needs.
Error Handling and Versioning
Traditional APIs often rely on status codes and predefined error messages, making error handling rigid and sometimes ambiguous, while Graph Query Language (GraphQL) offers more granular and precise error reporting within the query response structure. Versioning in traditional REST APIs typically involves creating new endpoints or maintaining multiple API versions, which can lead to fragmentation and increased maintenance overhead. In contrast, GraphQL eliminates strict versioning by allowing clients to request only the data they need, enabling seamless schema evolution without breaking existing queries.
Performance and Scalability Considerations
Traditional APIs often suffer from over-fetching or under-fetching data, leading to inefficiencies that impact performance and scalability, especially under high load conditions. Graph Query Languages like GraphQL enable precise data selection in a single request, reducing network overhead and accelerating response times. This fine-grained querying enhances scalability by optimizing server resource utilization and improving client-side performance in distributed systems.
Ecosystem and Tooling Comparison
Traditional APIs often rely on REST architecture with fixed endpoints and rigid response structures, limiting flexibility in data retrieval. Graph Query Languages like GraphQL offer a more dynamic ecosystem with powerful tooling for real-time data fetching, schema introspection, and tailored queries, enhancing developer experience and integration efficiency. The growing ecosystem around GraphQL includes robust libraries, developer tools, and community-driven extensions, outpacing traditional REST APIs in adaptability and developer productivity.
Use Cases: Choosing the Right API Architecture
Traditional APIs excel in simple, well-defined operations such as CRUD tasks on fixed endpoints, making them ideal for microservices and RESTful web services. Graph Query Languages like GraphQL offer flexibility by allowing clients to request precisely the data they need, which suits complex applications with interconnected data models, such as social networks and real-time analytics. Selecting the right API architecture depends on factors like data complexity, client requirements, and the need for efficient data fetching and aggregation.
Related Important Terms
RESTful Endpoints
Traditional RESTful endpoints require multiple requests to retrieve related data, often leading to over-fetching or under-fetching of information, whereas Graph Query Language (GraphQL) allows clients to specify exactly what data they need in a single query, optimizing network efficiency. REST APIs use fixed URL endpoints mapped to server resources, while GraphQL operates through a flexible schema and query system that reduces the number of round-trips between client and server.
Over-fetching
Traditional APIs often cause over-fetching by returning entire resource objects regardless of client needs, increasing data payload and slowing performance. Graph Query Language enables precise data querying, allowing clients to request only necessary fields and reducing bandwidth usage effectively.
Under-fetching
Traditional APIs commonly suffer from under-fetching, forcing clients to make multiple requests to retrieve all necessary data, which increases latency and reduces efficiency. Graph Query Languages like GraphQL resolve this issue by allowing clients to request precisely the data they need in a single query, minimizing over-fetching and under-fetching problems.
Data Aggregation Layer
Traditional API architectures often rely on fixed endpoints and multiple requests to different services for data retrieval, leading to increased latency and over-fetching issues. Graph Query Language streamlines the data aggregation layer by enabling clients to request precisely the needed data in a single query, reducing network overhead and improving performance efficiency.
Schema Stitching
Traditional API architectures rely on REST endpoints that require multiple round-trips for nested data retrieval, whereas Graph Query Language enables unified and efficient data fetching through schema stitching, which merges multiple schemas into a single graph. Schema stitching optimizes query performance and developer experience by allowing seamless integration of disparate data sources into a cohesive GraphQL API.
API Gateway Orchestration
Traditional API gateways handle orchestration by routing fixed REST endpoints, often resulting in multiple over-fetching or under-fetching issues. Graph query languages enable API gateway orchestration with precise data aggregation and real-time query flexibility, reducing latency and improving client-driven data retrieval efficiency.
Federation (GraphQL)
GraphQL Federation enables seamless integration of multiple GraphQL services into a unified graph, enhancing data aggregation across distributed microservices compared to traditional REST APIs which require multiple endpoints handling. Federation reduces over-fetching and under-fetching issues by allowing clients to query precisely what they need from a single endpoint while maintaining service ownership and independence.
Query Batching
Traditional APIs often require multiple network requests to fetch related data, leading to increased latency and bandwidth usage. Graph Query Languages like GraphQL enable query batching by allowing clients to request nested and related data in a single query, reducing round-trips and improving performance.
Resolver Chaining
Resolver chaining in Graph Query Language enables multiple nested data requests with efficient, declarative execution, contrasting with traditional APIs where separate endpoint calls increase latency and complexity. This method reduces over-fetching by resolving dependent fields in a single query, optimizing data retrieval compared to rigid RESTful API designs.
n+1 Query Problem
Traditional APIs often suffer from the n+1 query problem, where multiple sequential database calls degrade performance by overfetching data. Graph Query Languages like GraphQL mitigate this issue by enabling clients to request precisely nested data in a single query, optimizing database interactions and reducing redundant requests.
Traditional API vs Graph Query Language Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com