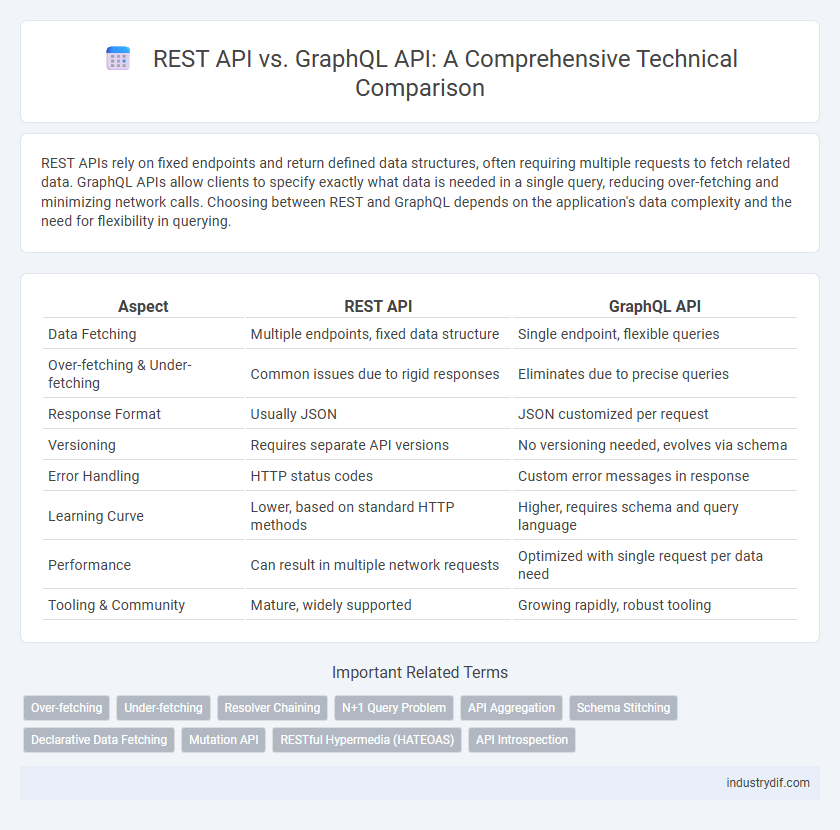
REST APIs rely on fixed endpoints and return defined data structures, often requiring multiple requests to fetch related data. GraphQL APIs allow clients to specify exactly what data is needed in a single query, reducing over-fetching and minimizing network calls. Choosing between REST and GraphQL depends on the application's data complexity and the need for flexibility in querying.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | REST API | GraphQL API |
|---|---|---|
| Data Fetching | Multiple endpoints, fixed data structure | Single endpoint, flexible queries |
| Over-fetching & Under-fetching | Common issues due to rigid responses | Eliminates due to precise queries |
| Response Format | Usually JSON | JSON customized per request |
| Versioning | Requires separate API versions | No versioning needed, evolves via schema |
| Error Handling | HTTP status codes | Custom error messages in response |
| Learning Curve | Lower, based on standard HTTP methods | Higher, requires schema and query language |
| Performance | Can result in multiple network requests | Optimized with single request per data need |
| Tooling & Community | Mature, widely supported | Growing rapidly, robust tooling |
Introduction to REST API and GraphQL API
REST API uses stateless HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE to manage resources through predefined endpoints, enabling straightforward CRUD operations. GraphQL API offers a flexible query language allowing clients to request exactly the data they need from a single endpoint, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching of information. Both APIs facilitate client-server communication but differ in data handling paradigms and query efficiency.
Core Architectural Principles
REST APIs rely on stateless client-server communication, resource-based endpoints, and standardized HTTP methods to manage data, promoting scalability and cacheability. GraphQL APIs use a single endpoint with flexible queries that allow clients to specify exactly the data they need, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching problems inherent in REST. The core architectural principle of REST centers on uniform interfaces and representational resources, while GraphQL emphasizes client-driven data retrieval and schema introspection for optimized performance and developer experience.
Data Fetching and Response Structure
REST API structures data fetching through multiple endpoints, each representing a specific resource, requiring multiple requests for related data, which can lead to over-fetching or under-fetching. GraphQL API provides a single endpoint that allows clients to specify exactly what data fields are needed, reducing bandwidth usage and improving performance by returning nested and precise data structures in one response. This makes GraphQL more efficient in complex data scenarios, while REST's fixed response schemas offer simplicity and caching advantages.
Query Flexibility and Efficiency
GraphQL API offers superior query flexibility by allowing clients to precisely specify the data they need, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching issues common in REST APIs. REST APIs rely on fixed endpoints that often return excessive or insufficient data, leading to multiple requests to aggregate information. This dynamic querying capability of GraphQL enhances efficiency, minimizes bandwidth usage, and accelerates client-server interactions compared to traditional REST API architectures.
Performance and Over-fetching/Under-fetching
REST API often suffers from over-fetching or under-fetching data due to fixed endpoints returning fixed data structures, which impacts performance by transferring unnecessary or insufficient information. GraphQL API optimizes performance by enabling clients to request exactly the data they need in a single query, thereby reducing payload size and minimizing network requests. This precise data retrieval in GraphQL enhances efficiency, especially in mobile and low-bandwidth environments where reducing data transfer is critical.
Versioning Strategies
REST APIs typically use versioning strategies such as URI versioning (e.g., /v1/resource), query parameter versioning, or custom headers to manage changes over time while maintaining backward compatibility. GraphQL APIs often avoid explicit versioning by enabling schema evolution through deprecation of fields and introduction of new types, allowing clients to query only the data they need without breaking existing queries. Effective versioning in REST preserves stable endpoints but may increase maintenance complexity, whereas GraphQL's version-free approach streamlines client-server integration by supporting flexible and incremental updates.
Error Handling Mechanisms
REST APIs typically rely on HTTP status codes like 4xx and 5xx to indicate errors, accompanied by standardized error messages in the response body, enabling straightforward client-side error detection and handling. GraphQL APIs encapsulate errors within the response's "errors" array while still returning a 200 OK status, allowing clients to receive partial data alongside error details for more granular resolution. This fundamental difference in error handling ensures REST provides immediate protocol-level feedback, whereas GraphQL supports complex query responses with embedded error information.
Security Considerations
REST API security primarily hinges on robust authentication methods such as OAuth 2.0 and the enforcement of HTTPS to protect data in transit. GraphQL APIs require careful query complexity analysis and depth limiting to prevent denial-of-service attacks due to overly expensive queries. Both approaches benefit from implementing proper authorization layers and input validation to mitigate injection attacks and unauthorized data access.
Tooling and Ecosystem Support
GraphQL APIs offer advanced tooling such as introspection, enabling powerful IDE integrations like GraphiQL and Apollo Studio for real-time query analysis and error detection. REST APIs benefit from widespread ecosystem support with mature tools like Swagger/OpenAPI for automated documentation, testing, and client generation. The choice depends on whether dynamic query exploration or established toolchains for standard CRUD operations are prioritized.
Use Cases and Best Practice Scenarios
REST API excels in applications requiring standardized CRUD operations and stateless communication, making it ideal for simple web services and microservices architecture. GraphQL API demonstrates superior performance in scenarios where clients need precise data fetching capabilities, complex querying, or multiple resource aggregation in a single request. Use REST for caching efficiency and scalability in resource-oriented services, while leveraging GraphQL for frontend-driven applications demanding flexibility and reduced over-fetching.
Related Important Terms
Over-fetching
REST API often leads to over-fetching by delivering fixed data structures that include unnecessary fields, causing inefficiencies in bandwidth and processing. GraphQL API allows clients to specify exact data requirements in queries, minimizing over-fetching and improving performance by transmitting only the needed information.
Under-fetching
REST APIs often suffer from under-fetching because they require multiple endpoints to retrieve related data, leading to incomplete responses and additional requests. GraphQL APIs mitigate under-fetching by allowing clients to specify exactly what data fields are needed in a single query, optimizing data retrieval and reducing network overhead.
Resolver Chaining
Resolver chaining in GraphQL APIs enables efficient data retrieval by allowing multiple related queries to be executed within a single request, reducing the need for additional round-trips unlike REST APIs where multiple endpoints are often called sequentially. This mechanism optimizes performance and flexibility, especially for complex data structures and nested resources, by resolving dependencies at the server level.
N+1 Query Problem
REST API often triggers the N+1 query problem by requiring multiple sequential requests to fetch nested resources, leading to excessive database queries and performance bottlenecks. GraphQL mitigates this issue by allowing clients to specify exactly what data they need in a single request, reducing redundant queries and optimizing data retrieval efficiency.
API Aggregation
REST APIs often require multiple round trips to aggregate data from different endpoints, leading to increased latency and complex client-side logic. GraphQL APIs enable efficient API aggregation by allowing clients to specify precise data requirements in a single request, reducing over-fetching and minimizing network overhead.
Schema Stitching
REST APIs rely on multiple endpoints representing fixed resources, limiting flexibility in data retrieval, whereas GraphQL APIs utilize schema stitching to combine multiple schemas into a single, unified API, enabling clients to request exactly the data they need in one query. Schema stitching enhances GraphQL by integrating different backend services into a cohesive graph, simplifying data aggregation and reducing network overhead compared to traditional REST architecture.
Declarative Data Fetching
REST API requires multiple endpoints for different resources, often leading to over-fetching or under-fetching of data, while GraphQL API enables declarative data fetching by allowing clients to specify exactly which fields and nested resources they need in a single query. This approach reduces network requests and optimizes performance by delivering precise and flexible data responses tailored to each client's requirements.
Mutation API
REST API mutations rely on multiple endpoints for different operations, often requiring several HTTP methods like POST, PUT, or DELETE to modify resources. GraphQL API mutations consolidate create, update, and delete operations into a single mutation endpoint, allowing precise data changes with minimal requests and optimized payloads.
RESTful Hypermedia (HATEOAS)
RESTful Hypermedia (HATEOAS) enhances REST APIs by embedding dynamic hyperlinks within responses, enabling clients to navigate resources and available actions seamlessly without prior knowledge of the API structure. Unlike GraphQL's single-endpoint schema querying, HATEOAS-driven REST APIs promote discoverability and adaptability through standardized media types and hypermedia controls, facilitating decoupled client-server evolution.
API Introspection
REST API lacks native support for schema introspection, requiring external documentation tools like Swagger or OpenAPI for endpoint discovery. GraphQL API inherently supports introspection queries, enabling clients to dynamically explore the schema, types, and fields, which enhances Development and debugging processes.
REST API vs GraphQL API Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com