On-premises infrastructure offers complete control and security by housing all data and applications locally within an organization's facilities. Hybrid cloud solutions combine on-premises systems with public and private cloud services to provide flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. Organizations leverage hybrid cloud models to balance sensitive data protection with the ability to scale resources dynamically based on demand.
Table of Comparison
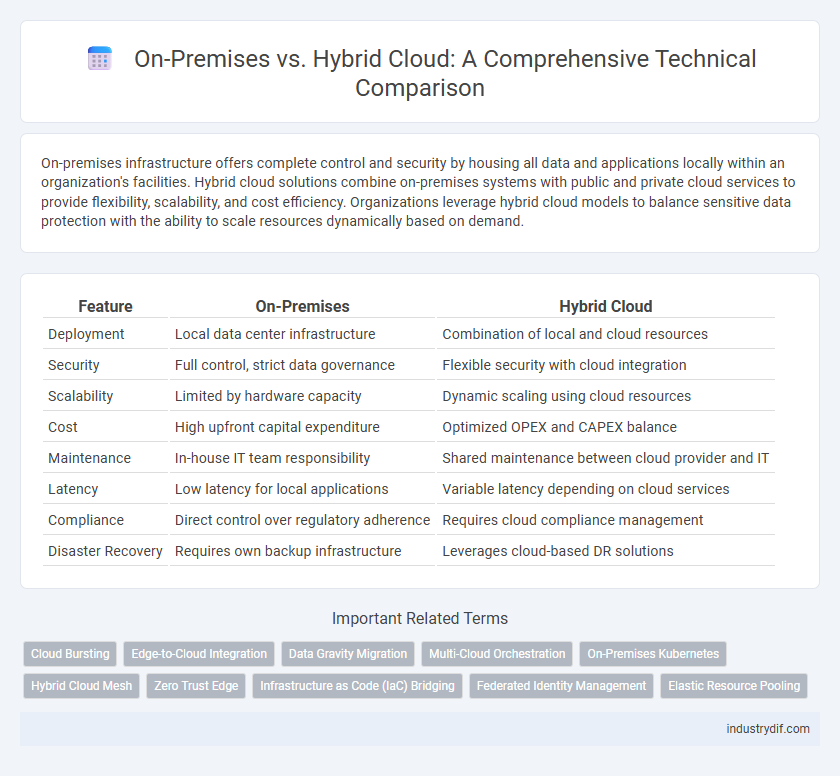
| Feature | On-Premises | Hybrid Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | Local data center infrastructure | Combination of local and cloud resources |
| Security | Full control, strict data governance | Flexible security with cloud integration |
| Scalability | Limited by hardware capacity | Dynamic scaling using cloud resources |
| Cost | High upfront capital expenditure | Optimized OPEX and CAPEX balance |
| Maintenance | In-house IT team responsibility | Shared maintenance between cloud provider and IT |
| Latency | Low latency for local applications | Variable latency depending on cloud services |
| Compliance | Direct control over regulatory adherence | Requires cloud compliance management |
| Disaster Recovery | Requires own backup infrastructure | Leverages cloud-based DR solutions |
Definition of On-Premises and Hybrid Cloud
On-premises refers to IT infrastructure and resources physically located within an organization's facilities, managed and operated exclusively by the internal IT team. Hybrid cloud combines on-premises infrastructure with public and private cloud services, enabling seamless workload portability, data integration, and scalability across multiple environments. This model enhances flexibility by leveraging both local control and cloud-based resources for optimized performance and cost efficiency.
Key Differences Between On-Premises and Hybrid Cloud
On-premises infrastructure involves maintaining physical servers and hardware within an organization's own data center, offering full control over data security and customization. Hybrid cloud integrates on-premises systems with public and private cloud services, enabling flexible resource allocation and scalability while optimizing workload distribution. Key differences include cost structure, with on-premises requiring significant upfront investment versus the operational expenditure model of hybrid cloud, as well as differences in maintenance responsibilities, scalability potential, and disaster recovery capabilities.
Infrastructure Architecture Comparison
On-premises infrastructure offers complete control over hardware, data security, and compliance by housing all resources within a local data center, ensuring low latency and direct access to physical servers. Hybrid cloud architecture integrates on-premises systems with public cloud services, enabling scalable workloads, flexible resource allocation, and improved disaster recovery through seamless data and application mobility. The hybrid model leverages virtualization, containerization, and software-defined networking to optimize performance, cost efficiency, and operational agility across heterogeneous environments.
Security and Compliance Considerations
On-premises environments offer direct control over data security and compliance, enabling organizations to implement tailored access controls and meet stringent regulatory requirements such as HIPAA or GDPR. Hybrid cloud models combine on-premises infrastructure with public cloud services, necessitating robust encryption, identity management, and continuous monitoring to maintain security across diverse environments. Ensuring consistent compliance frameworks and real-time threat detection is critical to mitigate risks associated with data transit and multi-jurisdictional regulations in hybrid deployments.
Scalability and Flexibility Analysis
On-premises infrastructure offers limited scalability due to fixed hardware capacity and longer upgrade cycles, while hybrid cloud environments enable dynamic resource allocation, supporting rapid scaling based on workload demand. Hybrid cloud flexibility allows seamless integration of private and public clouds, optimizing performance and cost-efficiency by shifting workloads between environments. Scalability metrics such as elastic compute capacity and automated provisioning highlight the hybrid cloud's superior adaptability compared to the static nature of on-premises systems.
Cost Implications and ROI
On-premises infrastructure entails significant upfront capital expenses for hardware acquisition, facility maintenance, and IT staffing, resulting in longer ROI timelines due to fixed depreciation costs. Hybrid cloud models optimize expenditure by combining scalable public cloud resources with existing on-premises assets, reducing capital outlays and enabling pay-as-you-go operational expenses that improve cost flexibility and accelerate ROI. Strategic allocation of workloads onto hybrid environments maximizes resource utilization and minimizes overall total cost of ownership (TCO), delivering a more balanced cost-benefit profile compared to solely on-premises deployments.
Performance and Latency Factors
On-premises environments typically provide lower latency and higher performance due to local resource availability and direct network access, minimizing data transfer times. Hybrid cloud solutions introduce variable latency influenced by internet bandwidth, cloud provider infrastructure, and geographic distance, potentially impacting performance-sensitive applications. Optimizing workload distribution between on-premises resources and cloud services is critical to balancing latency and computational efficiency in hybrid deployments.
Integration with Legacy Systems
On-premises environments offer direct and seamless integration with legacy systems, ensuring low latency and full control over existing infrastructure. Hybrid cloud architectures enable businesses to extend legacy capabilities by selectively offloading workloads to the cloud while maintaining critical operations on-premises. Effective integration strategies leverage APIs, middleware, and virtualization to bridge legacy systems with cloud resources, optimizing performance and continuity.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
On-premises solutions provide robust security and control for industries with strict compliance requirements like finance and healthcare, ensuring sensitive data remains within corporate firewalls. Hybrid cloud environments enable retail and manufacturing sectors to achieve scalability and flexibility by combining on-premises infrastructure with public cloud resources for peak demand and disaster recovery. Use cases such as big data analytics, AI model training, and IoT deployments benefit from hybrid architectures by leveraging both local processing power and cloud-based services for optimized performance and cost efficiency.
Future Trends in Hybrid Cloud Adoption
Hybrid cloud adoption is rapidly increasing due to its ability to combine on-premises infrastructure with public cloud resources, offering enhanced scalability, flexibility, and cost efficiency. Emerging technologies such as AI-driven automation, edge computing integration, and advanced security frameworks are driving the evolution of hybrid cloud architectures. Industry forecasts predict hybrid cloud market growth at a CAGR of over 20% through 2028, reflecting its critical role in digital transformation strategies.
Related Important Terms
Cloud Bursting
Cloud bursting enables on-premises infrastructure to handle peak workloads by dynamically extending capacity to a hybrid cloud environment, optimizing resource utilization and minimizing costs. This approach ensures seamless scalability during demand spikes without over-provisioning physical hardware.
Edge-to-Cloud Integration
Edge-to-cloud integration enhances hybrid cloud environments by enabling seamless data processing and real-time analytics closer to data sources, reducing latency and bandwidth usage compared to traditional on-premises infrastructure. Leveraging edge devices alongside cloud resources optimizes operational efficiency and scalability while maintaining data sovereignty and security requirements critical for industries like manufacturing and healthcare.
Data Gravity Migration
Data gravity migration significantly impacts the choice between on-premises and hybrid cloud solutions, as large volumes of data stored on-premises create latency challenges when transferred to cloud environments. Hybrid cloud architectures mitigate these issues by enabling data processing and storage closer to the source, optimizing performance and reducing transfer costs.
Multi-Cloud Orchestration
Multi-cloud orchestration enables seamless management of applications and workloads across on-premises and hybrid cloud environments by automating deployment, scaling, and resource allocation. Leveraging orchestration tools like Kubernetes and Terraform enhances operational efficiency, reduces latency, and ensures compliance with data sovereignty regulations in complex multi-cloud setups.
On-Premises Kubernetes
On-premises Kubernetes deployments offer full control over infrastructure, providing enhanced security and compliance for sensitive workloads while minimizing latency by keeping data and applications close to users. This setup empowers organizations to customize container orchestration environments with dedicated hardware resources, avoiding dependencies on external cloud providers.
Hybrid Cloud Mesh
Hybrid Cloud Mesh integrates multiple cloud environments and on-premises infrastructure through a unified orchestration layer, enabling seamless workload mobility, enhanced security, and consistent policy enforcement across diverse platforms. This architecture improves operational efficiency by automating network connectivity, optimizing resource allocation, and providing centralized management for complex hybrid deployments.
Zero Trust Edge
Zero Trust Edge architectures enhance security by enforcing strict access controls and continuous verification at the network perimeter, making them essential for both on-premises and hybrid cloud environments. Integrating Zero Trust Edge with hybrid cloud deployments enables seamless protection across distributed resources while maintaining compliance and minimizing attack surfaces.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Bridging
On-premises infrastructure benefits from Infrastructure as Code (IaC) by enabling automated provisioning and consistent configuration management, reducing manual errors and accelerating deployment cycles. Hybrid cloud environments leverage IaC to seamlessly bridge on-premises resources with public cloud services, ensuring unified infrastructure orchestration and policy enforcement across diverse platforms.
Federated Identity Management
Federated Identity Management in on-premises environments enables centralized control over user authentication but can be limited by local infrastructure constraints, whereas hybrid cloud solutions integrate on-premises systems with cloud services to provide seamless, secure, and scalable identity federation across multiple platforms. Implementing federated identity in a hybrid cloud architecture enhances access management efficiency by leveraging standards like SAML and OAuth for unified authentication across diverse environments.
Elastic Resource Pooling
On-premises environments limit resource scalability due to fixed hardware capacity, while hybrid cloud architectures enable elastic resource pooling by dynamically allocating workloads across private and public cloud infrastructures. This elasticity enhances performance, optimizes costs, and ensures seamless resource availability during peak demand periods.
On-Premises vs Hybrid Cloud Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com