Waterfall follows a linear and sequential approach, making it difficult to integrate security testing early in the development cycle, which can lead to delayed identification of vulnerabilities. DevSecOps embeds security practices within the continuous integration and delivery pipeline, enabling real-time threat detection and faster remediation during development. This proactive integration enhances overall software security while maintaining agility and efficiency.
Table of Comparison
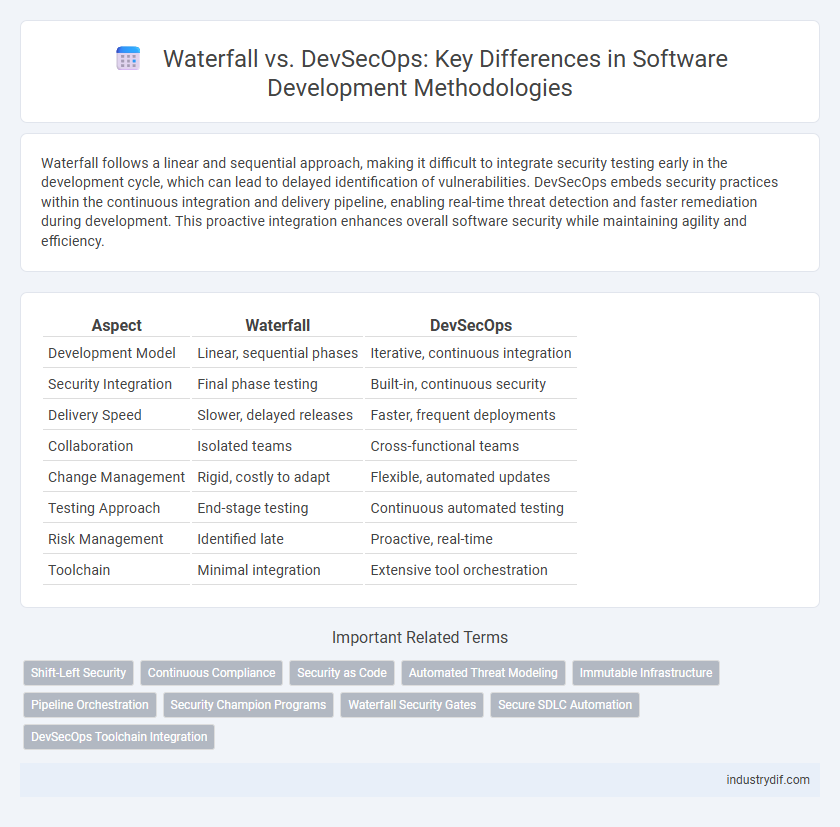
| Aspect | Waterfall | DevSecOps |
|---|---|---|
| Development Model | Linear, sequential phases | Iterative, continuous integration |
| Security Integration | Final phase testing | Built-in, continuous security |
| Delivery Speed | Slower, delayed releases | Faster, frequent deployments |
| Collaboration | Isolated teams | Cross-functional teams |
| Change Management | Rigid, costly to adapt | Flexible, automated updates |
| Testing Approach | End-stage testing | Continuous automated testing |
| Risk Management | Identified late | Proactive, real-time |
| Toolchain | Minimal integration | Extensive tool orchestration |
Introduction to Waterfall and DevSecOps
Waterfall is a linear, sequential software development methodology characterized by distinct phases such as requirements, design, implementation, verification, and maintenance, with minimal iteration between stages. DevSecOps integrates development, security, and operations into a continuous development pipeline, enabling automated testing, security checks, and rapid deployment. While Waterfall emphasizes structured progress and documentation, DevSecOps prioritizes agility, collaboration, and security throughout the software lifecycle.
Key Principles of Waterfall Methodology
The Waterfall methodology is characterized by a linear and sequential design process, where each phase must be completed before the next begins, emphasizing thorough documentation and upfront planning. Key principles include fixed project scope, defined deliverables, and milestone-based progress tracking, which ensure systematic control and predictability. This approach contrasts with iterative frameworks by prioritizing a structured, stage-gated progression that minimizes change during development.
Core Concepts of DevSecOps
DevSecOps integrates security practices directly into the software development lifecycle, emphasizing automation, continuous integration, and continuous delivery to identify and remediate vulnerabilities early. Unlike Waterfall's linear and sequential approach, DevSecOps promotes collaboration between development, security, and operations teams, accelerating deployment while maintaining robust security standards. Core concepts include automated security testing, infrastructure as code, and real-time monitoring, ensuring security is embedded from code commit to production.
Waterfall vs DevSecOps: Process Differences
Waterfall follows a linear, sequential approach with distinct phases such as requirements, design, implementation, testing, and deployment, emphasizing documentation and fixed timelines. DevSecOps integrates development, security, and operations into continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, promoting automation, collaboration, and rapid feedback loops. The key process difference lies in Waterfall's rigid phase gate model versus DevSecOps' iterative, automated workflows enabling faster security integration and delivery.
Security Integration: Waterfall vs DevSecOps
Waterfall integrates security primarily at predefined milestones, resulting in delayed vulnerability detection and limited flexibility in addressing emerging threats. DevSecOps embeds security continuously throughout the development lifecycle with automated testing and real-time monitoring, significantly enhancing risk mitigation and compliance. This proactive, iterative security integration reduces exposure and accelerates secure software delivery.
Collaboration and Team Dynamics Comparison
Waterfall methodology features a linear, siloed approach where collaboration occurs primarily within distinct phases, often limiting cross-functional team interaction and slowing feedback loops. In contrast, DevSecOps fosters continuous collaboration among development, security, and operations teams, enhancing real-time communication and rapid issue resolution. This integrated team dynamic accelerates delivery cycles and promotes shared responsibility for security and quality throughout the software lifecycle.
Speed, Flexibility, and Scalability
Waterfall's linear structure limits flexibility and slows delivery, making rapid adaptation to change challenging, whereas DevSecOps integrates continuous feedback and automation, enhancing speed and responsiveness. DevSecOps enables scalable security practices embedded throughout the development lifecycle, contrasting with Waterfall's isolated security phases that hinder scalability and slow remediation. The iterative nature of DevSecOps supports scalable infrastructure and dynamic resource allocation, promoting faster deployment cycles and more efficient handling of evolving project requirements.
Risk Management Approaches
Waterfall employs a linear risk management approach with distinct phases for risk identification, assessment, and mitigation, usually documented upfront, which can lead to delayed detection of security vulnerabilities. DevSecOps integrates continuous risk assessment and real-time threat detection using automated tools throughout the development lifecycle, enabling proactive vulnerability management and faster incident response. This continuous integration of security practices reduces potential risks earlier and aligns with agile workflows, enhancing overall system resilience.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Waterfall methodology involves sequential phases that prioritize documentation and formal approvals, which can simplify compliance with strict regulatory standards by maintaining clear audit trails. DevSecOps integrates security and compliance checks continuously within the software development lifecycle, enabling faster adaptation to evolving regulations and automated policy enforcement. Organizations facing highly dynamic regulatory environments benefit from DevSecOps' real-time compliance monitoring, whereas industries with rigid, well-defined compliance requirements may find Waterfall's structured approach more suitable.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Waterfall methodology offers a linear, structured process ideal for projects with well-defined requirements and minimal expected changes, ensuring predictable timelines and deliverables. DevSecOps integrates development, security, and operations through continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD), promoting agile responsiveness and enhanced security within dynamic environments. Organizations should evaluate factors like project complexity, team expertise, regulatory demands, and desired release frequency to determine whether Waterfall's predictability or DevSecOps' flexibility aligns best with their strategic objectives.
Related Important Terms
Shift-Left Security
Waterfall employs a linear, sequential approach that delays security testing until late stages, increasing risks and remediation costs. DevSecOps integrates shift-left security by embedding automated security checks early in the development pipeline, enabling continuous vulnerability detection and faster threat mitigation.
Continuous Compliance
Waterfall development follows a linear, sequential approach with compliance checks primarily at the end, often leading to delayed identification of security risks. DevSecOps integrates continuous compliance by embedding automated security testing and policy enforcement throughout the development pipeline, enabling real-time risk mitigation and faster, more secure software delivery.
Security as Code
Waterfall follows a linear, sequential approach where security is often implemented at the end, increasing vulnerability risks and delayed threat detection. DevSecOps integrates Security as Code throughout continuous integration and deployment pipelines, enabling automated vulnerability scanning, compliance checks, and real-time risk mitigation.
Automated Threat Modeling
Automated threat modeling in DevSecOps integrates continuous security assessments into the development pipeline, enabling real-time identification and mitigation of vulnerabilities much faster than the traditional Waterfall approach. This automation streamlines risk analysis, reducing manual efforts and enhancing proactive security in dynamic, iterative development environments.
Immutable Infrastructure
Waterfall methodology follows a linear, sequential approach, often resulting in slower integration of security measures, whereas DevSecOps promotes continuous security integration through automated pipelines. Immutable infrastructure in DevSecOps ensures consistent, repeatable deployments by replacing components rather than modifying them, significantly reducing configuration drift and enhancing system reliability compared to the static environments typical in Waterfall projects.
Pipeline Orchestration
Waterfall methodology relies on sequential pipeline orchestration with distinct, linear phases, limiting flexibility and delaying security integration until later stages. DevSecOps enhances pipeline orchestration by embedding continuous security checks and automated feedback loops within agile, iterative workflows, ensuring faster, secure software delivery.
Security Champion Programs
Waterfall methodologies often lack integrated security champion programs, leading to delayed vulnerability identification and remediation. In contrast, DevSecOps embeds Security Champions within agile teams, enhancing continuous security awareness, rapid threat detection, and proactive risk mitigation throughout the development lifecycle.
Waterfall Security Gates
Waterfall security gates enforce strict, sequential checkpoints for security reviews, vulnerability assessments, and compliance validation before progressing stages, enhancing control but often delaying development cycles. These rigid gates contrast with DevSecOps' continuous integration of security, which embeds real-time threat detection and automated testing throughout the software lifecycle to accelerate deployment without compromising safety.
Secure SDLC Automation
Waterfall methodology relies on sequential development phases with limited automation, often resulting in slower identification and mitigation of security vulnerabilities. DevSecOps integrates continuous security testing and automated compliance checks within the Secure SDLC, enhancing security posture through real-time risk detection and faster remediation cycles.
DevSecOps Toolchain Integration
DevSecOps toolchain integration automates security testing, continuous monitoring, and compliance verification within the software development lifecycle, enabling faster vulnerability detection and remediation compared to the linear Waterfall model. This integrated approach ensures seamless collaboration between development, security, and operations teams, enhancing overall software quality and reducing time-to-market.
Waterfall vs DevSecOps Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com