Express delivery offers fast, reliable shipping by utilizing professional couriers and optimized logistics networks to ensure timely arrival of packages. Crowdshipping leverages peer-to-peer networks, allowing individuals to transport goods along their existing travel routes, often resulting in cost savings and increased flexibility. Both methods cater to different needs, with express delivery prioritizing speed and consistency, while crowdshipping emphasizes community involvement and sustainability.
Table of Comparison
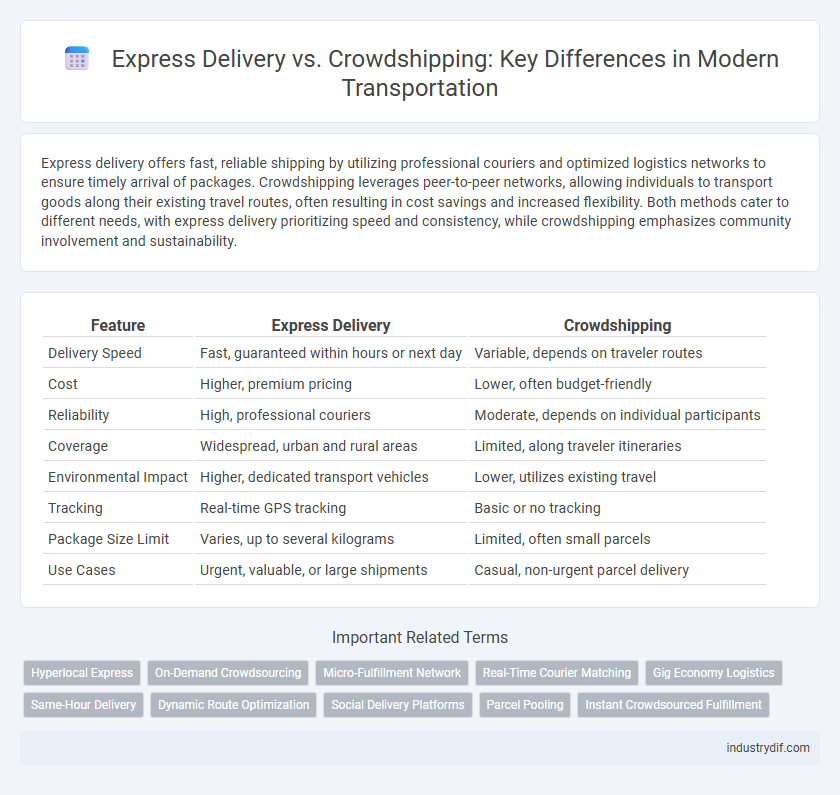
| Feature | Express Delivery | Crowdshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Speed | Fast, guaranteed within hours or next day | Variable, depends on traveler routes |
| Cost | Higher, premium pricing | Lower, often budget-friendly |
| Reliability | High, professional couriers | Moderate, depends on individual participants |
| Coverage | Widespread, urban and rural areas | Limited, along traveler itineraries |
| Environmental Impact | Higher, dedicated transport vehicles | Lower, utilizes existing travel |
| Tracking | Real-time GPS tracking | Basic or no tracking |
| Package Size Limit | Varies, up to several kilograms | Limited, often small parcels |
| Use Cases | Urgent, valuable, or large shipments | Casual, non-urgent parcel delivery |
Overview of Express Delivery and Crowdshipping
Express delivery leverages dedicated logistics networks to provide fast, reliable parcel shipments with guaranteed timeframes, often utilized by businesses requiring urgent, time-sensitive transportation. Crowdshipping, on the other hand, harnesses the power of local travelers and gig economy participants to deliver packages, offering flexible, cost-effective solutions particularly suited for last-mile delivery and peer-to-peer shipping. Both models address diverse consumer needs but differ in operational scale, speed, and infrastructure reliance.
Key Differences Between Express Delivery and Crowdshipping
Express delivery relies on professional couriers and centralized logistics networks to guarantee fast, time-sensitive parcel shipments, often within the same day or overnight. Crowdshipping leverages decentralized, peer-to-peer transportation by utilizing travelers or local commuters to carry packages, offering flexible routes and potentially lower costs. Key differences include service reliability, delivery speed, cost structure, and the scale of operational oversight.
Speed and Reliability Comparison
Express delivery services guarantee rapid shipping times by utilizing dedicated logistics networks and priority handling, ensuring consistent reliability for time-sensitive parcels. Crowdshipping leverages local couriers and ride-sharing drivers, offering flexible and potentially faster options in urban areas, but with variable reliability due to decentralized operations. Studies indicate express delivery maintains higher on-time rates, while crowdshipping excels in last-mile speed during peak congestion periods.
Cost Efficiency in Both Models
Express delivery offers predictable pricing structures with higher costs due to dedicated logistics and faster shipping times, appealing to businesses prioritizing reliability. Crowdshipping leverages local travelers to reduce expenses by utilizing unused vehicle capacity, significantly lowering last-mile delivery costs but with variable delivery times. Cost efficiency in express delivery hinges on volume and scale, while crowdshipping depends on network density and effective matching of shipments to drivers.
Technology Integration in Delivery Services
Express delivery services leverage advanced logistics software, real-time tracking, and automated sorting systems to ensure fast and reliable parcel handling. Crowdshipping integrates mobile applications and GPS technology to connect individual couriers with nearby delivery requests, optimizing route efficiency and reducing delivery times through decentralized networks. Both models utilize data analytics and cloud computing to enhance operational transparency and customer satisfaction.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Considerations
Express delivery often relies on dedicated logistics networks with higher carbon emissions per package due to rapid transit and air transport use. Crowdshipping leverages existing travel routes and unused vehicle capacity, significantly reducing overall environmental footprint through shared resources and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing crowdshipping promotes sustainable transportation by minimizing energy consumption and aligning with eco-friendly supply chain practices.
Customer Experience and Service Levels
Express delivery offers guaranteed fast transit times and reliable tracking, ensuring customers receive their packages quickly with high service predictability. Crowdshipping leverages local, peer-to-peer networks to provide flexible, cost-effective delivery options that can enhance convenience in last-mile fulfillment but may vary in speed and reliability. Customer experience in express delivery centers on speed and consistency, while crowdshipping emphasizes personalization and adaptability, often with trade-offs in service level guarantees.
Scalability and Flexibility in Operations
Express delivery services offer high scalability through established logistics networks and automated sorting systems, enabling rapid expansion across urban and suburban areas. Crowdshipping leverages decentralized, peer-to-peer delivery models that provide exceptional flexibility by utilizing everyday travelers and local couriers, adapting efficiently to fluctuating demand and diverse parcel sizes. Combining these approaches can optimize operational efficiency, balancing predictable scale with dynamic responsiveness in last-mile transportation.
Security and Package Safety Concerns
Express delivery services implement strict tracking systems and secure handling protocols to minimize the risk of package loss or damage, ensuring high security standards throughout the transit process. Crowdshipping relies on a decentralized network of couriers, raising concerns about inconsistent vetting procedures and potential vulnerabilities in protecting sensitive items. While express delivery offers standardized security measures, crowdshipping requires enhanced trust mechanisms and robust verification to address package safety challenges effectively.
Future Trends in Express Delivery and Crowdshipping
Future trends in express delivery emphasize the integration of AI-driven route optimization and drone technology to reduce transit times and enhance efficiency. Crowdshipping is evolving with increased reliance on decentralized networks and real-time tracking systems that leverage social platforms and mobile apps for flexible, community-based parcel transport. Both models are expected to converge with sustainable logistics solutions and predictive analytics driving smarter, greener last-mile delivery services.
Related Important Terms
Hyperlocal Express
Hyperlocal express delivery leverages local couriers to ensure rapid, same-day shipments within a limited geographic area, optimizing delivery speed and reducing carbon footprint. Crowdshipping, by utilizing community members as couriers, enhances flexibility and cost-efficiency but may face challenges in consistency and reliability compared to dedicated hyperlocal express services.
On-Demand Crowdsourcing
On-demand crowdsourcing in transportation leverages a distributed network of local, non-professional couriers to provide flexible, real-time express delivery services, often resulting in faster and more cost-effective solutions compared to traditional logistics companies. This model enhances last-mile delivery efficiency by dynamically matching delivery requests with nearby crowdshippers through digital platforms, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
Micro-Fulfillment Network
Express delivery leverages centralized micro-fulfillment centers to ensure rapid order processing and last-mile delivery within urban areas, optimizing inventory distribution and reducing delivery times. Crowdshipping complements this by utilizing local couriers and real-time routing, enhancing the flexibility and scalability of the micro-fulfillment network while lowering operational costs.
Real-Time Courier Matching
Express delivery leverages centralized logistics and proprietary courier networks to ensure guaranteed delivery timelines, while crowdshipping utilizes real-time courier matching through mobile platforms to dynamically connect senders with nearby independent couriers. Real-time courier matching enhances route optimization and reduces delivery latency by utilizing geolocation data and algorithm-driven assignments in both models.
Gig Economy Logistics
Express delivery services leverage centralized logistics networks for fast, reliable parcel transportation, while crowdshipping utilizes gig economy workers to decentralize last-mile delivery, enhancing flexibility and reducing costs. The gig economy in logistics drives innovative crowdshipping models that optimize route efficiency and customer convenience through real-time data and app-based coordination.
Same-Hour Delivery
Express delivery guarantees same-hour delivery through dedicated logistics networks and professional couriers, ensuring reliability and speed for urgent shipments. Crowdshipping leverages nearby community members as couriers, offering flexible same-hour delivery options that can optimize last-mile efficiency but may vary in consistency and service quality.
Dynamic Route Optimization
Dynamic route optimization in express delivery uses advanced algorithms and real-time traffic data to prioritize speed and reliability, ensuring timely parcel arrivals through fixed courier networks. Crowdshipping leverages decentralized drivers and adaptive routing, dynamically adjusting routes based on driver availability and demand patterns, enhancing flexibility but risking consistency in delivery timeframes.
Social Delivery Platforms
Social delivery platforms leverage crowdshipping models by connecting local couriers with express delivery demands, enabling faster, cost-effective, and eco-friendly last-mile logistics. These platforms optimize route efficiency and package tracking while enhancing community engagement compared to traditional express delivery services.
Parcel Pooling
Parcel pooling in express delivery consolidates multiple shipments into a single load for faster, more reliable transport with predictable schedules, enhancing efficiency across logistics networks. Crowdshipping leverages decentralized local couriers to share parcel delivery tasks dynamically, reducing last-mile costs and expanding coverage but facing challenges in consistency and parcel tracking.
Instant Crowdsourced Fulfillment
Instant crowdsourced fulfillment leverages local individuals to expedite package delivery, reducing transit time and increasing flexibility compared to traditional express delivery services. This decentralized model enhances last-mile efficiency by dynamically matching demand with nearby crowdshippers using real-time data and mobile platforms.
Express Delivery vs Crowdshipping Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com