Trucking remains a dominant force in freight transportation due to its established infrastructure and cost efficiency for long hauls. Electric trucks offer significant benefits in reducing carbon emissions and lowering fuel expenses, making them ideal for urban delivery and short routes. The transition from traditional trucking to electric trucks depends on advancements in battery technology and the expansion of charging networks.
Table of Comparison
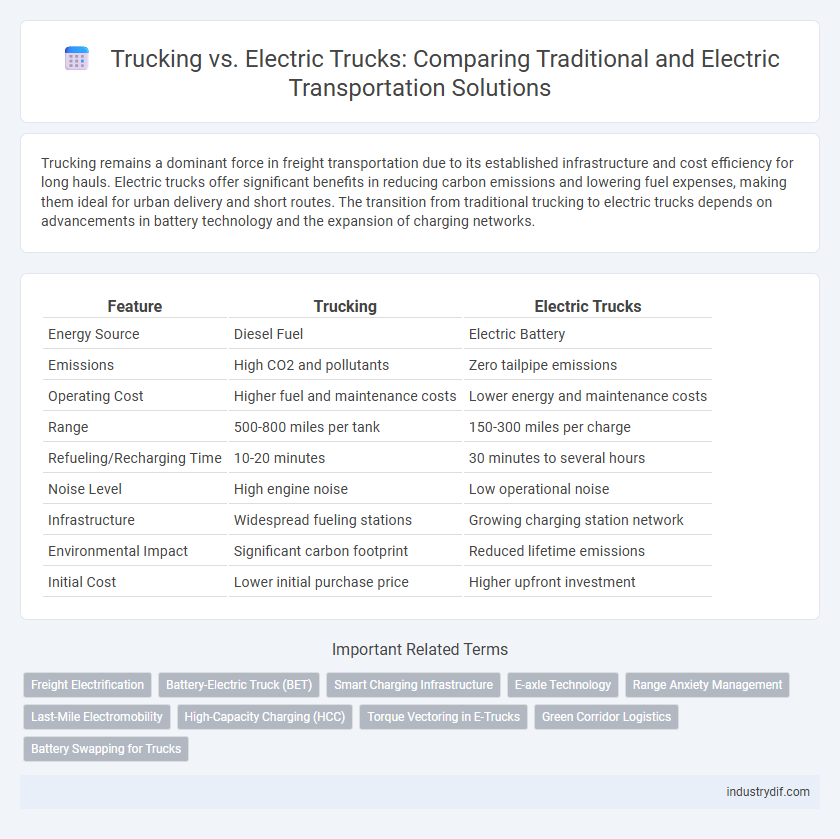
| Feature | Trucking | Electric Trucks |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Diesel Fuel | Electric Battery |
| Emissions | High CO2 and pollutants | Zero tailpipe emissions |
| Operating Cost | Higher fuel and maintenance costs | Lower energy and maintenance costs |
| Range | 500-800 miles per tank | 150-300 miles per charge |
| Refueling/Recharging Time | 10-20 minutes | 30 minutes to several hours |
| Noise Level | High engine noise | Low operational noise |
| Infrastructure | Widespread fueling stations | Growing charging station network |
| Environmental Impact | Significant carbon footprint | Reduced lifetime emissions |
| Initial Cost | Lower initial purchase price | Higher upfront investment |
Introduction to Traditional Trucking and Electric Trucks
Traditional trucking relies heavily on diesel-powered engines, dominating freight transport due to established infrastructure and long-range capabilities. Electric trucks leverage battery technology, offering reduced emissions and lower operational costs but currently face limitations in range and charging infrastructure. Advancements in electric vehicle technology and expanding charging networks are closing these gaps, positioning electric trucks as a sustainable alternative for future transportation.
Key Differences Between Diesel and Electric Trucks
Diesel trucks rely on internal combustion engines fueled by petroleum, offering long-range capabilities and quick refueling but producing higher emissions and noise pollution. Electric trucks use battery-powered electric motors, resulting in lower operating costs, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and quieter operation, but their range is limited by battery capacity and charging infrastructure. The total cost of ownership for electric trucks is decreasing due to advances in battery technology and government incentives promoting sustainable transportation solutions.
Environmental Impact: Emissions and Sustainability
Electric trucks significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional diesel-powered trucking by relying on renewable energy sources and producing zero tailpipe emissions. Diesel trucks contribute heavily to air pollution and carbon dioxide output, exacerbating climate change and health issues. Transitioning to electric trucks supports sustainability goals by lowering the transportation sector's carbon footprint and decreasing dependence on fossil fuels.
Operational Costs: Fuel, Maintenance, and Repairs
Electric trucks significantly reduce operational costs compared to traditional diesel trucks by lowering fuel expenses, as electricity is cheaper per mile than diesel fuel. Maintenance costs are also decreased due to fewer moving parts in electric drivetrains, resulting in less frequent repairs and downtime. Repair costs tend to be lower for electric trucks, with regenerative braking systems reducing brake wear and advanced diagnostics minimizing unexpected failures.
Performance and Range Comparison
Electric trucks offer significantly lower emissions and reduced fuel costs compared to traditional diesel trucking, making them environmentally and economically advantageous for fleet operators. While electric trucks generally have a shorter range--typically between 150 to 300 miles per charge--diesel trucks can exceed 1,000 miles on a full tank, providing longer continuous operation without refueling. Performance-wise, electric trucks deliver instant torque and quieter operation, but may face challenges in payload capacity and charging infrastructure compared to established diesel truck logistics.
Infrastructure and Charging Challenges
Electric trucks face significant infrastructure and charging challenges compared to traditional trucking, as widespread high-capacity charging stations are still underdeveloped across major freight corridors. The limited availability of fast chargers and the need for substantial electrical grid upgrades hinder the scalability of electric trucking fleets. Meanwhile, diesel trucks benefit from an extensive, decades-old fueling infrastructure offering quick refueling and easy access nationwide.
Regulatory Compliance and Incentives
Electric trucks benefit from increasingly stringent emissions regulations, aligning with global efforts to reduce carbon footprints in the transportation sector. Governments offer substantial incentives such as tax credits, grants, and reduced registration fees to accelerate the adoption of electric trucks, enhancing regulatory compliance cost-effectively. Traditional trucking faces rising costs related to fuel emissions standards and potential penalties, making electric trucks a strategically favorable alternative for logistics companies aiming to meet environmental mandates.
Fleet Transition Strategies and Considerations
Fleet transition strategies for trucking involve assessing total cost of ownership, including fuel savings, maintenance, and vehicle lifespan when shifting from diesel to electric trucks. Considerations include charging infrastructure availability, route optimization for battery range, and potential incentives for adopting zero-emission vehicles. Effective transition plans balance operational efficiency, environmental impact, and regulatory compliance to ensure seamless integration of electric trucks into existing logistics networks.
Market Adoption and Industry Trends
Trucking continues to dominate freight transportation with established infrastructure and widespread market adoption, accounting for over 70% of goods moved by road in the U.S. However, electric trucks are rapidly gaining traction due to stricter emissions regulations and advancements in battery technology, with market projections indicating a CAGR of 20% through 2030. Industry trends reveal major logistics companies investing heavily in electric fleets to reduce carbon footprint and operational costs, signaling a transformative shift in long-haul and last-mile delivery sectors.
Future Outlook for Trucking and Electric Vehicles
Electric trucks are rapidly transforming the future of the trucking industry with advancements in battery technology, increased range, and government incentives promoting zero-emission vehicles. Traditional diesel trucking remains vital due to established infrastructure and longer routes, but the shift towards electric fleets is accelerating to meet stringent environmental regulations and reduce operational costs. Industry projections estimate electric trucks will capture a significant market share by 2030, driven by sustainability goals and innovations in autonomous driving systems.
Related Important Terms
Freight Electrification
Freight electrification is transforming trucking by replacing diesel-powered vehicles with electric trucks that offer lower emissions and reduced fuel costs. Advances in battery technology and expanded charging infrastructure are accelerating the adoption of electric trucks for long-haul freight transportation.
Battery-Electric Truck (BET)
Battery-Electric Trucks (BET) offer a sustainable alternative to traditional diesel trucking by utilizing advanced lithium-ion batteries that reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 70% during operation. While BETs have higher upfront costs, they provide lower maintenance expenses and energy costs over their lifecycle, making them increasingly viable for regional freight transport.
Smart Charging Infrastructure
Smart charging infrastructure for electric trucks utilizes advanced grid management systems and real-time data analytics to optimize energy use, reduce charging times, and minimize operational costs. This technology supports sustainable trucking by enabling efficient load balancing and integrating renewable energy sources, offering a competitive edge over traditional diesel-powered trucks in logistics and freight transport.
E-axle Technology
Electric trucks equipped with advanced e-axle technology deliver higher efficiency and improved torque control compared to traditional trucking powertrains, reducing energy consumption and emissions. The e-axle integrates the electric motor, transmission, and differential into a single unit, enhancing vehicle performance and simplifying maintenance in commercial transportation fleets.
Range Anxiety Management
Electric trucks are advancing with improved battery technologies offering ranges up to 300-400 miles per charge, effectively reducing range anxiety for long-haul transportation. Traditional diesel trucking still dominates due to its refueling speed and extensive fueling infrastructure, but electric trucks benefit from telematics and route optimization software that enhance range management and operational efficiency.
Last-Mile Electromobility
Last-mile electromobility is transforming trucking by replacing traditional diesel trucks with electric trucks that offer lower emissions and reduced operational costs in urban deliveries. Electric trucks excel in last-mile transportation due to their quieter operation, zero tailpipe emissions, and increased efficiency in stop-and-go traffic, making them ideal for sustainable logistics solutions.
High-Capacity Charging (HCC)
High-capacity charging (HCC) technology significantly reduces downtime for electric trucks, enabling faster turnaround compared to traditional trucking refueling methods. This advancement supports extended range capabilities and increased fleet efficiency, making electric trucks a competitive option for long-haul freight transport.
Torque Vectoring in E-Trucks
Electric trucks leverage advanced torque vectoring systems to optimize power distribution across multiple electric motors, enhancing traction, stability, and maneuverability compared to traditional trucking. This technology improves handling on diverse terrains and reduces tire wear, leading to increased efficiency and lower operational costs for freight transportation.
Green Corridor Logistics
Green Corridor Logistics leverages electric trucks to reduce carbon emissions and enhance sustainability in long-haul freight transport compared to traditional diesel trucking. Electric trucks offer lower operational costs and improved energy efficiency, making them a pivotal solution for eco-friendly supply chain management along designated green corridors.
Battery Swapping for Trucks
Battery swapping technology for electric trucks significantly reduces downtime compared to traditional charging methods, enabling faster turnaround in long-haul transportation. This innovation enhances operational efficiency and supports sustainable trucking by minimizing reliance on fossil fuels and optimizing fleet management.
Trucking vs Electric Trucks Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com