Logistics involves the traditional management of the flow of goods, focusing on fixed processes and scheduled deliveries to ensure efficiency and cost control. Elastic logistics adapts dynamically to changing demand patterns and disruptions by leveraging real-time data and scalable resources, enhancing flexibility and responsiveness. This approach reduces delays and optimizes inventory levels while maintaining customer satisfaction in fast-paced supply chains.
Table of Comparison
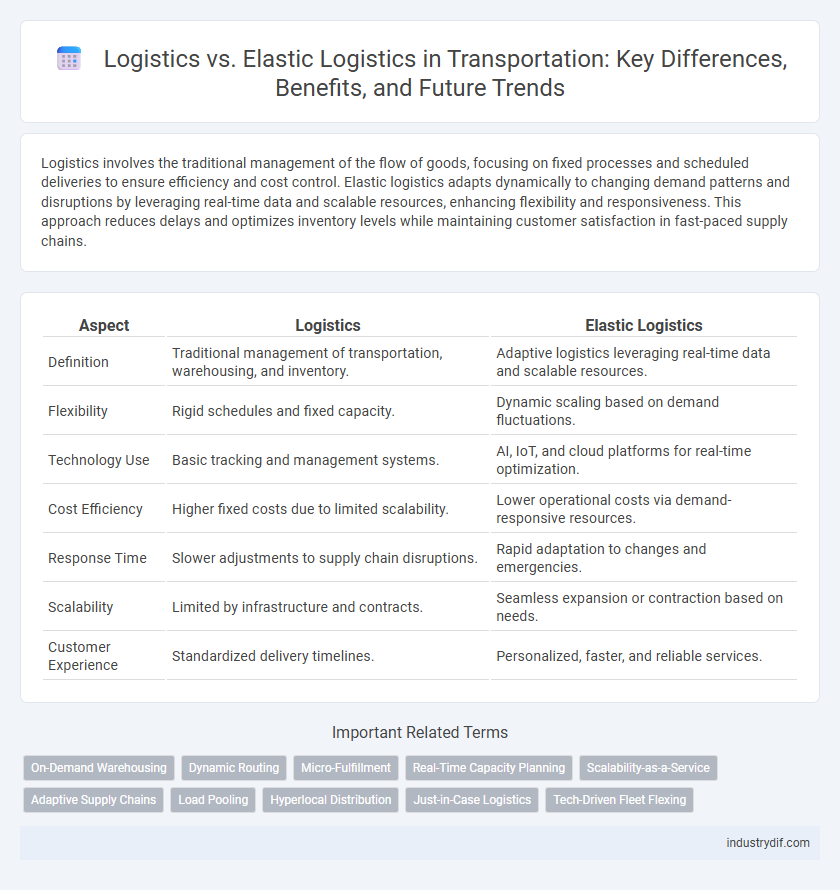
| Aspect | Logistics | Elastic Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional management of transportation, warehousing, and inventory. | Adaptive logistics leveraging real-time data and scalable resources. |
| Flexibility | Rigid schedules and fixed capacity. | Dynamic scaling based on demand fluctuations. |
| Technology Use | Basic tracking and management systems. | AI, IoT, and cloud platforms for real-time optimization. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher fixed costs due to limited scalability. | Lower operational costs via demand-responsive resources. |
| Response Time | Slower adjustments to supply chain disruptions. | Rapid adaptation to changes and emergencies. |
| Scalability | Limited by infrastructure and contracts. | Seamless expansion or contraction based on needs. |
| Customer Experience | Standardized delivery timelines. | Personalized, faster, and reliable services. |
Defining Logistics and Elastic Logistics
Logistics encompasses the systematic planning, implementation, and management of the efficient flow and storage of goods, services, and related information from origin to consumption. Elastic logistics integrates advanced technologies and dynamic resource allocation to adapt supply chain operations in real time, enhancing flexibility and responsiveness to fluctuating demand. This approach leverages cloud computing, AI, and IoT to optimize transportation routes, inventory levels, and delivery schedules for increased efficiency.
Key Differences Between Traditional and Elastic Logistics
Traditional logistics relies on fixed schedules, predetermined routes, and static warehousing, emphasizing cost-efficiency and predictability in transportation management. Elastic logistics incorporates real-time data, dynamic routing, and flexible resource allocation to rapidly adapt to demand fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. This approach leverages advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and cloud computing to optimize delivery speed, reduce inventory costs, and enhance overall operational agility.
Core Components of Conventional Logistics
Core components of conventional logistics encompass transportation, warehousing, inventory management, order fulfillment, and demand forecasting. These elements work together to ensure the efficient movement and storage of goods across supply chains. Conventional logistics relies heavily on static infrastructure and fixed operational procedures to maintain consistency and control.
The Rise of Elastic Logistics in Modern Supply Chains
The rise of elastic logistics in modern supply chains transforms traditional logistics by enabling real-time scalability and flexibility to meet fluctuating demand. This adaptive approach leverages advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, and cloud computing to optimize inventory management, transportation routes, and delivery schedules dynamically. Companies adopting elastic logistics experience improved responsiveness, cost-efficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction in complex global distribution networks.
Advantages of Elastic Logistics Over Traditional Models
Elastic logistics offers superior scalability and flexibility by dynamically adjusting resources based on real-time demand, reducing operational costs compared to traditional fixed-capacity logistics. It enhances supply chain resilience through adaptive routing and rapid response to disruptions, improving delivery speed and customer satisfaction. Integration with advanced technologies such as IoT and AI allows elastic logistics to optimize inventory management and fleet utilization more effectively than conventional models.
Technology’s Role in Elastic Logistics
Technology drives elastic logistics by enabling real-time data analytics, IoT integration, and AI-powered demand forecasting, which allow dynamic adjustment of supply chains to fluctuating market conditions. Unlike traditional logistics, elastic logistics leverages cloud-based platforms and machine learning algorithms to optimize resource allocation and improve responsiveness. This technological advancement enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and supports scalable, flexible transportation networks capable of adapting to sudden changes in demand.
Common Challenges in Implementing Elastic Logistics
Elastic logistics faces common challenges such as integrating advanced technology with existing supply chain systems, ensuring real-time data accuracy for dynamic resource allocation, and managing fluctuating demand while maintaining cost efficiency. The complexity of coordinating multiple stakeholders and adapting infrastructure quickly can result in operational delays and increased risk. Overcoming these barriers requires significant investment in digital platforms and workforce training to achieve the flexibility promised by elastic logistics models.
Impact on Cost Optimization and Efficiency
Logistics traditionally involves fixed routes and schedules, leading to predictable but often less flexible cost structures. Elastic logistics leverages real-time data and adaptive routing strategies, significantly enhancing cost optimization by minimizing idle time and reducing fuel consumption. The dynamic nature of elastic logistics improves operational efficiency by aligning supply chain activities with fluctuating demand patterns, leading to better resource utilization and lower overall transportation expenses.
Case Studies: Elastic Logistics in Action
Elastic logistics adapts to fluctuating demand by dynamically scaling resources, demonstrated in Amazon's warehouse operations where automation and AI optimize inventory flow during peak seasons. UPS leverages elastic logistics through real-time route adjustments and variable fleet deployment, enhancing delivery speed and reducing costs. These case studies highlight the efficiency of elastic logistics in managing supply chain complexity with increased flexibility and responsiveness.
The Future of Logistics: Trends and Predictions
The future of logistics centers on the integration of elastic logistics, which leverages real-time data and cloud computing to dynamically scale supply chain operations based on demand fluctuations, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs compared to traditional logistics models. Advanced AI algorithms and IoT devices enable predictive analytics, allowing companies to anticipate disruptions and optimize routing, inventory management, and delivery schedules with greater precision. This shift towards elastic logistics fosters increased flexibility, agility, and sustainability in transportation networks, positioning it as a key driver of innovation and competitive advantage in the evolving logistics landscape.
Related Important Terms
On-Demand Warehousing
On-demand warehousing revolutionizes traditional logistics by providing flexible storage solutions that scale dynamically with fluctuating demand, minimizing fixed costs and optimizing inventory management. Elastic logistics leverages real-time data and networked warehouse spaces to enhance supply chain agility, ensuring faster delivery and reduced lead times compared to conventional logistics models.
Dynamic Routing
Dynamic routing in traditional logistics relies on fixed schedules and predetermined routes, often resulting in inefficiencies and increased costs due to static planning. Elastic logistics employs real-time data and adaptive algorithms to optimize routes dynamically, improving delivery speed, reducing fuel consumption, and enhancing overall supply chain responsiveness.
Micro-Fulfillment
Micro-fulfillment centers enhance logistics efficiency by enabling faster, localized delivery through automated storage and retrieval systems, reducing transportation costs and last-mile challenges. Elastic logistics adapts dynamically to demand fluctuations by scaling micro-fulfillment resources in real-time, optimizing inventory distribution and improving supply chain responsiveness.
Real-Time Capacity Planning
Real-time capacity planning in logistics leverages data analytics and IoT sensors to optimize fleet utilization, reduce delays, and adapt swiftly to demand fluctuations. Elastic logistics enhances this by dynamically reallocating resources and routes using AI-driven insights, ensuring seamless scalability and cost-effective performance under variable conditions.
Scalability-as-a-Service
Scalability-as-a-Service in logistics enables dynamic adaptation of supply chain capacity based on real-time demand, contrasting traditional logistics with fixed infrastructure. Elastic logistics leverages cloud-based platforms and IoT integration to optimize resource allocation, reduce operational costs, and enhance responsiveness across transportation networks.
Adaptive Supply Chains
Elastic logistics transforms traditional supply chains by integrating real-time data analytics and IoT devices to enable adaptive responses to demand fluctuations and disruptions. Unlike standard logistics, it enhances supply chain resilience through dynamic resource allocation, predictive forecasting, and agile routing strategies.
Load Pooling
Load pooling in traditional logistics consolidates multiple shipments to optimize transportation efficiency and reduce costs by maximizing vehicle capacity. Elastic logistics enhances load pooling by dynamically adjusting routes and resources in real-time, leveraging advanced algorithms and data analytics to improve flexibility, reduce delivery times, and increase supply chain responsiveness.
Hyperlocal Distribution
Hyperlocal distribution enhances traditional logistics by leveraging elastic logistics frameworks that adapt dynamically to real-time demand fluctuations within localized areas, optimizing delivery routes and reducing transit times. This approach integrates advanced data analytics and flexible resource allocation to improve efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and customer satisfaction in last-mile transportation.
Just-in-Case Logistics
Just-in-case logistics relies on maintaining high inventory levels to buffer against supply chain disruptions, increasing storage and transportation costs. Elastic logistics adapts dynamically to fluctuations in demand and supply by leveraging real-time data and flexible transportation resources, reducing overhead and improving responsiveness.
Tech-Driven Fleet Flexing
Tech-driven fleet flexing in elastic logistics leverages real-time data analytics, IoT sensors, and AI algorithms to dynamically adjust transportation resources based on fluctuating demand and delivery requirements. This contrasts with traditional logistics, which relies on fixed schedules and static asset allocation, resulting in less operational agility and increased costs.
Logistics vs Elastic Logistics Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com