Logistics focuses on optimizing individual transport modes to improve efficiency and reduce costs within supply chains. Synchromodality integrates multiple transport modes dynamically, allowing real-time shifts based on demand, disruptions, or cost changes, enhancing flexibility and sustainability. This approach minimizes environmental impact while maximizing operational responsiveness and resource utilization.
Table of Comparison
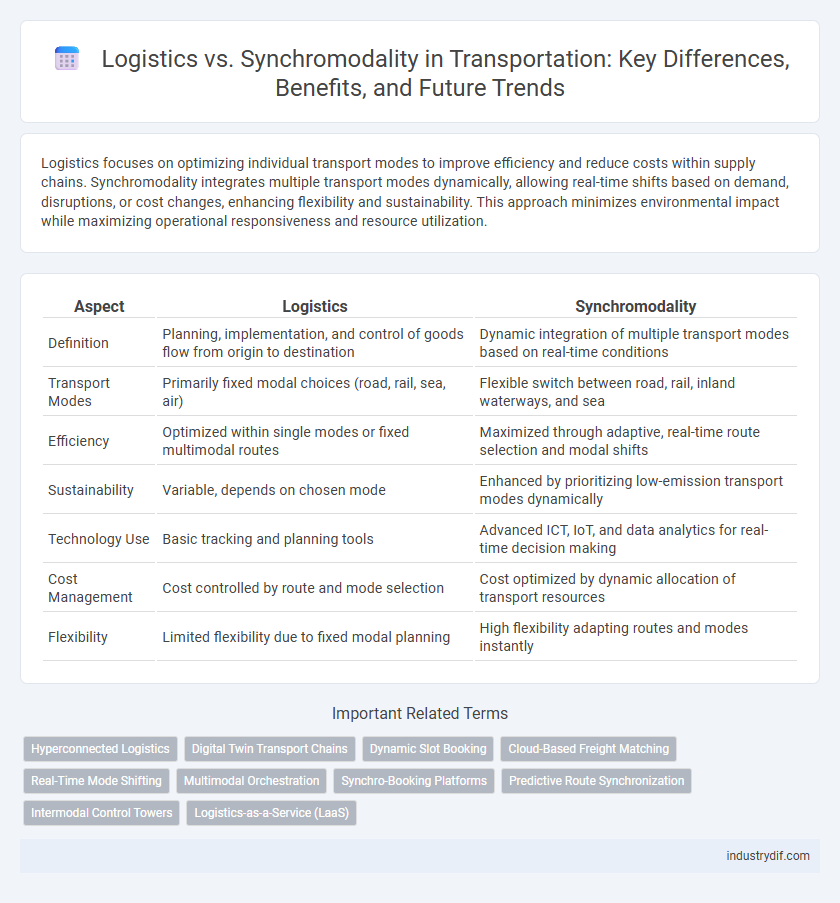
| Aspect | Logistics | Synchromodality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Planning, implementation, and control of goods flow from origin to destination | Dynamic integration of multiple transport modes based on real-time conditions |
| Transport Modes | Primarily fixed modal choices (road, rail, sea, air) | Flexible switch between road, rail, inland waterways, and sea |
| Efficiency | Optimized within single modes or fixed multimodal routes | Maximized through adaptive, real-time route selection and modal shifts |
| Sustainability | Variable, depends on chosen mode | Enhanced by prioritizing low-emission transport modes dynamically |
| Technology Use | Basic tracking and planning tools | Advanced ICT, IoT, and data analytics for real-time decision making |
| Cost Management | Cost controlled by route and mode selection | Cost optimized by dynamic allocation of transport resources |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility due to fixed modal planning | High flexibility adapting routes and modes instantly |
Understanding Logistics: Key Concepts and Functions
Logistics encompasses the planning, implementation, and control of efficient transportation and storage of goods from origin to consumption to meet customer requirements. Key functions include inventory management, order fulfillment, warehousing, and transportation coordination, which optimize supply chain performance and reduce operational costs. Understanding these core logistics components is essential for designing effective distribution networks and ensuring seamless delivery in global trade.
What is Synchromodality? A Modern Approach Explained
Synchromodality is a modern logistics strategy that integrates multiple transport modes, such as rail, road, and waterways, into a dynamic, real-time network to optimize efficiency and sustainability. It enables flexible, data-driven decision-making to shift cargo seamlessly between modes based on current conditions, reducing delays and minimizing costs. This approach enhances supply chain resilience and environmental performance by leveraging digital technologies and collaborative planning.
Core Differences: Logistics vs Synchromodality
Logistics primarily involves planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient movement and storage of goods from origin to destination, focusing on cost-efficiency and reliability. Synchromodality emphasizes real-time coordination across multiple transport modes, enhancing flexibility and responsiveness by dynamically switching between options based on current conditions and demand. The core difference lies in logistics' fixed routing strategies versus synchromodality's adaptive, integrated approach to multimodal transport networks.
Benefits of Traditional Logistics Management
Traditional logistics management offers reliable scheduling and consistent control over supply chain processes, ensuring timely deliveries and minimizing disruptions. It enables companies to optimize inventory levels and improve cost efficiency through well-established transportation routes and partnerships. This approach also provides transparency and accountability, enhancing customer satisfaction and operational predictability.
Advantages of Synchromodal Transport Solutions
Synchromodal transport solutions enhance supply chain flexibility by enabling real-time switching between transport modes such as rail, road, and inland waterways. This dynamic approach reduces transit times and carbon emissions while optimizing resource utilization and costs. Advanced digital platforms and data analytics drive synchromodality, improving transparency and responsiveness compared to traditional logistics models.
Integration of Digital Technologies in Both Models
Logistics increasingly relies on advanced digital technologies such as AI, IoT, and blockchain to optimize supply chain visibility, automate processes, and improve real-time decision-making. Synchromodality integrates digital platforms to enable dynamic, real-time coordination of multiple transport modes, enhancing flexibility, efficiency, and sustainability in freight movement. Both models leverage digital innovation, but synchromodality uniquely focuses on seamless modal switching through real-time data integration and collaborative communication among stakeholders.
Flexibility and Real-Time Adaptation in Synchromodality
Synchromodality offers superior flexibility and real-time adaptation compared to traditional logistics by seamlessly integrating multiple transportation modes through advanced digital platforms. This dynamic approach enables instant rerouting and resource allocation based on live data, reducing delays and optimizing network efficiency. Consequently, synchromodal systems enhance supply chain responsiveness and sustainability in fluctuating market conditions.
Environmental Impact: Comparing Sustainability Outcomes
Logistics traditionally relies on single-mode transportation methods, often leading to higher carbon emissions and resource consumption due to less efficient routing and load optimization. Synchromodality enhances environmental sustainability by dynamically integrating multiple transport modes like rail, road, and waterways, reducing greenhouse gas emissions through optimized energy usage and decreased dependency on fossil fuels. This coordinated approach promotes lower environmental impact by maximizing load factors and minimizing empty runs, supporting the transition to greener supply chains.
Cost Efficiency: Logistics versus Synchromodal Systems
Logistics systems traditionally rely on fixed transport modes and routes, often leading to higher costs due to underutilized capacity and inflexible scheduling. Synchromodal systems enhance cost efficiency by dynamically selecting the most economical combination of transport modes based on real-time data and demand, reducing empty runs and optimizing load factors. This flexibility in synchromodality minimizes transportation expenses and environmental impact while improving overall supply chain responsiveness.
Future Trends: The Evolution from Logistics to Synchromodality
Future trends in transportation highlight a significant evolution from traditional logistics, characterized by siloed, mode-specific operations, to synchromodality, which emphasizes real-time coordination and integration of multiple transport modes for optimal efficiency. Synchromodality leverages advanced digital platforms, IoT, and AI technologies to enable dynamic routing, enhanced asset utilization, and reduced environmental impact. This shift supports sustainable supply chains by fostering flexibility, resilience, and the ability to respond swiftly to demand fluctuations and disruptions.
Related Important Terms
Hyperconnected Logistics
Hyperconnected logistics leverages advanced digital technologies to integrate various transportation modes seamlessly, enabling real-time data exchange and dynamic route optimization. Unlike traditional logistics, synchromodality emphasizes flexible, demand-driven multimodal transport solutions that reduce costs and environmental impact by synchronizing shipments across rail, road, and waterways.
Digital Twin Transport Chains
Digital Twin Transport Chains enhance logistic operations by creating real-time, virtual replicas of physical transport networks, enabling dynamic optimization and predictive analytics. Synchromodality leverages these digital twins to seamlessly integrate multiple transport modes, improving flexibility and efficiency in supply chain management.
Dynamic Slot Booking
Dynamic slot booking enhances logistics efficiency by enabling real-time allocation and adjustment of transport slots based on demand fluctuations, reducing idle times and congestion. Synchromodality integrates this with seamless mode transfers, optimizing resource use and improving overall supply chain responsiveness.
Cloud-Based Freight Matching
Cloud-based freight matching enhances logistics efficiency by leveraging real-time data integration and algorithmic route optimization, reducing empty miles and improving load consolidation. Synchromodality complements this by dynamically switching between transportation modes through a unified digital platform, further optimizing supply chain flexibility and sustainability.
Real-Time Mode Shifting
Real-time mode shifting in logistics leverages advanced data analytics and IoT to optimize transport routes by dynamically switching between different transport modes, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs. Synchromodality integrates this approach by enabling seamless coordination among multiple carriers and modes, ensuring real-time responsiveness and maximizing resource utilization across the supply chain.
Multimodal Orchestration
Logistics involves managing the flow of goods through multiple transportation modes, while synchromodality optimizes this process by dynamically adapting routes and modes in real-time based on efficiency and availability. Multimodal orchestration integrates various transport options seamlessly, enhancing flexibility, reducing costs, and improving delivery reliability in complex supply chains.
Synchro-Booking Platforms
Synchro-booking platforms enable dynamic coordination across multiple transport modes, optimizing capacity utilization and reducing transit times in synchromodality systems. These platforms leverage real-time data and advanced algorithms to synchronize shipments, enhancing flexibility and efficiency compared to traditional logistics approaches.
Predictive Route Synchronization
Predictive route synchronization in logistics leverages real-time data analytics and AI to optimize delivery schedules, reducing transit times and costs by anticipating route disruptions and demand fluctuations. Synchromodality enhances this approach by integrating multiple transport modes into a single, adaptive network, enabling dynamic rerouting and resource allocation for maximal efficiency and sustainability.
Intermodal Control Towers
Intermodal Control Towers enhance logistics efficiency by integrating real-time data across multiple transport modes, enabling synchronized decision-making and optimized cargo movement. Synchromodality leverages these control towers to dynamically shift freight routes and modes based on capacity, cost, and environmental impact, promoting flexible, demand-driven supply chain management.
Logistics-as-a-Service (LaaS)
Logistics-as-a-Service (LaaS) transforms traditional logistics by integrating cloud-based platforms to enable real-time, flexible transportation resource allocation, enhancing efficiency and responsiveness compared to conventional models. Synchromodality leverages dynamic, multimodal transport options within a LaaS framework, optimizing supply chains through seamless transitions between modes while minimizing costs and environmental impact.
Logistics vs Synchromodality Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com