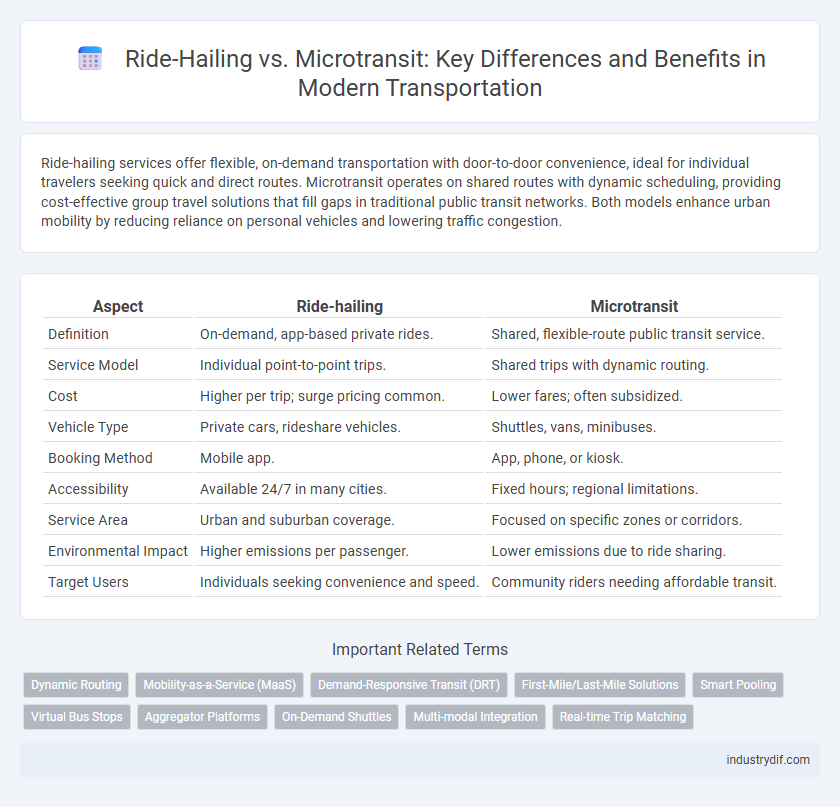
Ride-hailing services offer flexible, on-demand transportation with door-to-door convenience, ideal for individual travelers seeking quick and direct routes. Microtransit operates on shared routes with dynamic scheduling, providing cost-effective group travel solutions that fill gaps in traditional public transit networks. Both models enhance urban mobility by reducing reliance on personal vehicles and lowering traffic congestion.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Ride-hailing | Microtransit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | On-demand, app-based private rides. | Shared, flexible-route public transit service. |
| Service Model | Individual point-to-point trips. | Shared trips with dynamic routing. |
| Cost | Higher per trip; surge pricing common. | Lower fares; often subsidized. |
| Vehicle Type | Private cars, rideshare vehicles. | Shuttles, vans, minibuses. |
| Booking Method | Mobile app. | App, phone, or kiosk. |
| Accessibility | Available 24/7 in many cities. | Fixed hours; regional limitations. |
| Service Area | Urban and suburban coverage. | Focused on specific zones or corridors. |
| Environmental Impact | Higher emissions per passenger. | Lower emissions due to ride sharing. |
| Target Users | Individuals seeking convenience and speed. | Community riders needing affordable transit. |
Understanding Ride-Hailing and Microtransit
Ride-hailing services like Uber and Lyft offer on-demand, app-based individual rides, providing flexible point-to-point transportation tailored to user schedules. Microtransit utilizes smaller vehicles operating on shared routes with dynamic scheduling to bridge the gap between fixed-route transit and ride-hailing, optimizing efficiency and coverage in urban and suburban areas. Both models leverage technology for real-time booking and routing, but microtransit emphasizes shared trips and fixed service zones to reduce operational costs and congestion.
Key Differences in Service Models
Ride-hailing services utilize on-demand, point-to-point transportation with dynamic routing and individual vehicle assignments, offering flexible door-to-door trips. Microtransit operates on fixed routes or zones with shared vehicles, emphasizing scheduled or semi-flexible stops to optimize capacity and reduce costs. Key differences include ride-hailing's personalized, real-time booking and microtransit's collective, route-based system designed for efficiency and scalability.
Technology Platforms and User Experience
Ride-hailing platforms leverage advanced GPS algorithms and mobile app integrations to provide on-demand, door-to-door service with personalized routing and real-time driver tracking. Microtransit systems utilize dynamic routing software and shared-vehicle technologies to optimize routes based on demand patterns, enhancing efficiency and reducing wait times for multiple passengers. Both technologies prioritize user experience by offering seamless booking interfaces, cashless payment options, and real-time updates, but ride-hailing emphasizes individual convenience while microtransit focuses on collective efficiency.
Fleet Composition and Vehicle Types
Ride-hailing services primarily utilize a diverse fleet of standard passenger vehicles, including sedans, SUVs, and electric cars, optimized for individual or small-group trips with flexible route planning. Microtransit systems employ larger capacity vehicles such as shuttles, minibuses, or vans designed for shared rides along fixed or semi-fixed routes, emphasizing efficiency and reduced operational costs. Fleet composition in microtransit often prioritizes vehicles with higher passenger capacity and accessibility features to serve multiple riders simultaneously, contrasting with the mostly single-passenger focus in ride-hailing fleets.
Pricing Structures and Affordability
Ride-hailing services typically use dynamic pricing models that adjust fares based on demand, distance, and time, often resulting in higher costs during peak hours. Microtransit offers more predictable and fixed pricing structures, enabling consistent affordability for regular commuters by integrating shared rides on designated routes. Affordability in microtransit is enhanced through subsidies and bulk-purchase options, making it a cost-effective alternative for group travel compared to the variable expenses of ride-hailing.
Scalability and Urban Integration
Ride-hailing services offer flexible, on-demand transportation with high scalability due to app-based dispatch and dynamic routing, enabling rapid expansion across urban areas. Microtransit systems blend fixed-route and demand-responsive transit, providing efficient urban integration by serving transit deserts and complementing existing public transport networks. Both models address scalability and integration differently, with ride-hailing focusing on individual convenience and microtransit enhancing collective urban mobility.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Ride-hailing services generate higher carbon emissions per passenger mile compared to microtransit due to lower vehicle occupancy rates and frequent empty trips. Microtransit systems, often utilizing shared routes and electric or low-emission vehicles, reduce overall environmental footprints by maximizing passenger capacity and minimizing congestion. Studies indicate microtransit can cut greenhouse gas emissions by up to 30% compared to traditional ride-hailing options in urban settings.
Regulatory Challenges and Policies
Ride-hailing services face regulatory challenges related to licensing, insurance requirements, and driver background checks, often resulting in conflicts with traditional taxi regulations. Microtransit systems require policies that integrate with public transit infrastructure, addressing issues such as route planning, fare integration, and data sharing to ensure operational efficiency and equity. Both models must navigate evolving privacy laws and safety standards while complying with local and regional transportation policies to promote sustainable urban mobility.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Ride-hailing services offer personalized, on-demand transportation but often lack affordability and accessibility for low-income or disabled passengers. Microtransit systems, utilizing shared vehicles on flexible routes, enhance inclusivity by providing wheelchair-accessible options and reduced fares for underserved communities. Integrating microtransit with public transit networks promotes equitable access and addresses mobility gaps in urban areas.
Future Trends in Urban Mobility
Ride-hailing services continue to expand with real-time data integration and AI-driven route optimization, enhancing personalized urban travel experiences. Microtransit is gaining traction through on-demand shared rides and flexible routing, effectively reducing congestion and emissions in densely populated cities. Future trends emphasize seamless multimodal integration, electric vehicle adoption, and smart infrastructure to create sustainable, efficient urban mobility ecosystems.
Related Important Terms
Dynamic Routing
Dynamic routing in ride-hailing services leverages real-time GPS data and demand patterns to optimize individual passenger pickups and drop-offs, enhancing efficiency and reducing wait times. In contrast, microtransit employs dynamic routing algorithms that adjust shared vehicle routes based on aggregated passenger requests, balancing flexibility with cost-effectiveness to serve multiple users simultaneously.
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS)
Ride-hailing services like Uber and Lyft provide on-demand, personalized transport solutions, while microtransit offers shared, flexible routes that bridge gaps in public transit networks. Integrating both within a Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) platform enhances urban mobility by optimizing route efficiency, reducing wait times, and promoting sustainable transportation options.
Demand-Responsive Transit (DRT)
Demand-Responsive Transit (DRT) offers a flexible, shared ride option that dynamically routes vehicles based on real-time passenger demand, contrasting with ride-hailing services where individual trips are directly requested and priced per ride. DRT systems optimize urban mobility by reducing congestion and operational costs through pooled transportation, enhancing accessibility in areas underserved by traditional fixed-route transit.
First-Mile/Last-Mile Solutions
Ride-hailing services provide flexible first-mile/last-mile transportation by connecting users directly to transit hubs, enhancing overall network accessibility with on-demand curb-to-curb options. Microtransit complements this by offering shared, fixed-route or dynamic shuttles that efficiently serve dense urban areas, reducing costs and congestion while bridging gaps within public transit systems.
Smart Pooling
Smart pooling technology enhances ride-hailing services by optimizing route matching and passenger grouping, thereby reducing travel time and operational costs compared to traditional microtransit systems. This approach leverages real-time data analytics and dynamic routing algorithms to improve efficiency and environmental sustainability in urban transportation networks.
Virtual Bus Stops
Virtual bus stops in ride-hailing platforms offer flexible, on-demand pick-up and drop-off locations, enhancing convenience compared to traditional microtransit fixed stops. By dynamically adjusting pick-up points using real-time data, virtual stops reduce waiting times and optimize route efficiency, improving overall passenger experience and operational costs.
Aggregator Platforms
Aggregator platforms in ride-hailing streamline user access to a diverse range of private drivers through real-time matching algorithms, enhancing efficiency and convenience. In contrast, microtransit aggregators coordinate shared, fixed-route or flexible-schedule services, optimizing capacity utilization and reducing urban congestion by integrating first- and last-mile connectivity.
On-Demand Shuttles
On-demand shuttles in microtransit offer dynamic routing and scheduling tailored to passenger demand, reducing wait times and optimizing vehicle occupancy compared to traditional ride-hailing services, which primarily focus on individual point-to-point trips. This approach enhances urban mobility efficiency by integrating multiple passengers into a shared vehicle, lowering per-trip emissions and traffic congestion while maintaining flexibility.
Multi-modal Integration
Ride-hailing services offer flexible, on-demand transport but often lack seamless integration with other transit modes, whereas microtransit systems prioritize multi-modal connectivity by coordinating fixed-route services with shared rides and last-mile solutions. Effective multi-modal integration enhances urban mobility by enabling smoother transfers between ride-hailing, buses, subways, and bike-sharing networks, reducing congestion and improving overall transit efficiency.
Real-time Trip Matching
Real-time trip matching in ride-hailing leverages advanced algorithms and GPS data to connect passengers with nearby drivers instantly, minimizing wait times and optimizing routes. Microtransit systems employ dynamic routing technology that aggregates multiple passengers traveling along similar paths, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing per-trip costs.
Ride-hailing vs Microtransit Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com