Route optimization uses predetermined data to plan the most efficient paths before trips begin, minimizing travel time and fuel consumption. Dynamic routing adapts routes in real-time based on current traffic conditions, accidents, or delays, improving flexibility and responsiveness. Combining both approaches enhances overall transportation efficiency by balancing planned efficiency with real-time adjustments.
Table of Comparison
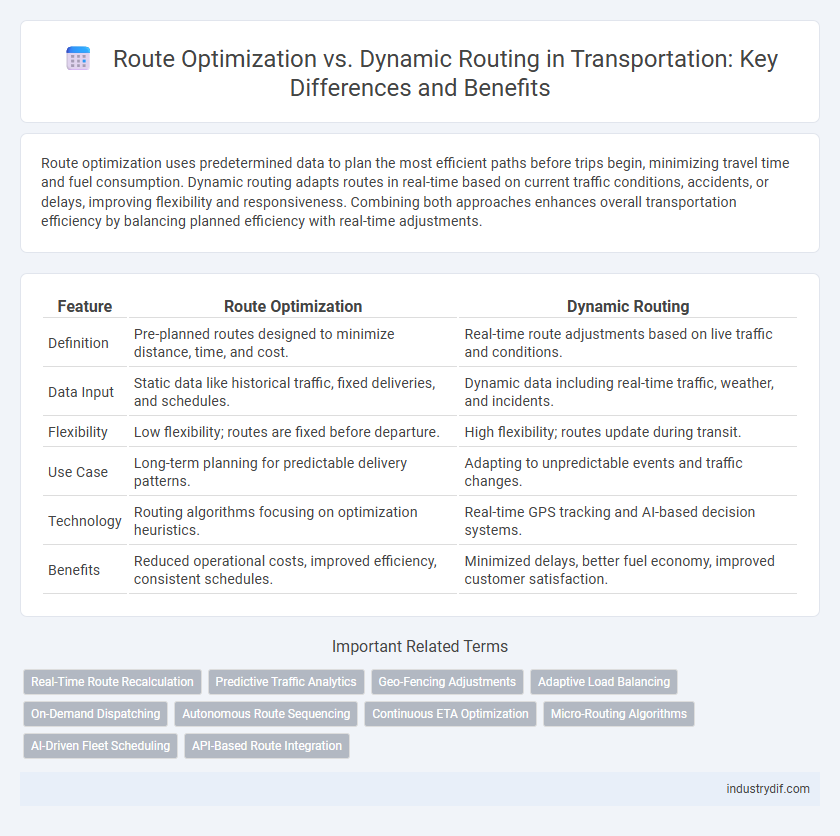
| Feature | Route Optimization | Dynamic Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-planned routes designed to minimize distance, time, and cost. | Real-time route adjustments based on live traffic and conditions. |
| Data Input | Static data like historical traffic, fixed deliveries, and schedules. | Dynamic data including real-time traffic, weather, and incidents. |
| Flexibility | Low flexibility; routes are fixed before departure. | High flexibility; routes update during transit. |
| Use Case | Long-term planning for predictable delivery patterns. | Adapting to unpredictable events and traffic changes. |
| Technology | Routing algorithms focusing on optimization heuristics. | Real-time GPS tracking and AI-based decision systems. |
| Benefits | Reduced operational costs, improved efficiency, consistent schedules. | Minimized delays, better fuel economy, improved customer satisfaction. |
Understanding Route Optimization in Transportation
Route optimization in transportation uses algorithms to determine the most efficient paths for vehicles, minimizing travel time, fuel consumption, and operational costs. It typically involves fixed routes scheduled in advance based on historical traffic data, delivery windows, and vehicle capacity. This approach contrasts with dynamic routing, which adjusts routes in real-time based on current traffic conditions and unexpected events.
What is Dynamic Routing?
Dynamic routing refers to real-time adjustment of transportation routes based on current traffic conditions, demand fluctuations, and unforeseen events to enhance delivery efficiency and reduce travel time. It leverages GPS data, traffic analytics, and machine learning algorithms to continuously update the optimal path for vehicles. This approach contrasts with static route optimization by enabling flexibility and responsiveness in complex and changing transportation networks.
Key Differences Between Route Optimization and Dynamic Routing
Route optimization computes the most efficient path before the trip, prioritizing factors like distance, traffic, and delivery windows to minimize cost and time. Dynamic routing adapts routes in real-time based on current conditions such as traffic congestion, accidents, and last-minute orders, enhancing flexibility and responsiveness. Key differences include pre-planned efficiency in route optimization versus on-the-fly adjustments inherent in dynamic routing, affecting operational agility and customer satisfaction.
Benefits of Route Optimization for Fleet Management
Route optimization enhances fleet management by reducing fuel consumption and minimizing delivery times through efficient route planning. It improves vehicle utilization and decreases maintenance costs by preventing unnecessary mileage and wear. These benefits lead to increased operational efficiency and higher customer satisfaction in transportation logistics.
Advantages of Dynamic Routing in Real-Time Scenarios
Dynamic routing enhances transportation efficiency by adapting routes in real-time based on current traffic conditions, weather updates, and unexpected road closures, reducing delays and fuel consumption. Unlike static route optimization, dynamic routing supports rapid decision-making, enabling fleets to respond promptly to changing circumstances and improve delivery accuracy. This real-time flexibility leads to better resource allocation, increased customer satisfaction, and lowered operational costs in logistics and transportation networks.
Technology Driving Route Optimization and Dynamic Routing
Advanced GPS technology and real-time data analytics drive route optimization by calculating the most efficient paths based on traffic patterns, road conditions, and delivery time windows. Dynamic routing leverages AI and machine learning algorithms to continuously adapt routes in response to changing conditions such as traffic congestion, accidents, or new service requests. Integration of IoT devices and cloud-based platforms enables seamless communication between vehicles and control centers, enhancing both route optimization and dynamic routing capabilities.
Cost Implications: Route Optimization vs Dynamic Routing
Route optimization leverages historical data and fixed parameters to minimize fuel consumption and labor costs through efficient pre-planned routes, resulting in predictable expenses and improved asset utilization. Dynamic routing adapts in real-time to traffic conditions, delivery windows, and unexpected disruptions, often increasing operational flexibility but potentially raising fuel and labor costs due to route variability. Businesses must weigh the lower, stable costs of route optimization against the potentially higher, fluctuating expenses of dynamic routing based on their delivery volume and service requirements.
Impact on Customer Satisfaction
Route optimization improves customer satisfaction by minimizing delivery times and ensuring consistent arrival windows through efficient pre-planned routes. Dynamic routing enhances responsiveness by adapting routes in real-time to avoid delays and address last-minute changes, leading to increased delivery reliability. Together, these approaches reduce wait times and improve overall service quality, directly boosting customer satisfaction in transportation.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Route optimization faces challenges such as static data reliance and limited adaptability to real-time conditions, requiring integration of advanced algorithms and real-time traffic data to improve accuracy. Dynamic routing demands robust, scalable systems capable of processing continuous data streams and adjusting routes instantly, necessitating investment in IoT sensors, machine learning models, and cloud computing infrastructure. Both methods benefit from hybrid approaches combining pre-planned routes with dynamic adjustments to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Future Trends in Transportation Routing Technologies
Route optimization leverages advanced algorithms and historical data to calculate the most efficient paths, reducing fuel consumption and delivery times. Dynamic routing integrates real-time traffic, weather, and demand fluctuations to adapt routes instantly, improving responsiveness and customer satisfaction. Future trends emphasize AI-driven predictive analytics and IoT connectivity, enabling hybrid systems that combine static optimization with real-time dynamic adjustments for maximal operational efficiency.
Related Important Terms
Real-Time Route Recalculation
Route optimization uses pre-planned algorithms to determine the most efficient path based on historical data and static variables, while dynamic routing continuously recalculates routes in real-time using live traffic, weather, and road condition updates to adapt to changing circumstances instantly. Real-time route recalculation enhances delivery speed, reduces fuel consumption, and improves overall fleet efficiency by responding immediately to unforeseen disruptions like accidents or traffic congestion.
Predictive Traffic Analytics
Route optimization leverages historical traffic data and fixed algorithms to determine the most efficient paths, while dynamic routing incorporates real-time predictive traffic analytics to adjust routes on-the-fly, minimizing delays and improving delivery accuracy. Predictive traffic models analyze patterns such as congestion trends, weather conditions, and incident reports to forecast traffic flow, enabling dynamic systems to proactively reroute vehicles for optimal travel times.
Geo-Fencing Adjustments
Route optimization enhances delivery efficiency by pre-planning the most efficient paths based on static geographic constraints, whereas dynamic routing adjusts routes in real-time using geo-fencing technology to respond to traffic changes, road closures, and delivery priorities. Geo-fencing adjustments enable automatic rerouting within defined virtual boundaries, improving responsiveness and reducing delays in transportation logistics.
Adaptive Load Balancing
Route optimization enhances transportation efficiency by pre-planning the most cost-effective paths based on static data, while dynamic routing employs real-time traffic and load conditions to adaptively balance vehicle assignments and avoid congestion. Adaptive load balancing in dynamic routing leverages live analytics to distribute transportation resources evenly, reducing delays and maximizing fleet utilization.
On-Demand Dispatching
Route optimization leverages algorithms to calculate the most efficient fixed paths based on historical data and predefined stops, minimizing fuel consumption and travel time. Dynamic routing adapts in real-time to traffic conditions and new requests, enabling on-demand dispatching that enhances fleet responsiveness and reduces customer wait times.
Autonomous Route Sequencing
Autonomous route sequencing leverages real-time data and AI algorithms to dynamically adjust delivery paths, enhancing efficiency beyond traditional route optimization methods that rely on static, pre-planned routes. This technology reduces travel time, fuel consumption, and operational costs by continuously recalibrating routes based on traffic conditions, vehicle status, and delivery priorities.
Continuous ETA Optimization
Route optimization focuses on planning the most efficient paths before trips begin, minimizing distance and time based on static data. Dynamic routing continuously updates Estimated Time of Arrival (ETA) by incorporating real-time traffic, road conditions, and delivery changes, ensuring adaptive and precise delivery schedules.
Micro-Routing Algorithms
Micro-routing algorithms enhance route optimization by using real-time data to dynamically adjust delivery paths at a granular level, improving efficiency and reducing travel time. Unlike static route optimization, dynamic routing leverages these algorithms to respond instantly to traffic conditions, delivery windows, and vehicle capacities, maximizing operational productivity.
AI-Driven Fleet Scheduling
AI-driven fleet scheduling enhances route optimization by leveraging real-time data and predictive analytics to minimize travel time and fuel consumption, while dynamic routing adapts instantly to changing traffic conditions and unforeseen disruptions, ensuring efficient delivery and improved customer satisfaction. Integrating machine learning algorithms into both strategies enables fleets to achieve superior operational efficiency, reduce costs, and maintain high service reliability in transportation networks.
API-Based Route Integration
API-based route integration enables dynamic routing by providing real-time data inputs such as traffic conditions, weather updates, and delivery priorities, which enhance route optimization algorithms. Unlike static route optimization, dynamic routing APIs adjust routes on-the-fly to improve efficiency, reduce fuel consumption, and increase on-time deliveries in transportation management systems.
Route Optimization vs Dynamic Routing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com