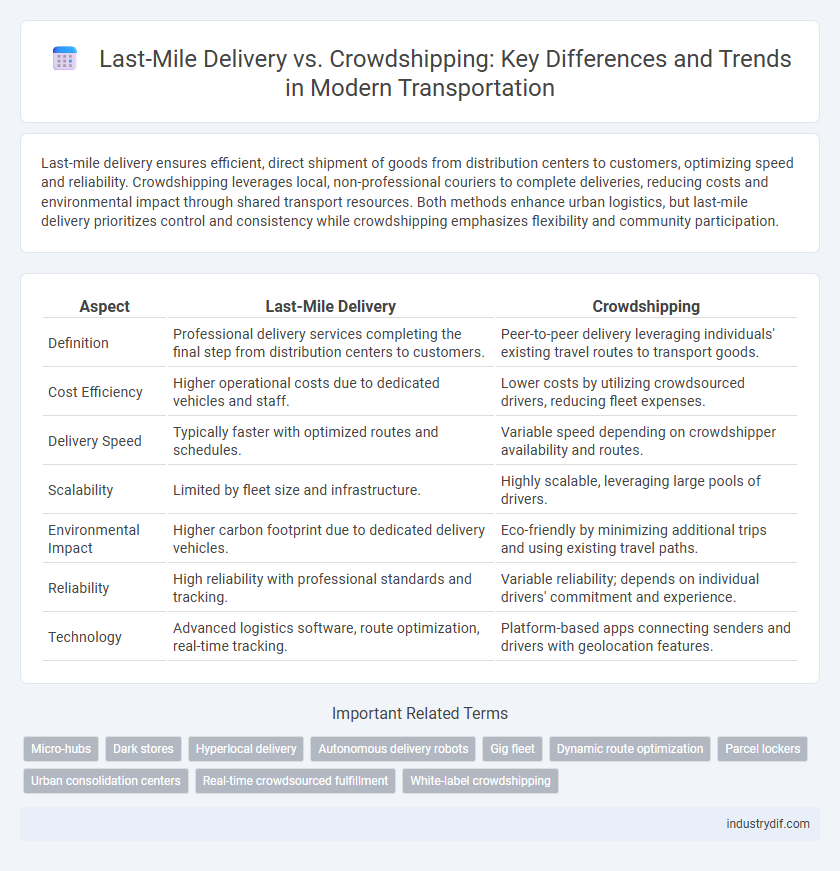
Last-mile delivery ensures efficient, direct shipment of goods from distribution centers to customers, optimizing speed and reliability. Crowdshipping leverages local, non-professional couriers to complete deliveries, reducing costs and environmental impact through shared transport resources. Both methods enhance urban logistics, but last-mile delivery prioritizes control and consistency while crowdshipping emphasizes flexibility and community participation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Last-Mile Delivery | Crowdshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Professional delivery services completing the final step from distribution centers to customers. | Peer-to-peer delivery leveraging individuals' existing travel routes to transport goods. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher operational costs due to dedicated vehicles and staff. | Lower costs by utilizing crowdsourced drivers, reducing fleet expenses. |
| Delivery Speed | Typically faster with optimized routes and schedules. | Variable speed depending on crowdshipper availability and routes. |
| Scalability | Limited by fleet size and infrastructure. | Highly scalable, leveraging large pools of drivers. |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint due to dedicated delivery vehicles. | Eco-friendly by minimizing additional trips and using existing travel paths. |
| Reliability | High reliability with professional standards and tracking. | Variable reliability; depends on individual drivers' commitment and experience. |
| Technology | Advanced logistics software, route optimization, real-time tracking. | Platform-based apps connecting senders and drivers with geolocation features. |
Defining Last-Mile Delivery and Crowdshipping
Last-mile delivery refers to the final step of the transportation process where goods are moved from a distribution hub to the end customer's location, emphasizing speed and efficiency in urban or suburban areas. Crowdshipping leverages a network of independent individuals who use their personal vehicles to deliver packages, offering flexible and cost-effective alternatives to traditional logistics. Both methods aim to optimize delivery performance but differ in their operational models and scalability.
Evolution of Urban Logistics
Last-mile delivery has evolved significantly with the rise of e-commerce, prioritizing speed, efficiency, and customer convenience in dense urban areas. Crowdshipping introduces a decentralized model leveraging local travelers and commuters to reduce delivery costs and environmental impact. This evolution in urban logistics fosters smarter, more sustainable distribution networks by integrating technology and collaborative economies.
Key Players in Last-Mile Delivery
Key players in last-mile delivery include global logistics giants such as DHL, FedEx, UPS, and Amazon Logistics, leveraging extensive networks and advanced technology to ensure fast and reliable parcel delivery. Emerging regional carriers and specialized startups focus on niche markets and urban centers, integrating electric vehicles and autonomous delivery systems to enhance efficiency. These companies compete by optimizing route planning, real-time tracking, and customer service, shaping the future landscape of last-mile delivery across metropolitan areas.
How Crowdshipping Platforms Operate
Crowdshipping platforms operate by leveraging a network of everyday commuters and travelers to deliver packages during their regular routes, optimizing existing travel patterns for efficient last-mile delivery. These platforms use real-time data and mobile applications to match senders with nearby crowdshippers, ensuring flexible and cost-effective parcel transit without traditional delivery infrastructure. By decentralizing delivery tasks, crowdshipping reduces logistical costs, environmental impact, and delivery times in urban and suburban areas.
Technology Driving Last-Mile Solutions
Advanced GPS tracking and route optimization algorithms significantly boost the efficiency of last-mile delivery by reducing transit times and fuel consumption. Crowdshipping leverages mobile app platforms to connect local couriers with nearby delivery requests, enhancing flexibility and scalability in dense urban areas. Integration of IoT devices and real-time data analytics enables dynamic rerouting and proactive issue detection, further refining last-mile logistics performance.
Cost Efficiency: Last-Mile vs Crowdshipping
Last-mile delivery often incurs higher costs due to dedicated logistics networks and fixed vehicle expenses, whereas crowdshipping leverages existing passenger trips to reduce last-mile expenditures significantly. Cost efficiency in last-mile delivery drops with increased urban congestion and fuel consumption, while crowdshipping utilizes decentralized, flexible routes that minimize operational overhead. Studies show crowdshipping can lower delivery costs by up to 30%, making it an attractive option for cost-sensitive e-commerce businesses.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Last-mile delivery and crowdshipping differ significantly in environmental impact, with crowdshipping typically reducing carbon emissions by leveraging existing passenger trips for parcel transport, thus minimizing additional vehicle use. Traditional last-mile delivery often relies on dedicated delivery vans, contributing to higher fuel consumption and increased air pollution in urban areas. An environmental impact assessment highlights that integrating crowdshipping can substantially lower greenhouse gas emissions by optimizing route efficiency and decreasing traffic congestion.
Customer Experience and Service Levels
Last-mile delivery focuses on reliable, timely shipments directly to customers, ensuring precise tracking and professional handling, which enhances customer satisfaction and trust. Crowdshipping leverages local, peer-to-peer networks to offer flexible, often faster delivery options, but may vary in service consistency and reliability. Both models strive to improve customer experience, with last-mile delivery excelling in standardized service levels and crowdshipping creating personalized, community-driven interactions.
Challenges and Limitations in Each Model
Last-mile delivery often faces challenges such as high operational costs, traffic congestion, and inefficient route planning, which contribute to delayed shipments and increased carbon emissions. Crowdshipping encounters limitations including variable service reliability, trust and security concerns, and inconsistent delivery times due to dependence on non-professional couriers. Both models struggle with scalability and maintaining customer satisfaction while balancing cost-efficiency and sustainability objectives in urban logistics.
Future Trends in Urban Delivery Logistics
Last-mile delivery is evolving through the integration of smart lockers, autonomous vehicles, and drone technology, enhancing efficiency and reducing urban congestion. Crowdshipping leverages local commuters and gig economy workers to create decentralized, flexible networks that optimize delivery speed and cost-effectiveness in densely populated areas. Future urban delivery logistics will increasingly combine these innovations, supported by AI-driven route optimization and real-time data analytics to meet growing e-commerce demands sustainably.
Related Important Terms
Micro-hubs
Last-mile delivery efficiency is significantly enhanced by the integration of micro-hubs, which serve as localized distribution points reducing transit times and urban congestion. Crowdshipping leverages these micro-hubs by enabling peer-to-peer parcel drop-offs and pickups, optimizing route flexibility and lowering last-mile costs through decentralized delivery networks.
Dark stores
Last-mile delivery leverages strategically located dark stores to expedite order fulfillment by serving as localized distribution hubs, reducing delivery times and enhancing inventory management efficiency. Crowdshipping integrates local couriers through digital platforms, enabling flexible last-mile solutions that capitalize on community-based networks while dark stores optimize stock accessibility and support rapid dispatch.
Hyperlocal delivery
Last-mile delivery optimizes hyperlocal transportation by minimizing transit time and costs through centralized logistics hubs and professional couriers. Crowdshipping leverages local community members as delivery agents, enhancing flexibility and scalability in hyperlocal delivery networks while reducing environmental impact.
Autonomous delivery robots
Autonomous delivery robots revolutionize last-mile delivery by providing efficient, contactless service that reduces operational costs and environmental impact. Crowdshipping leverages local couriers but faces scalability challenges, whereas autonomous robots ensure consistent performance and real-time route optimization for urban logistics.
Gig fleet
Last-mile delivery relies on dedicated gig fleets that ensure timely parcel drop-offs within urban areas, leveraging optimized routing and real-time tracking for efficiency. Crowdshipping, utilizing decentralized gig workers through peer-to-peer logistics platforms, enhances flexibility and reduces operational costs by tapping into existing travel routes and available capacity.
Dynamic route optimization
Dynamic route optimization leverages real-time data and machine learning algorithms to enhance efficiency in last-mile delivery by continuously adjusting routes based on traffic, delivery windows, and vehicle capacity. Crowdshipping further amplifies the benefits of dynamic routing by utilizing a decentralized network of local travelers who can adapt routes flexibly, reducing delivery times and costs while increasing scalability and sustainability.
Parcel lockers
Parcel lockers streamline last-mile delivery by providing secure, self-service locations that reduce failed delivery attempts and increase efficiency in urban areas. Crowdshipping leverages local couriers who use parcel lockers as convenient drop-off and pick-up points, enabling faster and more flexible delivery options while minimizing traffic congestion.
Urban consolidation centers
Urban consolidation centers streamline last-mile delivery by centralizing goods for efficient distribution, reducing traffic congestion and emissions in dense city areas. Crowdshipping leverages local commuters for flexible parcel handoffs but often lacks the structured coordination and environmental benefits provided by urban consolidation centers.
Real-time crowdsourced fulfillment
Last-mile delivery leverages dedicated logistics networks to ensure timely parcel arrival, while crowdshipping utilizes real-time crowdsourced fulfillment by engaging local individuals to transport goods, enhancing flexibility and reducing operational costs. Real-time tracking and dynamic routing in crowdshipping platforms optimize delivery efficiency and customer satisfaction by matching nearby couriers with immediate delivery requests.
White-label crowdshipping
White-label crowdshipping leverages local, non-professional couriers to optimize last-mile delivery, reducing costs and increasing scalability for e-commerce businesses. This approach enhances delivery speed and customer experience by utilizing a distributed network while maintaining brand visibility through customizable, white-label platforms.
Last-Mile Delivery vs Crowdshipping Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com