Taxi services provide a reliable and regulated mode of transportation with fixed fares and experienced drivers, ensuring passenger safety and convenience. E-hailing platforms offer the advantage of real-time booking, flexible payment options, and dynamic pricing, appealing to tech-savvy users seeking quick and efficient rides. Comparing cost, availability, and user experience helps determine the best choice for individual travel needs.
Table of Comparison
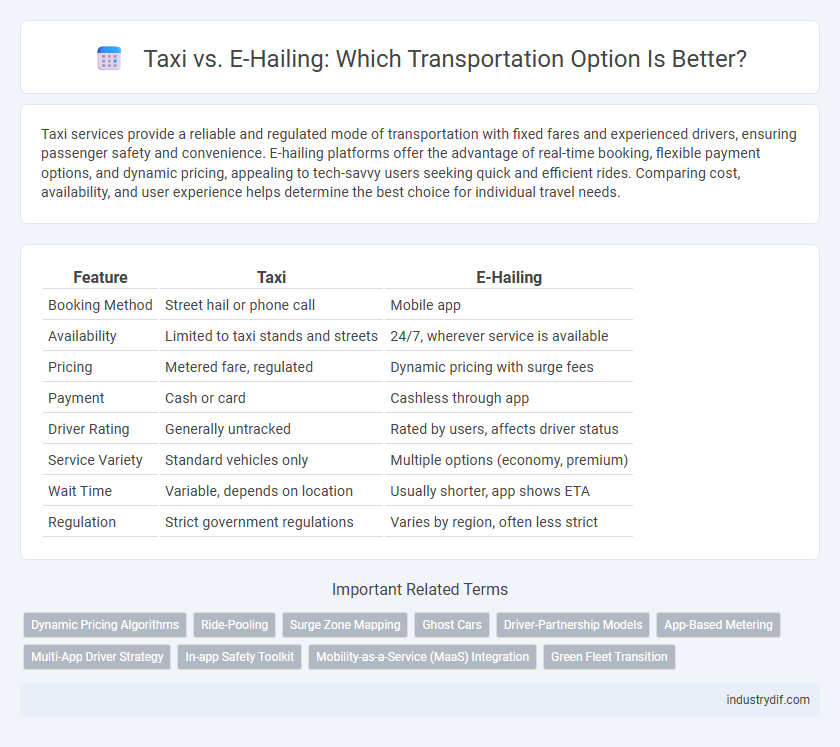
| Feature | Taxi | E-Hailing |
|---|---|---|
| Booking Method | Street hail or phone call | Mobile app |
| Availability | Limited to taxi stands and streets | 24/7, wherever service is available |
| Pricing | Metered fare, regulated | Dynamic pricing with surge fees |
| Payment | Cash or card | Cashless through app |
| Driver Rating | Generally untracked | Rated by users, affects driver status |
| Service Variety | Standard vehicles only | Multiple options (economy, premium) |
| Wait Time | Variable, depends on location | Usually shorter, app shows ETA |
| Regulation | Strict government regulations | Varies by region, often less strict |
Overview of Taxi and E-Hailing Services
Taxi services operate on traditional street-hail or phone-booked models with regulated fares and licensed drivers, ensuring established reliability and safety standards. E-hailing services utilize mobile app technology for booking rides, offering dynamic pricing and GPS tracking, which enhances convenience and real-time service updates. Both options provide distinct benefits, with taxis being preferred for immediate availability and e-hailing favored for digital payment integration and user reviews.
Key Differences Between Taxis and E-Hailing
Taxis traditionally operate with licensed drivers and meters, offering street hailing or pre-booked rides, while e-hailing services use smartphone apps to connect passengers with drivers in real-time through GPS technology. E-hailing platforms often provide transparent fare estimates, cashless payments, and user ratings, enhancing convenience and accountability compared to taxis. Regulatory frameworks for taxis are generally stricter, involving mandatory inspections and fixed rates, whereas e-hailing services face evolving regulations adapting to their digital business models.
Pricing Structures: Metered vs Dynamic
Taxi services typically operate on a metered pricing structure based on distance and time, offering fixed and predictable fares regulated by local authorities. E-hailing platforms utilize dynamic pricing algorithms that adjust fares according to demand, traffic conditions, and time of day, often resulting in higher costs during peak hours or special events. The contrast between the transparent, standardized taxi fares and the variable, surge-driven e-hailing prices significantly influences consumer choice and market competition.
Booking and Accessibility Comparison
Taxi services offer immediate street hailing with fixed rates and regulated availability, while e-hailing platforms provide on-demand booking through mobile apps, featuring dynamic pricing and real-time driver tracking. E-hailing apps improve accessibility by connecting users with a broader network of drivers, including options for different vehicle types and contactless payments. Taxi access remains steady in urban cores but lacks the convenience and customization found in e-hailing services.
Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance
Taxi services operate under long-established regulatory frameworks that mandate licensing, fare controls, and driver background checks to ensure passenger safety and fair competition. E-hailing platforms face evolving compliance requirements, including digital data privacy laws, dynamic pricing regulations, and geo-fencing mandates imposed by local governments. Regulatory divergence often impacts market access, operational costs, and service standards between traditional taxis and app-based ride-hailing companies.
Service Availability and Coverage
Taxi services often operate within fixed zones and are readily available in urban centers, offering immediate roadside pickups. E-hailing platforms leverage GPS technology and extensive driver networks to provide broader coverage across metropolitan and suburban areas, enhancing accessibility and reducing wait times. Both service models adapt differently to demand patterns, with e-hailing typically delivering greater service availability during off-peak hours.
Safety and Security Measures
Taxi services often implement regulated safety protocols, including licensed drivers and regular vehicle inspections, ensuring consistent passenger protection. E-hailing platforms enhance security through real-time GPS tracking, driver background checks, and in-app emergency features, offering passengers immediate assistance if needed. Both transportation options prioritize safety but leverage different technologies and regulatory frameworks to maintain secure travel experiences.
Environmental Impact: Traditional vs Digital
Traditional taxis, often relying on older combustion engines, contribute significantly to urban air pollution and carbon emissions due to lower fuel efficiency and idling time. E-hailing services leverage digital platforms to optimize ride-sharing and route efficiency, potentially reducing per-trip emissions and traffic congestion. However, the total environmental benefit depends on vehicle types used, with electric or hybrid vehicles enhancing e-hailing's positive impact compared to conventional taxis.
User Experience and Satisfaction
Taxi services often provide a consistent and familiar user experience with regulated fares and professional drivers, which appeals to passengers seeking reliability and safety. E-hailing platforms enhance user satisfaction by offering convenience through app-based booking, real-time tracking, and diverse payment options, catering to tech-savvy and time-sensitive users. Customer reviews and ratings on e-hailing apps contribute to improved service quality and personalized experiences, distinguishing them from traditional taxis.
Future Trends in Urban Mobility
E-hailing platforms are projected to dominate urban mobility by integrating autonomous vehicles and AI-driven route optimization, enhancing efficiency and reducing congestion. Traditional taxis face challenges adapting to contactless payments and dynamic pricing models preferred by digital-native consumers. Urban planners emphasize multimodal connectivity, where e-hailing complements public transit, supporting sustainable, tech-forward transportation ecosystems.
Related Important Terms
Dynamic Pricing Algorithms
Dynamic pricing algorithms in e-hailing platforms adjust ride fares in real-time based on demand, traffic conditions, and driver availability, creating a flexible pricing model unlike traditional taxis that use fixed rates. This dynamic system enables e-hailing services to balance supply and demand efficiently, often leading to higher prices during peak hours compared to the static fare structure of conventional taxis.
Ride-Pooling
Ride-pooling in e-hailing platforms significantly reduces transportation costs and carbon emissions by optimizing routes and sharing rides among multiple passengers with similar destinations. Traditional taxis offer limited ride-pooling options, resulting in less efficient urban transport and higher environmental impact compared to app-based e-hailing services.
Surge Zone Mapping
Surge zone mapping in e-hailing platforms uses real-time data analytics and GPS to dynamically adjust fares based on demand fluctuations, offering more transparent and flexible pricing compared to traditional taxis. This advanced mapping improves driver allocation and passenger convenience by highlighting high-demand areas where surge pricing applies, optimizing urban transportation efficiency.
Ghost Cars
Ghost cars in e-hailing services refer to vehicles that appear available in apps but are either inactive or deliberately positioned to manipulate supply data, causing inefficiencies and misleading passengers. Traditional taxis avoid ghost car issues due to centralized dispatch and physical meter regulations, ensuring genuine availability and consistent service reliability.
Driver-Partnership Models
Traditional taxi driver-partnership models typically involve medallion ownership or leasing agreements, creating fixed costs and limited flexibility for drivers. In contrast, e-hailing platforms adopt a scalable gig economy model, offering drivers greater autonomy, dynamic pricing, and real-time ride allocation systems.
App-Based Metering
App-based metering in e-hailing services uses dynamic pricing algorithms that adjust fares based on demand, distance, and traffic conditions, offering transparent real-time fare estimates unlike traditional taxi meters. This technology enhances efficiency and convenience by enabling cashless payments, digital ride tracking, and instant driver-rider communication through mobile applications.
Multi-App Driver Strategy
Multi-app driver strategy enhances income stability by leveraging both traditional taxi services and e-hailing platforms like Uber, Lyft, and Grab, optimizing ride requests and reducing downtime. Utilizing multiple apps increases market reach and allows dynamic pricing exploitation, improving overall earnings and operational efficiency.
In-app Safety Toolkit
E-hailing platforms integrate advanced in-app safety toolkits featuring real-time GPS tracking, emergency SOS buttons, and driver verification to enhance passenger security. Traditional taxis often lack these digital safety measures, making e-hailing services a preferred choice for tech-savvy travelers seeking increased protection.
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) Integration
E-hailing platforms seamlessly integrate with Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) ecosystems by offering real-time digital booking, cashless payments, and multimodal trip planning, enhancing urban mobility efficiency. Traditional taxis often face challenges in MaaS integration due to reliance on manual dispatch systems and limited digital interoperability, impacting user experience and service scalability.
Green Fleet Transition
Taxi services are increasingly adopting hybrid and electric vehicles to reduce carbon emissions and comply with environmental regulations, while e-hailing platforms prioritize rapid integration of green fleets through dynamic incentives and driver partnerships. The green fleet transition in transportation hinges on government policies, investment in charging infrastructure, and consumer demand for sustainable mobility options.
Taxi vs E-Hailing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com