Carpooling reduces traffic congestion and lowers individual commuting costs by sharing rides among passengers with similar routes. Microtransit offers flexible, on-demand transportation services using smaller vehicles, bridging the gap between fixed-route public transit and private cars. Both solutions promote sustainability and efficiency by optimizing vehicle occupancy and reducing carbon emissions in urban transportation networks.
Table of Comparison
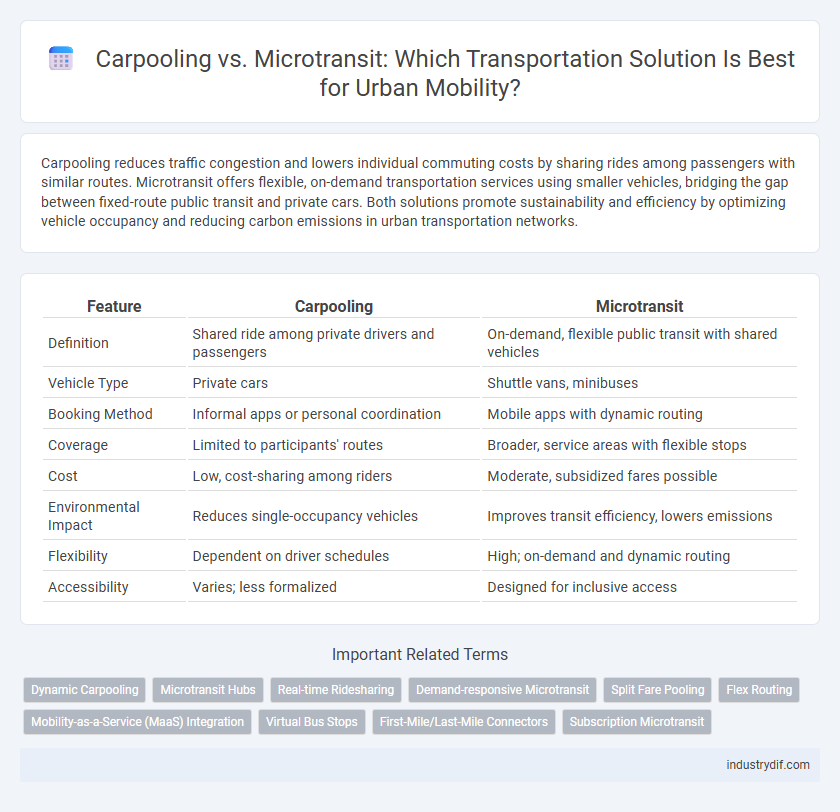
| Feature | Carpooling | Microtransit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared ride among private drivers and passengers | On-demand, flexible public transit with shared vehicles |
| Vehicle Type | Private cars | Shuttle vans, minibuses |
| Booking Method | Informal apps or personal coordination | Mobile apps with dynamic routing |
| Coverage | Limited to participants' routes | Broader, service areas with flexible stops |
| Cost | Low, cost-sharing among riders | Moderate, subsidized fares possible |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces single-occupancy vehicles | Improves transit efficiency, lowers emissions |
| Flexibility | Dependent on driver schedules | High; on-demand and dynamic routing |
| Accessibility | Varies; less formalized | Designed for inclusive access |
Overview of Carpooling and Microtransit
Carpooling involves multiple individuals sharing a private vehicle to travel together, reducing costs and traffic congestion while promoting environmental benefits through lowered emissions. Microtransit operates as an on-demand shared transportation service, blending the flexibility of ride-hailing with the efficiency of public transit, often managed via mobile apps for route optimization. Both modes aim to enhance urban mobility but differ in scalability and operational control, with carpooling relying on user initiative and microtransit offering structured service routes.
Key Differences Between Carpooling and Microtransit
Carpooling involves private vehicle sharing among a fixed group of passengers traveling along similar routes, offering cost-effective and eco-friendly commutes with flexible departure times. Microtransit operates as a technology-powered, demand-responsive public transit service using vans or shuttles to provide dynamic routing and scheduling within specific zones. Key differences include carpooling's reliance on personal coordination versus microtransit's centralized platform management, varying levels of scalability, and the integration of digital booking systems to optimize routes and reduce wait times.
Benefits of Carpooling for Urban Mobility
Carpooling reduces traffic congestion by decreasing the number of single-occupancy vehicles on urban roads, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions and improved air quality. It offers cost savings for commuters through shared fuel expenses and parking fees while promoting social interaction and community building. Enhanced flexibility and convenience compared to fixed-route microtransit make carpooling an attractive option for diverse urban commuters seeking efficient, sustainable transportation alternatives.
Advantages of Microtransit Services
Microtransit services offer flexible routing and on-demand scheduling, reducing wait times and improving convenience compared to fixed-route carpooling. These services utilize advanced technology for real-time tracking and dynamic ride matching, enhancing efficiency and passenger experience. Microtransit also supports better coverage in low-density areas, providing more equitable access to transportation options.
Cost Comparison: Carpooling vs Microtransit
Carpooling significantly reduces individual transportation costs by sharing fuel expenses and tolls among passengers, making it an economical option for daily commutes. Microtransit services, while offering flexible routes and on-demand convenience, often come with higher per-trip fares due to operational costs like driver wages and vehicle maintenance. Comparing average expenditures, carpooling typically costs 30-50% less per passenger than microtransit, especially in suburban and urban scenarios with consistent travel patterns.
Environmental Impact of Shared Transportation
Carpooling significantly reduces carbon emissions per passenger by maximizing vehicle occupancy and minimizing individual car usage, leading to lower fuel consumption and traffic congestion. Microtransit services utilize efficient routing algorithms and smaller vehicles to optimize passenger loads, further decreasing greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional private car travel. Both shared transportation modes contribute to sustainable urban mobility by promoting resource efficiency and reducing the overall environmental footprint of daily commutes.
Technology’s Role in Carpooling and Microtransit
Technology in carpooling leverages GPS tracking, mobile apps, and real-time matching algorithms to connect riders efficiently, reducing wait times and improving route optimization. Microtransit employs similar digital platforms combined with dynamic routing software and on-demand booking systems, enabling flexible, shared rides that adapt to fluctuating passenger demand. Advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence play a crucial role in both modes, enhancing service reliability, minimizing operational costs, and promoting sustainable urban mobility.
User Experience and Accessibility
Carpooling offers a personalized and flexible user experience with direct routes and familiar pickup locations, enhancing comfort and convenience. Microtransit provides accessible, demand-responsive transportation through app-based booking, real-time tracking, and dynamic routing, accommodating users without private vehicles or with limited mobility. Both modes improve last-mile connectivity but differ in scalability and adaptability to diverse urban transit needs.
Integration with Public Transit Networks
Carpooling offers flexible, demand-driven ride options that can complement fixed-route public transit by providing first-mile and last-mile connectivity. Microtransit systems utilize app-based booking and dynamically routed shuttles, enhancing the reach of transit networks in areas underserved by traditional buses or trains. Integrating both solutions with public transit schedules and fare systems optimizes urban mobility, reduces traffic congestion, and lowers carbon emissions.
Future Trends in Shared Transportation Solutions
Carpooling and microtransit represent pivotal trends in the evolution of shared transportation solutions, with microtransit offering flexible, on-demand routing that effectively complements traditional carpool models. Advances in AI and real-time data analytics are driving efficiency and personalized user experiences in microtransit systems, positioning them as scalable alternatives to fixed-route public transit. Emerging sustainability goals and urban congestion challenges increase adoption of these shared mobility options, highlighting their role in reducing emissions and enhancing regional connectivity.
Related Important Terms
Dynamic Carpooling
Dynamic carpooling leverages real-time data and algorithms to match passengers with drivers efficiently, reducing traffic congestion and lowering emissions compared to traditional microtransit models. By enabling flexible, on-demand shared rides, dynamic carpooling enhances urban mobility and maximizes vehicle occupancy rates, contributing to sustainable transportation solutions.
Microtransit Hubs
Microtransit hubs serve as centralized nodes that facilitate flexible, on-demand shared rides, optimizing routes based on real-time data to reduce wait times and improve coverage compared to traditional carpooling. These hubs integrate technology and transit services, enhancing first-mile/last-mile connectivity and supporting sustainable urban mobility.
Real-time Ridesharing
Real-time ridesharing in carpooling optimizes route efficiency by dynamically matching passengers traveling in similar directions, significantly reducing individual costs and emissions. Microtransit uses flexible, demand-responsive vehicles that adapt routes based on live requests, enhancing last-mile connectivity and minimizing wait times in urban environments.
Demand-responsive Microtransit
Demand-responsive microtransit offers flexible, on-demand transportation services that dynamically adjust routes based on real-time passenger requests, providing greater efficiency and coverage compared to fixed-route carpooling systems. Unlike traditional carpooling, microtransit reduces wait times and optimizes fleet utilization by leveraging advanced algorithms for route optimization and capacity management.
Split Fare Pooling
Split fare pooling in carpooling allows passengers to share ride costs directly through apps, reducing individual expenses and encouraging ride-sharing among commuters. Microtransit platforms integrate split fare pooling with dynamic routing and flexible scheduling, optimizing route efficiency while maintaining cost-effectiveness for multiple passengers.
Flex Routing
Flex routing in carpooling allows riders to share trips with slight detours based on passenger locations, optimizing vehicle occupancy and reducing emissions. Microtransit utilizes dynamic routing algorithms to adapt routes in real-time, improving service efficiency and coverage while maintaining flexibility for passenger pickups and drop-offs.
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) Integration
Carpooling enhances Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) integration by providing flexible, cost-effective shared rides that reduce traffic congestion and lower emissions, seamlessly complementing public transit options. Microtransit offers adaptive, on-demand shuttle services optimized through real-time data, enabling efficient route planning and first-mile/last-mile connectivity within MaaS platforms.
Virtual Bus Stops
Virtual bus stops in microtransit systems optimize flexible routing and scheduling, reducing wait times and increasing ride efficiency compared to fixed-location carpooling pickups. This dynamic approach leverages real-time data to improve accessibility and minimize detours, enhancing urban mobility and lowering operational costs.
First-Mile/Last-Mile Connectors
Carpooling offers a flexible and cost-effective first-mile/last-mile solution by maximizing vehicle occupancy and reducing individual trips, while microtransit provides dynamic, on-demand shuttle services with optimized routing to enhance accessibility in less dense areas. Both approaches improve connectivity to main transit hubs, but microtransit leverages real-time data and advanced scheduling algorithms to adapt routes and schedules efficiently.
Subscription Microtransit
Subscription microtransit offers a flexible, on-demand transportation service that optimizes route efficiency and reduces individual car usage, making it a sustainable alternative to traditional carpooling. By leveraging real-time data and AI-driven scheduling, subscription microtransit enhances commuter convenience while lowering environmental impact and urban congestion.
Carpooling vs Microtransit Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com