Taxi services offer traditional, meter-based fares and are easily hailed on the street or at designated stands, providing immediate and reliable transportation. Ride-hailing platforms use smartphone apps to connect passengers with drivers, offering upfront pricing and cashless transactions for convenience. Both options cater to different user preferences, with taxis often preferred for spontaneous trips and ride-hailing chosen for pre-booked, personalized rides.
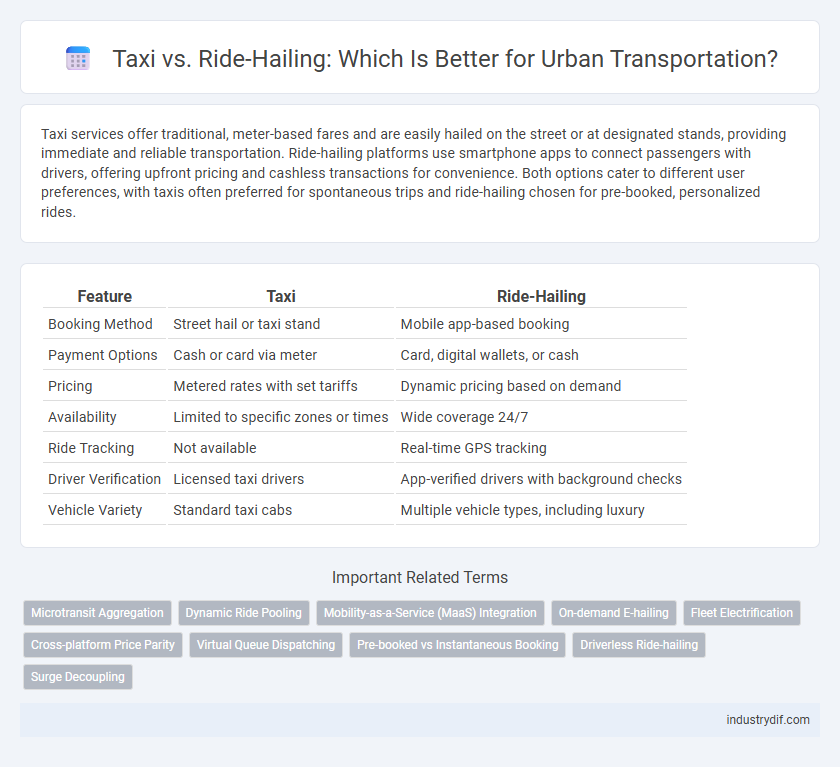
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Taxi | Ride-Hailing |
|---|---|---|
| Booking Method | Street hail or taxi stand | Mobile app-based booking |
| Payment Options | Cash or card via meter | Card, digital wallets, or cash |
| Pricing | Metered rates with set tariffs | Dynamic pricing based on demand |
| Availability | Limited to specific zones or times | Wide coverage 24/7 |
| Ride Tracking | Not available | Real-time GPS tracking |
| Driver Verification | Licensed taxi drivers | App-verified drivers with background checks |
| Vehicle Variety | Standard taxi cabs | Multiple vehicle types, including luxury |
Overview of Taxi and Ride-Hailing Services
Taxi services operate through licensed drivers and metered fares, often hailed on the street or pre-booked via phone, ensuring regulated pricing and standardized safety measures. Ride-hailing platforms like Uber and Lyft use smartphone apps to connect passengers with nearby drivers, offering dynamic pricing and cashless transactions based on demand and supply algorithms. Both options serve urban transportation needs but differ in accessibility, payment methods, and regulatory oversight, impacting user experience and market reach.
Key Differences Between Taxis and Ride-Hailing
Taxis operate under regulated fare structures and can be hailed directly on the street or found at designated taxi stands, while ride-hailing services use app-based platforms to connect passengers with drivers who set flexible pricing based on demand. Taxi drivers typically undergo rigorous licensing and background checks mandated by local governments, whereas ride-hailing drivers are subject to company-specific screening processes that vary widely. Payment methods for taxis usually involve cash or card terminals in the vehicle, contrasting with ride-hailing's cashless, app-integrated payment systems that enhance convenience and transparency for users.
Regulatory Frameworks: Taxis vs Ride-Hailing
Taxi services operate under stringent government regulations, including mandatory licensing, fixed fare structures, and rigorous safety standards, ensuring consistent consumer protection. Ride-hailing platforms function within evolving regulatory frameworks that emphasize digital platform accountability, data privacy, dynamic pricing models, and often less stringent traditional licensing requirements. The divergence in regulatory approaches reflects challenges in balancing innovation with public safety and fairness in the transportation sector.
Pricing Models: Metered Fare vs Dynamic Pricing
Taxi pricing relies on metered fares based on distance and time, providing predictable and regulated costs for passengers. Ride-hailing services use dynamic pricing models that fluctuate with demand, time, and location, potentially increasing prices during peak hours. This dynamic approach offers flexibility but can lead to higher and less transparent costs compared to traditional taxi fares.
Service Availability and Coverage Comparison
Taxi services typically offer consistent availability in urban centers but may have limited coverage in suburban or rural areas, relying on street hails or dispatch calls. Ride-hailing platforms leverage GPS and mobile app technology to provide expansive coverage across diverse locations, including underserved regions, with on-demand booking and dynamic pricing models. This extensive network and real-time tracking enable ride-hailing services to adapt quickly to demand fluctuations, enhancing overall service accessibility compared to conventional taxis.
Licensing and Driver Requirements
Taxi drivers must obtain specific licenses and undergo rigorous background checks, including vehicle inspections and local regulatory compliance, to operate legally in their jurisdictions. Ride-hailing drivers typically need a valid driver's license, proof of insurance, and must pass platform-specific screening processes, which may include background checks and vehicle standards but often have less stringent regulatory oversight compared to traditional taxi services. Licensing requirements for taxis are usually more standardized and heavily regulated by city or municipal authorities, while ride-hailing companies operate under state or regional policies that vary widely and can impact driver eligibility and vehicle qualifications.
Impact on Urban Mobility and Congestion
Ride-hailing services have significantly altered urban mobility by increasing the availability of on-demand transportation, yet they often contribute to higher traffic congestion compared to traditional taxis due to an increase in vehicle miles traveled and empty trips while waiting for passengers. Studies show ride-hailing vehicles can add up to 30% more traffic within city centers, exacerbating congestion and limiting road efficiency. Meanwhile, taxis, regulated with fixed routes and pick-up zones, tend to have fewer deadhead miles, potentially reducing their overall impact on urban traffic flow.
Passenger Safety and Service Standards
Taxi services often adhere to strict local regulations, including background checks for drivers and vehicle inspections, ensuring a baseline of passenger safety. Ride-hailing platforms implement app-based tracking, driver ratings, and cashless payments, enhancing transparency and accountability for service quality. Comparing both, taxis provide regulated safety standards while ride-hailing leverages technology for real-time monitoring and user feedback to maintain service reliability.
Technological Innovations in Taxi and Ride-Hailing
Technological innovations in taxi services include GPS integration, digital meters, and mobile payment systems that enhance route optimization and fare accuracy. Ride-hailing platforms leverage advanced algorithms, AI-driven demand prediction, and seamless app-based booking to provide real-time vehicle tracking and dynamic pricing. Both sectors continue to evolve with electric vehicle integration and autonomous driving technologies, aiming to improve efficiency, safety, and user experience.
Future Trends in Urban Transportation Services
Ride-hailing platforms are rapidly integrating autonomous vehicle technology and AI-driven route optimization to enhance efficiency and reduce urban congestion. Taxi services are adapting by incorporating real-time digital booking and dynamic pricing models to compete with the convenience of app-based rides. Urban transportation is shifting towards multimodal, data-driven ecosystems prioritizing sustainability, accessibility, and seamless operator integration.
Related Important Terms
Microtransit Aggregation
Taxi services operate on fixed routes and fares with licensed drivers, while ride-hailing platforms use microtransit aggregation to dynamically connect passengers with nearby drivers through app-based algorithms, optimizing route efficiency and reducing wait times. This integration of microtransit aggregation enhances urban mobility by pooling demand, lowering operational costs, and providing flexible, on-demand transportation options compared to traditional taxi models.
Dynamic Ride Pooling
Dynamic ride pooling in ride-hailing services optimizes routes by matching multiple passengers with overlapping journeys, significantly reducing wait times and lowering costs compared to traditional taxi services. This technology leverages real-time data and advanced algorithms to enhance vehicle occupancy rates and efficiency, offering a more sustainable and scalable transportation solution.
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) Integration
Taxi services traditionally operate on fixed routes and pricing schemes, limiting their integration with Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) platforms; ride-hailing apps, leveraging real-time data and dynamic pricing models, offer seamless multi-modal transportation options that enhance user convenience and system efficiency. MaaS integration prioritizes flexible booking, payment consolidation, and personalized travel planning, which ride-hailing services support more effectively than conventional taxis.
On-demand E-hailing
On-demand e-hailing services offer enhanced convenience and real-time tracking compared to traditional taxi services, leveraging GPS technology and mobile apps to connect passengers with nearby drivers instantly. These platforms optimize routes and pricing dynamically, providing more efficient and cost-effective transportation options in urban areas.
Fleet Electrification
Taxi fleets increasingly integrate electric vehicles (EVs) to reduce carbon emissions and operating costs, highlighting benefits such as lower maintenance and fuel expenses. Ride-hailing companies accelerate fleet electrification by leveraging data analytics and incentives to optimize EV deployment and enhance urban sustainability goals.
Cross-platform Price Parity
Taxi services traditionally maintain fixed pricing regulated by local authorities, whereas ride-hailing platforms utilize dynamic pricing models based on demand, often leading to significant price disparities across different apps. Cross-platform price parity remains limited as ride-hailing companies use surge pricing algorithms and promotions that taxis do not, resulting in varying fare structures depending on the service used and the time of day.
Virtual Queue Dispatching
Virtual queue dispatching in ride-hailing platforms enhances efficiency by dynamically assigning drivers based on real-time demand and location data, reducing passenger wait times compared to traditional taxi services that rely on street hails or fixed dispatch systems. This technology leverages GPS tracking and predictive algorithms to streamline trip allocation, optimize driver utilization, and improve overall urban mobility.
Pre-booked vs Instantaneous Booking
Taxi services often rely on pre-booked rides scheduled in advance, ensuring guaranteed availability and fixed pricing for passengers. Ride-hailing platforms emphasize instantaneous booking through mobile apps, offering real-time vehicle tracking and dynamic pricing based on demand.
Driverless Ride-hailing
Driverless ride-hailing services leverage autonomous vehicle technology to enhance safety, reduce operational costs, and increase availability compared to traditional taxi services reliant on human drivers. These autonomous fleets utilize real-time data analytics and AI algorithms to optimize route efficiency and passenger experience, revolutionizing urban transportation infrastructure.
Surge Decoupling
Surge decoupling in ride-hailing separates pricing from demand spikes, enabling more stable fares compared to traditional taxi surge pricing that fluctuates sharply during peak times. This approach optimizes customer cost predictability while allowing dynamic driver incentives without directly inflating passenger prices.
Taxi vs Ride-hailing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com