Traditional supply chains rely on centralized databases and manual processes, which can lead to inefficiencies, delays, and lack of transparency in transportation management. Blockchain-enabled supply chains offer decentralized, immutable ledgers that enhance traceability, reduce fraud, and streamline communication between all parties involved. This technology improves real-time tracking, optimizes route planning, and increases overall operational efficiency in transportation logistics.
Table of Comparison
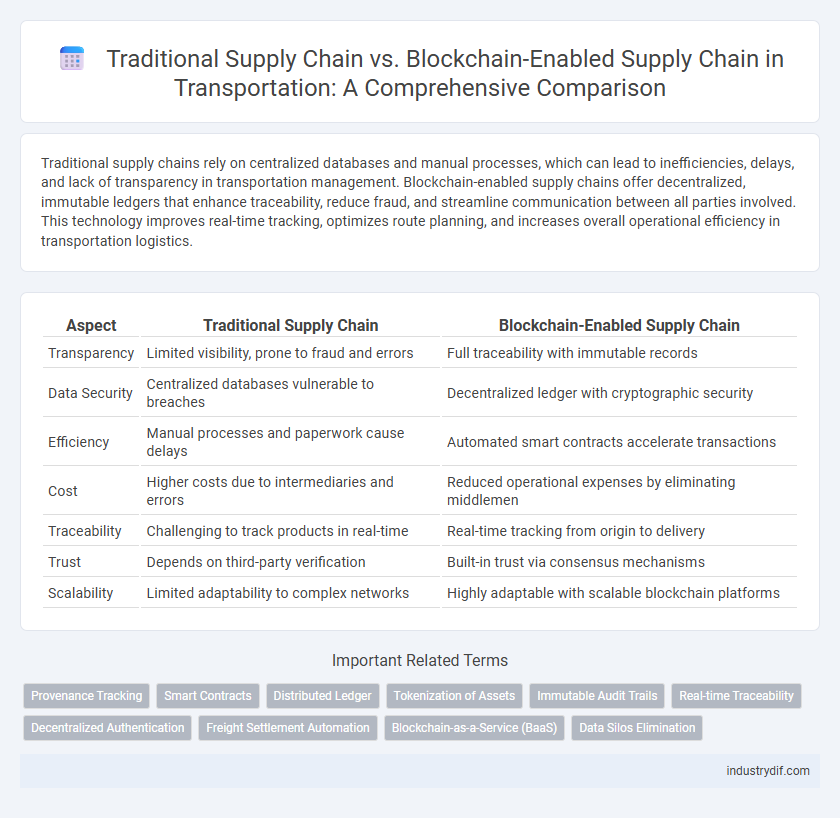
| Aspect | Traditional Supply Chain | Blockchain-Enabled Supply Chain |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Limited visibility, prone to fraud and errors | Full traceability with immutable records |
| Data Security | Centralized databases vulnerable to breaches | Decentralized ledger with cryptographic security |
| Efficiency | Manual processes and paperwork cause delays | Automated smart contracts accelerate transactions |
| Cost | Higher costs due to intermediaries and errors | Reduced operational expenses by eliminating middlemen |
| Traceability | Challenging to track products in real-time | Real-time tracking from origin to delivery |
| Trust | Depends on third-party verification | Built-in trust via consensus mechanisms |
| Scalability | Limited adaptability to complex networks | Highly adaptable with scalable blockchain platforms |
Overview of Traditional Supply Chain Systems
Traditional supply chain systems rely on centralized databases and manual record-keeping, which often results in delays, errors, and lack of real-time visibility. These systems depend heavily on intermediaries for data verification and transaction processing, leading to increased operational costs and reduced transparency. Inventory tracking, shipment status, and payment reconciliation are typically fragmented, causing inefficiencies and challenges in demand forecasting within transportation logistics.
Introduction to Blockchain-Enabled Supply Chains
Blockchain-enabled supply chains revolutionize transportation by enhancing transparency and traceability through decentralized ledger technology. Each transaction or shipment record is immutably stored, allowing real-time tracking and reducing fraud and errors common in traditional supply chains. This innovation improves efficiency, lowers costs, and strengthens trust among stakeholders including manufacturers, carriers, and logistics providers.
Key Differences in Data Transparency
Traditional supply chains rely on centralized databases, which often result in limited data transparency and delayed information sharing among stakeholders. Blockchain-enabled supply chains utilize decentralized ledgers, providing real-time, immutable access to transaction data and increasing transparency across all parties. This enhanced visibility reduces fraud, improves traceability, and facilitates faster dispute resolution in transportation logistics.
Security and Traceability in Both Models
Traditional supply chains face challenges in security and traceability due to centralized data storage, increasing vulnerability to fraud, data tampering, and delays in information sharing. Blockchain-enabled supply chains enhance security through decentralized, immutable ledgers that provide real-time, transparent tracking of goods and transactions across multiple stakeholders. This immutable and transparent nature improves traceability, reduces fraud, and ensures data integrity throughout the transportation and logistics process.
Impact on Efficiency and Speed
Traditional supply chains often suffer from delays due to manual processes, lack of real-time visibility, and complex intermediaries, limiting overall efficiency and speed in transportation logistics. Blockchain-enabled supply chains streamline operations by providing decentralized, immutable ledgers that enhance transparency, reduce errors, and facilitate faster transaction settlements. Real-time data sharing and automated smart contracts significantly accelerate shipment tracking and customs clearance, resulting in improved transportation efficiency and speed.
Cost Implications for Transportation
Traditional supply chains incur high transportation costs due to inefficiencies such as manual documentation, delayed payments, and lack of real-time tracking. Blockchain-enabled supply chains reduce these expenses by providing transparent, automated processes that minimize fraud, lower administrative overhead, and optimize route planning through accurate, immutable data records. Studies show blockchain integration can decrease transportation costs by up to 20% through enhanced coordination and improved asset utilization.
Risk Management and Fraud Prevention
Traditional supply chains often face challenges in risk management and fraud prevention due to limited transparency and reliance on manual record-keeping, which increases the likelihood of errors and unauthorized transactions. Blockchain-enabled supply chains enhance risk management by providing immutable, real-time visibility of every transaction and asset movement, significantly reducing the chances of fraud through decentralized verification. This technology enables automated smart contracts that enforce compliance and streamline audits, minimizing human intervention and potential vulnerabilities.
Integration with Existing Transportation Infrastructure
Traditional supply chains rely heavily on legacy transportation infrastructure, which often limits real-time data sharing and end-to-end visibility across multiple stakeholders. Blockchain-enabled supply chains enhance integration by providing a decentralized ledger that securely records every transaction and shipment update, improving transparency and synchronization among carriers, ports, warehouses, and customs authorities. This seamless integration supports more efficient route planning, reduces delays, and facilitates automated compliance with regulatory requirements across complex transportation networks.
Challenges in Blockchain Adoption
Traditional supply chains face challenges such as lack of transparency, delayed information sharing, and limited traceability, which impact efficiency and trust. Blockchain-enabled supply chains encounter adoption barriers including high implementation costs, scalability issues, and regulatory uncertainties that hinder widespread integration. Overcoming these challenges requires advancements in technology, clear legal frameworks, and industry collaboration to unlock blockchain's full potential in transportation logistics.
Future Trends in Supply Chain Modernization
Blockchain-enabled supply chains enhance transparency and traceability, reducing fraud and errors compared to traditional supply chains reliant on manual record-keeping and centralized databases. Future trends in supply chain modernization include the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors with blockchain technology to provide real-time asset tracking and condition monitoring. Smart contracts automate compliance and payments, driving efficiency and responsiveness in global transportation networks.
Related Important Terms
Provenance Tracking
Traditional supply chains rely on centralized databases that are vulnerable to errors and fraud, limiting reliable provenance tracking for transportation goods. Blockchain-enabled supply chains provide immutable, transparent records that enhance provenance tracking by ensuring every transaction and movement of goods is securely verified and accessible in real time.
Smart Contracts
Traditional supply chains rely on manual processes and intermediaries, leading to delays and increased costs, whereas blockchain-enabled supply chains use smart contracts to automate verification and payment, enhancing transparency and efficiency. Smart contracts execute predefined rules automatically, reducing disputes and enabling real-time tracking in transportation logistics.
Distributed Ledger
Traditional supply chains rely on centralized databases for record-keeping, which can lead to data inconsistencies, delays, and reduced transparency in transportation management. Blockchain-enabled supply chains utilize distributed ledger technology to provide immutable, real-time tracking of goods, enhancing security, traceability, and trust across all transportation stakeholders.
Tokenization of Assets
Tokenization of assets in blockchain-enabled supply chains enhances transparency and traceability by converting physical goods into digital tokens that represent ownership and provenance, reducing fraud and inefficiencies present in traditional supply chains. This digital transformation streamlines asset transfers, enables real-time tracking, and fosters trust among stakeholders through immutable ledger records.
Immutable Audit Trails
Traditional supply chains often struggle with opaque record-keeping, leading to data tampering and lack of trust in transaction histories. Blockchain-enabled supply chains provide immutable audit trails through decentralized ledgers, enhancing transparency, traceability, and fraud prevention across transportation networks.
Real-time Traceability
Traditional supply chains often suffer from delayed data updates and limited visibility, causing inefficiencies in real-time shipment tracking and inventory management. Blockchain-enabled supply chains provide decentralized, immutable ledgers that enhance transparency and enable real-time traceability, improving accuracy and trust across the transportation network.
Decentralized Authentication
Traditional supply chains rely on centralized authentication systems that are vulnerable to single points of failure and fraud, causing delays and increased costs in transportation logistics. Blockchain-enabled supply chains use decentralized authentication to enhance data transparency, secure real-time tracking, and improve trust among stakeholders, resulting in streamlined transportation operations and reduced risk of counterfeit goods.
Freight Settlement Automation
Traditional supply chain freight settlement relies heavily on manual processes, paper-based documentation, and multiple intermediaries, leading to delays, errors, and increased costs. Blockchain-enabled supply chain automates freight settlement through decentralized ledger technology, ensuring real-time transparency, enhanced security, and faster reconciliation between shippers, carriers, and brokers.
Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS)
Traditional supply chains often suffer from limited transparency and slower reconciliation processes, whereas blockchain-enabled supply chains using Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) provide real-time tracking, enhanced security, and immutable ledgers that significantly reduce fraud and errors. BaaS platforms enable transportation companies to integrate blockchain technology without extensive infrastructure investment, streamlining operations and improving traceability across global logistics networks.
Data Silos Elimination
Blockchain-enabled supply chains eliminate data silos by providing a decentralized and transparent ledger accessible to all participants, ensuring real-time sharing and verification of transportation data. Traditional supply chains often suffer from fragmented information flows between carriers, warehouses, and suppliers, leading to delays and errors in shipment tracking and inventory management.
Traditional supply chain vs blockchain-enabled supply chain Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com