Mineral water contains naturally occurring minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which contribute to its unique taste and potential health benefits. Alkaline water has a higher pH level, usually above 7, which may help neutralize acid in the body and support better hydration. Choosing between mineral water and alkaline water depends on individual health needs and taste preferences.
Table of Comparison
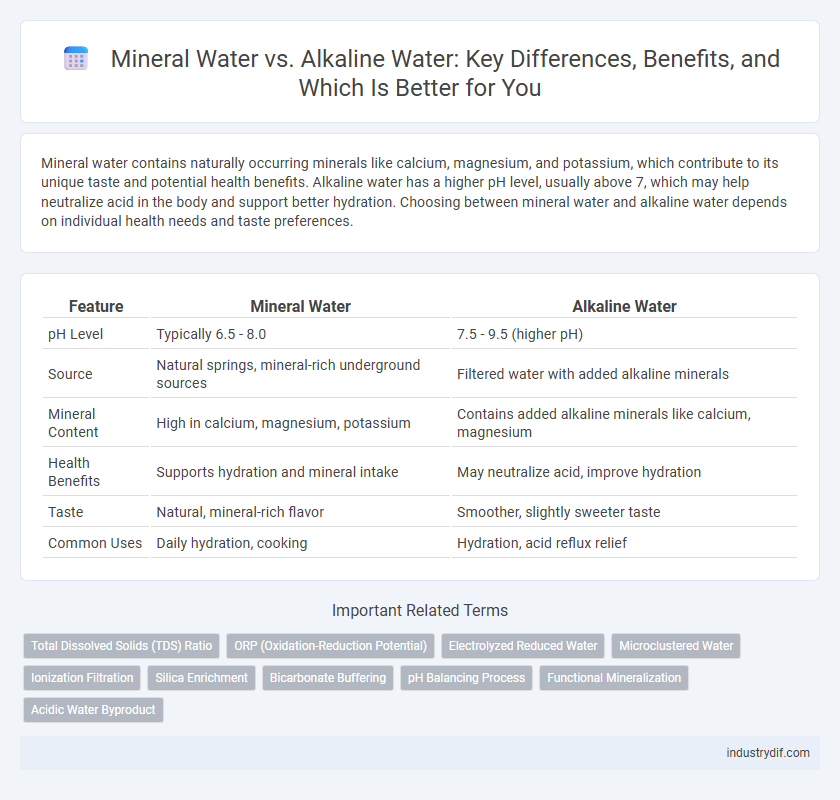
| Feature | Mineral Water | Alkaline Water |
|---|---|---|
| pH Level | Typically 6.5 - 8.0 | 7.5 - 9.5 (higher pH) |
| Source | Natural springs, mineral-rich underground sources | Filtered water with added alkaline minerals |
| Mineral Content | High in calcium, magnesium, potassium | Contains added alkaline minerals like calcium, magnesium |
| Health Benefits | Supports hydration and mineral intake | May neutralize acid, improve hydration |
| Taste | Natural, mineral-rich flavor | Smoother, slightly sweeter taste |
| Common Uses | Daily hydration, cooking | Hydration, acid reflux relief |
Introduction to Mineral Water and Alkaline Water
Mineral water contains naturally occurring minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium, sourced from protected underground reservoirs. Alkaline water has a higher pH level, typically above 7.5, due to added alkaline minerals like bicarbonate, calcium, and magnesium or through ionization processes. The unique mineral composition and pH levels influence hydration, taste, and potential health benefits.
Source and Composition Differences
Mineral water originates from natural springs and contains various minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium absorbed from surrounding rocks, offering essential nutrients. Alkaline water undergoes ionization or mixing with alkaline compounds, resulting in a higher pH level, typically above 7, which aims to neutralize acidity in the body. The primary difference lies in mineral content derived from geological sources in mineral water, compared to artificially altered pH and mineral balance in alkaline water.
Mineral Content Analysis
Mineral water contains essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium naturally dissolved from underground sources, contributing to hydration and electrolyte balance. Alkaline water typically features a higher pH level, often above 8, with added minerals such as bicarbonates and silicates designed to neutralize acidity in the body. Analyzing mineral content reveals that mineral water offers a more diverse and naturally occurring mineral profile, while alkaline water emphasizes specific alkaline minerals aimed at maintaining pH balance.
pH Levels and Alkalinity Explained
Mineral water typically has a neutral to slightly alkaline pH ranging from 6.5 to 8.0 due to dissolved minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which influence its alkalinity. Alkaline water, however, generally features a higher pH level of 8.5 to 9.5, achieved either naturally through mineral content or artificially via ionization processes. The increased alkalinity in alkaline water is believed to neutralize acid in the bloodstream, potentially improving hydration and buffering acidity in the body.
Health Claims: Scientific Evidence
Mineral water contains natural minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which can support hydration and bone health, backed by studies highlighting its electrolyte balance benefits. Alkaline water, characterized by a higher pH level (usually above 7.5), is claimed to neutralize acid in the body, but scientific evidence for significant health advantages remains limited and inconclusive. Research indicates consuming regular water adequately supports bodily functions, while more robust clinical trials are needed to substantiate alkaline water's purported impacts on acid-base balance and chronic disease prevention.
Hydration Efficiency Comparison
Mineral water contains essential minerals like calcium and magnesium that support cellular hydration and electrolyte balance, enhancing overall water absorption efficiency. Alkaline water, with a higher pH level typically between 8 and 9, may neutralize acidity and improve hydration rates by facilitating better water molecule absorption. Studies suggest that alkaline water could potentially increase hydration efficiency during intense physical activity due to its smaller cluster size and pH-driven cellular uptake advantages.
Taste and Sensory Characteristics
Mineral water has a distinct taste due to its natural mineral content, often featuring subtle hints of calcium, magnesium, and sodium that provide a crisp and refreshing flavor. Alkaline water typically has a smoother, less sharp taste, with a slightly sweet or flat profile resulting from its higher pH and added bicarbonates. Sensory characteristics of mineral water are influenced by its source geology, while alkaline water's taste depends on its pH level and ionization process.
Safety and Regulatory Standards
Mineral water is regulated by stringent safety standards ensuring natural mineral content and source purity, often monitored by agencies like the FDA or EFSA. Alkaline water undergoes specific testing for pH levels and potential additives, with regulatory oversight varying by country but generally requiring compliance with potable water safety guidelines. Both types aim to meet health standards, yet consumers should verify certifications and source transparency to ensure safety.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Mineral water sales have surged globally due to rising health awareness and the growing preference for natural mineral content, with markets in Europe and Asia leading consumption rates. Alkaline water is gaining traction among younger consumers seeking pH-balanced hydration and potential detoxifying benefits, reflected in increased product launches and social media endorsements. Consumer preferences reveal a shift towards functional beverages, driving innovation and premium pricing in both mineral and alkaline water segments.
Choosing the Right Water for Your Needs
Mineral water contains essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which support hydration and overall health, making it ideal for everyday consumption. Alkaline water, with a higher pH level typically above 7.5, may help neutralize acidity in the body and improve digestion, appealing to those with acid reflux or acid-base balance concerns. Selecting the right water depends on individual health goals, dietary needs, and personal preferences regarding taste and mineral content.
Related Important Terms
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) Ratio
Mineral water typically contains a Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) ratio ranging from 150 to 500 mg/L, which indicates a higher concentration of essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium. Alkaline water usually has a lower TDS ratio, around 50 to 200 mg/L, with a pH level above 7 that neutralizes acidity and supports hydration.
ORP (Oxidation-Reduction Potential)
Mineral water typically has a positive ORP, indicating a greater oxidizing potential, while alkaline water exhibits a negative ORP, signifying stronger antioxidant properties that can neutralize free radicals. The negative ORP in alkaline water is often attributed to its higher pH and mineral content, which may provide benefits in reducing oxidative stress.
Electrolyzed Reduced Water
Electrolyzed Reduced Water (ERW), a type of alkaline water, contains molecular hydrogen and a higher pH level that may provide antioxidant benefits compared to standard mineral water, which primarily offers essential minerals like calcium and magnesium. Studies suggest ERW's unique electrolysis process enhances hydration and reduces oxidative stress, differentiating it from traditional mineral water's mineral content-focused health effects.
Microclustered Water
Microclustered water, a form of mineral or alkaline water, contains smaller molecular clusters that enhance hydration and efficient nutrient absorption at the cellular level. Scientific studies indicate microclustered water's reduced surface tension improves bioavailability and antioxidant properties, distinguishing it from regular mineral or alkaline water.
Ionization Filtration
Mineral water contains naturally occurring minerals filtered through geological layers, providing essential electrolytes like calcium and magnesium without chemical alteration. Alkaline water undergoes ionization filtration, which uses an electrolysis process to raise pH levels and increase hydroxide ion concentration, aiming to neutralize acidity in the body.
Silica Enrichment
Mineral water naturally contains varying levels of silica, a beneficial trace mineral that supports skin health and bone strength, while alkaline water is often artificially enhanced to increase pH but may have inconsistent silica content. Silica enrichment in mineral water occurs through natural geological processes, making its bioavailability more effective compared to the often synthetic modifications in alkaline water.
Bicarbonate Buffering
Mineral water contains natural bicarbonates that contribute to its buffering capacity, helping maintain pH balance in the body by neutralizing excess acids. Alkaline water, often enhanced with added bicarbonates, offers a higher pH level that supports the body's acid-base equilibrium through effective bicarbonate buffering.
pH Balancing Process
Mineral water contains naturally occurring minerals and maintains a neutral pH of around 7, supporting hydration without altering the body's pH balance. Alkaline water, with a higher pH typically between 8 and 9, undergoes electrolysis or mineral infusion to neutralize acidity and promote pH balance in the bloodstream.
Functional Mineralization
Functional mineralization in mineral water refers to the natural presence of essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which contribute to hydration and electrolyte balance. Alkaline water, enhanced through ionization or added minerals, promotes a higher pH level that may help neutralize acidity in the body while offering similar hydration benefits.
Acidic Water Byproduct
Mineral water contains natural minerals like calcium and magnesium but typically has a neutral pH, while alkaline water is specifically enhanced to have a higher pH, often above 8. Acidic water byproduct, often a result of electrolysis in alkaline water systems, can cause corrosion and may negatively impact skin and environmental surfaces if not properly managed.
Mineral Water vs Alkaline Water Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com