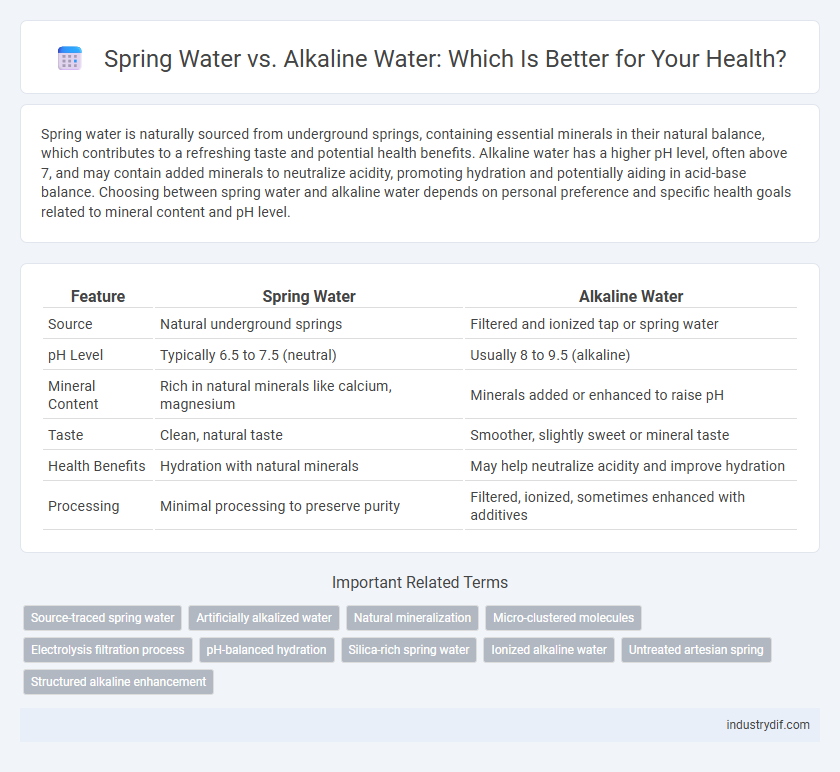
Spring water is naturally sourced from underground springs, containing essential minerals in their natural balance, which contributes to a refreshing taste and potential health benefits. Alkaline water has a higher pH level, often above 7, and may contain added minerals to neutralize acidity, promoting hydration and potentially aiding in acid-base balance. Choosing between spring water and alkaline water depends on personal preference and specific health goals related to mineral content and pH level.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spring Water | Alkaline Water |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural underground springs | Filtered and ionized tap or spring water |
| pH Level | Typically 6.5 to 7.5 (neutral) | Usually 8 to 9.5 (alkaline) |
| Mineral Content | Rich in natural minerals like calcium, magnesium | Minerals added or enhanced to raise pH |
| Taste | Clean, natural taste | Smoother, slightly sweet or mineral taste |
| Health Benefits | Hydration with natural minerals | May help neutralize acidity and improve hydration |
| Processing | Minimal processing to preserve purity | Filtered, ionized, sometimes enhanced with additives |
Understanding Spring Water: Definition and Sources
Spring water originates from natural underground sources where water flows to the surface through rock formations, often enriched with essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium. It is typically collected at protected springs to preserve its purity, distinguishing it from treated municipal water and providing a naturally balanced mineral content. Understanding the geological source of spring water is crucial, as it influences taste, mineral composition, and potential health benefits compared to alkaline water.
What Is Alkaline Water? Properties and Production
Alkaline water has a higher pH level than regular spring water, typically ranging from 8 to 10, which is believed to neutralize acid in the bloodstream and provide antioxidant benefits. It contains essential minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium, contributing to its alkaline properties and distinct taste. Production methods include natural alkaline springs, where water passes through mineral-rich rocks, and electrolysis, which uses an ionizer to raise the water's pH by separating acidic and alkaline components.
Key Mineral Content: Spring Water vs. Alkaline Water
Spring water contains natural minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which vary depending on the source and contribute to its refreshing taste and potential health benefits. Alkaline water typically has added minerals like calcium, magnesium, and bicarbonate to increase pH levels, often exceeding 7.5, which may help neutralize acidity in the body. Both types provide essential minerals, but spring water offers a naturally occurring balance, while alkaline water's mineral content is usually enhanced for alkaline properties.
pH Levels Explained: Natural vs. Enhanced Alkalinity
Spring water naturally maintains a pH level typically ranging from 6.5 to 8.0, reflecting its balanced mineral content sourced directly from underground aquifers. Alkaline water, often enhanced through added minerals such as calcium, magnesium, or potassium, boasts a higher pH level usually between 8.5 and 9.5, designed to neutralize acidity in the body. Understanding these pH differences highlights how natural spring water offers a neutral, mineral-rich hydration option, while enhanced alkaline water targets specific health benefits by increasing alkalinity.
Health Benefits: Comparing Claims of Spring and Alkaline Water
Spring water, naturally sourced from underground springs, contains essential minerals like calcium and magnesium that support hydration and electrolyte balance. Alkaline water, with a higher pH level typically above 7.5, is claimed to neutralize acid in the body and improve metabolism, though scientific evidence remains limited. Both types offer unique mineral profiles, but hydration benefits largely depend on overall water intake quality and individual health needs.
Taste and Sensory Differences
Spring water offers a natural, crisp taste due to its balanced mineral content, often featuring subtle earthy and sweet notes that enhance its refreshing quality. Alkaline water typically presents a smoother, slightly flat sensation with a higher pH level that can impart a mild, sometimes metallic or salty aftertaste. Sensory differences are influenced by mineral composition, with spring water's variability creating a more complex flavor profile compared to the consistent but less nuanced taste of alkaline water.
Sourcing and Purification Processes
Spring water is sourced directly from natural underground reservoirs and is typically filtered through rock layers that enrich it with minerals before bottling, often requiring minimal purification to preserve its natural composition. Alkaline water, on the other hand, undergoes a purification process such as reverse osmosis or filtration and is then enhanced with minerals or alkaline additives to raise its pH level. The distinctions in sourcing and purification reflect the natural mineral content in spring water versus the engineered balance in alkaline water.
Environmental Impact: Bottled Spring Water vs. Alkaline Water
Bottled spring water often has a higher environmental footprint due to plastic waste and transportation emissions tied to natural source extraction. Alkaline water, especially when produced through home filtration systems, typically reduces plastic use and carbon emissions by eliminating frequent bottled purchases. Life cycle assessments reveal spring water's extraction and bottling processes contribute significantly more to resource depletion and pollution compared to alkaline water filtration alternatives.
Safety, Regulation, and Standards
Spring water is naturally sourced from underground aquifers and is subject to strict FDA regulations ensuring it meets safety and purity standards before bottling. Alkaline water, often enhanced through filtration or additives to increase pH, lacks specific regulatory standards, leading to variability in quality and safety across brands. Consumers should prioritize products with clear testing certifications and transparency regarding pH levels, mineral content, and source verification.
Choosing the Right Water: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right water between spring water and alkaline water depends on factors such as pH level, mineral content, and intended health benefits. Spring water typically offers natural minerals and a neutral pH, supporting hydration and essential nutrient intake. Alkaline water provides a higher pH and may aid in neutralizing acid in the body, but individual needs and medical conditions should guide the choice for optimal hydration and wellness.
Related Important Terms
Source-traced spring water
Source-traced spring water originates from natural springs where water is filtered through underground rock formations, preserving essential minerals and maintaining a balanced pH. Unlike alkaline water, which is often artificially ionized, source-traced spring water provides a natural mineral composition that supports hydration and electrolyte balance.
Artificially alkalized water
Artificially alkalized water is created by adding minerals or using an electrolysis process to increase pH levels, distinguishing it from natural spring water, which maintains its balanced mineral content without chemical alteration. While spring water offers naturally occurring minerals and a stable pH, artificially alkalized water emphasizes enhanced alkalinity intended to neutralize acid in the body but may lack the trace minerals found in natural sources.
Natural mineralization
Spring water contains natural mineralization derived from underground sources, preserving essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium that contribute to its pure taste and health benefits. Alkaline water, often artificially enhanced to increase pH levels, may lack the balanced and naturally occurring minerals found in genuine spring water.
Micro-clustered molecules
Spring water contains naturally occurring minerals and maintains a neutral pH, while alkaline water is artificially ionized to increase its pH level above 7. Micro-clustered molecules in alkaline water are claimed to enhance hydration by allowing quicker absorption, although scientific evidence remains limited compared to the well-studied benefits of natural spring water.
Electrolysis filtration process
Spring water is naturally sourced from underground aquifers, maintaining its mineral content without requiring electrolysis, while alkaline water often undergoes electrolysis filtration to increase pH by separating acidic and alkaline minerals. Electrolysis filtration enhances alkaline water's antioxidant properties and potential health benefits by producing ionized, mineral-enriched water with a balanced pH typically above 8.0.
pH-balanced hydration
Spring water contains a natural pH typically ranging from 6.5 to 7.5, offering balanced hydration with essential minerals like calcium and magnesium. Alkaline water usually has a higher pH of 8 to 9.5, which may help neutralize acidity in the body but its impact on overall hydration remains subject to scientific debate.
Silica-rich spring water
Silica-rich spring water contains naturally occurring silicon dioxide, known for its potential benefits in promoting skin health and supporting bone strength, making it distinct from alkaline water, which primarily focuses on pH balance to reduce acidity in the body. Studies suggest that the bioavailability of silica in spring water enhances collagen synthesis compared to the mineral composition-driven effects of alkaline water.
Ionized alkaline water
Ionized alkaline water contains a higher pH level due to the process of electrolysis, which increases hydroxide ions and reduces acidity, potentially neutralizing body acid and promoting better hydration. In contrast, spring water is naturally sourced and rich in minerals but lacks the altered pH and ionization benefits found in alkalized water.
Untreated artesian spring
Untreated artesian spring water, sourced from confined aquifers under natural pressure, maintains its natural mineral content and purity without chemical alteration, offering a balanced pH and rich mineral profile unlike artificially alkalized water. This water type provides essential trace minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium, supporting hydration and overall health through its naturally occurring alkaline properties.
Structured alkaline enhancement
Structured alkaline water undergoes a process that reorganizes water molecules into a hexagonal cluster, enhancing absorption and hydration compared to traditional spring water. This structured alkaline enhancement increases pH levels and mineral content, promoting better antioxidant properties and supporting balanced body acidity.
Spring water vs alkaline water Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com