Mineral water contains naturally occurring minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium that support hydration and overall health. Hydrogen water is infused with molecular hydrogen, which may provide antioxidant benefits and reduce inflammation. Choosing between mineral water and hydrogen water depends on individual preferences for taste, health goals, and specific mineral content.
Table of Comparison
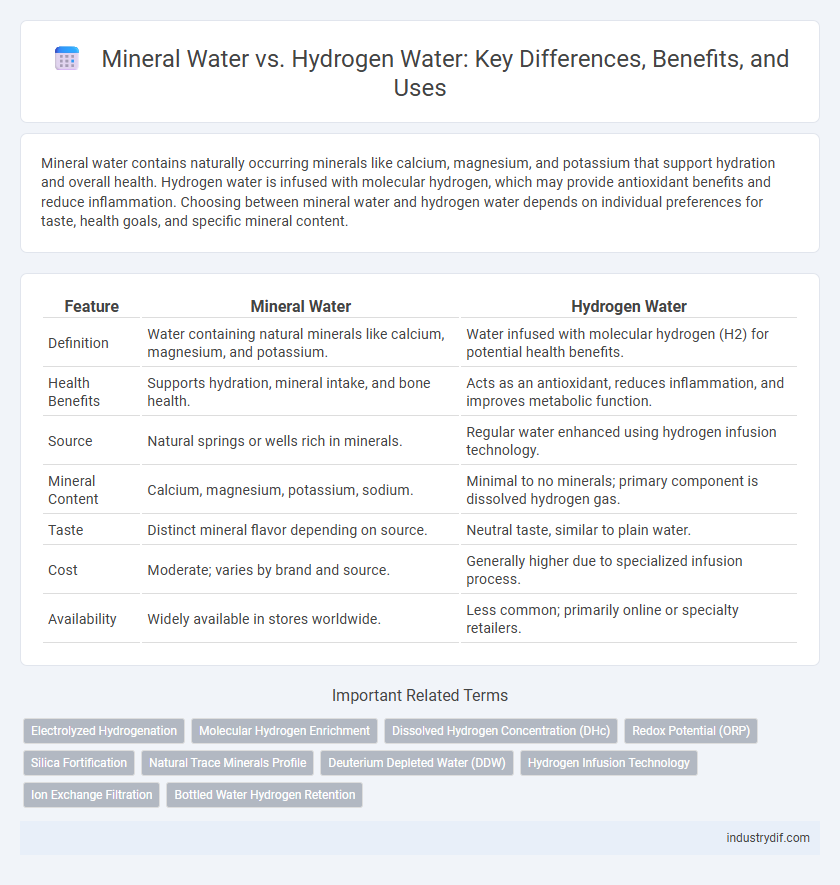
| Feature | Mineral Water | Hydrogen Water |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Water containing natural minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium. | Water infused with molecular hydrogen (H2) for potential health benefits. |
| Health Benefits | Supports hydration, mineral intake, and bone health. | Acts as an antioxidant, reduces inflammation, and improves metabolic function. |
| Source | Natural springs or wells rich in minerals. | Regular water enhanced using hydrogen infusion technology. |
| Mineral Content | Calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium. | Minimal to no minerals; primary component is dissolved hydrogen gas. |
| Taste | Distinct mineral flavor depending on source. | Neutral taste, similar to plain water. |
| Cost | Moderate; varies by brand and source. | Generally higher due to specialized infusion process. |
| Availability | Widely available in stores worldwide. | Less common; primarily online or specialty retailers. |
Understanding Mineral Water: Composition and Sources
Mineral water is naturally sourced from underground springs, enriched with minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium essential for health. Its unique composition varies based on geological formations, providing trace elements that support hydration and bodily functions. Common sources include well-known springs such as San Pellegrino and Evian, recognized for their distinct mineral profiles.
What is Hydrogen Water? Defining the New Trend
Hydrogen water is regular water infused with molecular hydrogen gas (H2), touted for its antioxidant properties and potential health benefits such as reducing inflammation and improving energy levels. Unlike mineral water, which naturally contains various minerals like calcium and magnesium contributing to taste and nutritional value, hydrogen water emphasizes molecular hydrogen concentration as its key feature. Recent studies highlight hydrogen water's ability to neutralize harmful free radicals, positioning it as a novel health trend beyond traditional mineral water consumption.
Key Differences: Mineral Water vs Hydrogen Water
Mineral water contains naturally occurring minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which contribute to its taste and health benefits, while hydrogen water is infused with molecular hydrogen aimed at providing antioxidant properties. The primary difference lies in mineral water's nutrient content versus hydrogen water's focus on reducing oxidative stress through dissolved hydrogen gas. Mineral water is sourced from natural springs, whereas hydrogen water is typically produced through electrolysis or by adding hydrogen tablets to purified water.
Health Benefits of Mineral Water
Mineral water is rich in essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which support bone health, muscle function, and cardiovascular wellness. The natural electrolytes in mineral water help maintain hydration balance and improve metabolic processes. Unlike hydrogen water, which primarily offers antioxidant properties, mineral water provides a comprehensive range of nutrients critical for overall health.
Potential Health Advantages of Hydrogen Water
Hydrogen water contains dissolved molecular hydrogen, which acts as a powerful antioxidant, potentially reducing oxidative stress and inflammation more effectively than traditional mineral water. Studies suggest that hydrogen water may improve energy metabolism, enhance recovery after exercise, and support cognitive function due to its ability to neutralize harmful free radicals. Unlike mineral water, which primarily provides essential minerals like calcium and magnesium, hydrogen water offers unique therapeutic benefits linked to cellular protection and anti-aging effects.
Taste and Texture: Sensory Comparison
Mineral water offers a crisp, slightly effervescent taste due to dissolved minerals like calcium and magnesium, providing a refreshing, clean texture. Hydrogen water tends to have a neutral flavor with a smoother, almost silky mouthfeel, attributed to the dissolved hydrogen gas which may enhance hydration perception. Sensory comparison reveals mineral water's distinct mineral notes contrast with hydrogen water's subtle softness, influencing consumer preference based on taste and texture sensitivity.
Safety and Quality Standards for Bottled Waters
Mineral water is sourced from natural springs and regulated by stringent safety standards ensuring consistent mineral content and contaminant-free purity, verified through rigorous testing protocols. Hydrogen water, infused with molecular hydrogen for potential antioxidant benefits, must adhere to safety guidelines that monitor hydrogen concentration and packaging integrity to prevent contamination and preserve efficacy. Both types of bottled waters comply with international quality standards such as ISO 22000 and FDA regulations to guarantee consumer safety and product reliability.
Environmental Impact of Production and Packaging
Mineral water production involves extracting water from natural springs, often resulting in ecosystem disruption and significant energy consumption during bottling and transport. Hydrogen water requires specialized infusion technology, which raises energy demands but may have a smaller extraction footprint compared to mineral sources. Both types typically rely on plastic packaging, contributing to environmental pollution unless recycled or replaced with sustainable materials.
Consumer Trends: Market Demand and Popularity
Consumer trends reveal a significant rise in demand for hydrogen water, driven by its marketed antioxidant properties and potential health benefits, attracting health-conscious buyers globally. Mineral water maintains consistent popularity due to its natural source minerals and perceived purity, especially in regions with quality spring access. Market data indicates a steady growth rate of over 15% annually for hydrogen water compared to a stable but mature mineral water segment.
Choosing the Right Water: Factors to Consider
Choosing between mineral water and hydrogen water depends on individual health goals and preferences. Mineral water is rich in essential minerals like calcium and magnesium that support bone density and electrolyte balance, while hydrogen water is infused with molecular hydrogen known for its antioxidant properties and potential to reduce inflammation. Consider factors such as mineral content, antioxidant benefits, taste, and specific health needs to determine the most suitable option for hydration.
Related Important Terms
Electrolyzed Hydrogenation
Mineral water is naturally rich in essential minerals like calcium and magnesium, supporting hydration and electrolyte balance, while hydrogen water undergoes electrolyzed hydrogenation to infuse molecular hydrogen, enhancing antioxidant properties and reducing oxidative stress. Electrolyzed hydrogen water typically contains dissolved hydrogen concentrations up to 1.6 ppm, promoting cellular energy production and anti-inflammatory effects beyond the basic mineral benefits found in natural mineral water.
Molecular Hydrogen Enrichment
Mineral water contains essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium naturally dissolved, while hydrogen water is enhanced with molecular hydrogen (H2) to provide antioxidant benefits by neutralizing free radicals. The enrichment of water with molecular hydrogen increases its potential to reduce oxidative stress, improve cellular health, and support metabolic processes compared to regular mineral water.
Dissolved Hydrogen Concentration (DHc)
Dissolved hydrogen concentration (DHc) in hydrogen water typically ranges from 0.5 to 1.6 parts per million (ppm), significantly higher than in mineral water, which contains negligible levels of dissolved hydrogen. Elevated DHc in hydrogen water enhances its antioxidant properties, potentially offering greater health benefits compared to traditional mineral water.
Redox Potential (ORP)
Mineral water typically has a positive oxidation-reduction potential (ORP), indicating its oxidizing properties, while hydrogen water exhibits a negative ORP, reflecting its strong antioxidant capacity by neutralizing free radicals. This negative ORP in hydrogen water enhances cellular protection against oxidative stress compared to the generally neutral to positive ORP levels found in mineral water.
Silica Fortification
Mineral water naturally contains silica, an essential trace mineral that supports bone health and skin elasticity, whereas hydrogen water is primarily valued for its antioxidant properties with minimal silica content. Silica fortification in mineral water enhances its beneficial effects on connective tissues and may contribute to overall wellness more effectively than hydrogen water lacking sufficient silica levels.
Natural Trace Minerals Profile
Natural trace minerals in mineral water, including calcium, magnesium, potassium, and sodium, contribute to essential electrolytes that support hydration and metabolic functions, while hydrogen water primarily focuses on dissolved molecular hydrogen known for its antioxidant properties but generally lacks a significant mineral content. Understanding the distinct mineral profiles helps consumers choose mineral water for nutrient supplementation and hydrogen water for potential therapeutic benefits.
Deuterium Depleted Water (DDW)
Deuterium Depleted Water (DDW) contains lower levels of deuterium, a heavy isotope of hydrogen, making it distinct from regular mineral water and hydrogen water by potentially enhancing cellular metabolism and reducing oxidative stress. Research on DDW highlights its role in promoting better hydration and supporting detoxification processes compared to traditional mineral or hydrogen-rich waters.
Hydrogen Infusion Technology
Hydrogen water, produced through advanced Hydrogen Infusion Technology, contains dissolved molecular hydrogen that offers potent antioxidant properties not found in conventional mineral water. This innovative process enhances water quality by increasing its hydrogen concentration, potentially improving hydration and reducing oxidative stress at a cellular level.
Ion Exchange Filtration
Ion exchange filtration in mineral water primarily removes hardness ions such as calcium and magnesium, enhancing purity while retaining essential minerals for taste and health benefits. In hydrogen water systems, ion exchange filtration is often combined with electrolysis to selectively reduce impurities and increase dissolved hydrogen concentration, boosting antioxidant properties.
Bottled Water Hydrogen Retention
Mineral water contains natural minerals like calcium and magnesium, offering a stable composition but limited hydrogen retention due to packaging exposure to air. Bottled hydrogen water features dissolved molecular hydrogen with antioxidant benefits, yet maintaining hydrogen concentration requires specialized, opaque, and airtight packaging to minimize gas leakage and preserve efficacy.
Mineral Water vs Hydrogen Water Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com