Potable water refers to water that is safe and suitable for human consumption, meeting health and safety standards to prevent contamination and waterborne diseases. Smart water systems integrate advanced technologies such as sensors and IoT to monitor water quality, usage, and distribution in real time, enhancing efficiency and sustainability. Combining potable water supplies with smart water management ensures reliable access to clean water while optimizing resource conservation and infrastructure maintenance.
Table of Comparison
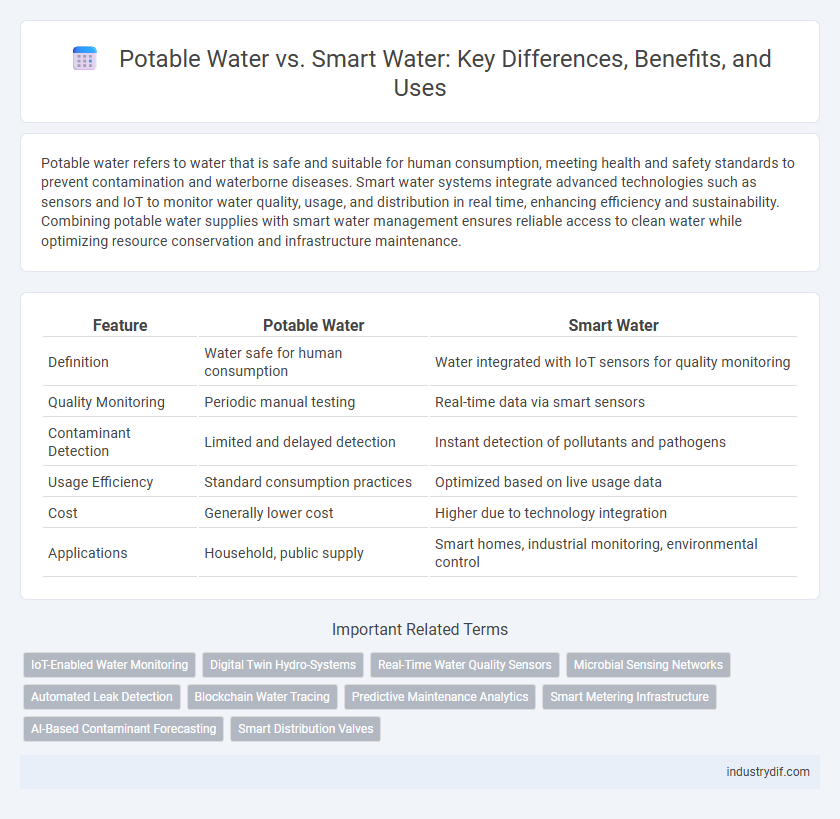
| Feature | Potable Water | Smart Water |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Water safe for human consumption | Water integrated with IoT sensors for quality monitoring |
| Quality Monitoring | Periodic manual testing | Real-time data via smart sensors |
| Contaminant Detection | Limited and delayed detection | Instant detection of pollutants and pathogens |
| Usage Efficiency | Standard consumption practices | Optimized based on live usage data |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher due to technology integration |
| Applications | Household, public supply | Smart homes, industrial monitoring, environmental control |
Definition of Potable Water
Potable water is defined as water safe for human consumption, meeting specific health standards set by regulatory authorities to ensure it is free from harmful contaminants such as pathogens, chemicals, and heavy metals. This type of water is essential for drinking, cooking, and sanitation, providing a reliable source of hydration and hygiene. Unlike smart water, which often incorporates enhanced mineral content and packaging technology, potable water emphasizes safety and purity as fundamental criteria.
Understanding Smart Water Technology
Smart water technology integrates sensors, data analytics, and IoT systems to monitor and manage potable water quality, distribution, and consumption in real-time. This technology enables early detection of contaminants, reduces water waste, and ensures consistent compliance with health standards. By leveraging smart water systems, utilities enhance resource efficiency and provide safer, more reliable potable water access to communities.
Key Differences Between Potable and Smart Water
Potable water refers to water that is safe for human consumption, meeting regulatory standards for contaminants and pathogens, while smart water incorporates advanced filtration and IoT technology to monitor and manage water quality in real-time. Key differences include the integration of sensors in smart water systems that track pH levels, temperature, and chemical content, enabling proactive maintenance and personalized hydration. Potable water standards rely on periodic testing, whereas smart water offers continuous data-driven insights to enhance safety, taste, and efficiency in water usage.
Water Purification Methods Compared
Potable water typically undergoes conventional purification methods such as filtration, chlorination, and UV treatment to remove pathogens and contaminants. Smart water systems integrate advanced purification technologies including real-time sensors, reverse osmosis, and IoT-enabled monitoring to ensure optimal water quality and efficiency. Comparative analysis highlights that smart water purification offers enhanced control, reduced chemical use, and continuous quality assessment compared to traditional potable water treatment.
Health and Safety Standards for Drinking Water
Potable water meets strict health and safety standards set by agencies like the EPA and WHO, ensuring it is free from harmful contaminants and safe for human consumption. Smart water incorporates advanced monitoring technologies such as real-time sensors to detect pollutants and maintain water quality consistently above regulatory limits. These innovations enhance drinking water safety by enabling rapid response to potential hazards and promoting optimal public health outcomes.
IoT Integration in Smart Water Systems
Smart water systems leverage IoT integration to monitor and manage potable water quality in real-time, enhancing safety and efficiency. Sensors embedded within these systems collect data on parameters like pH, turbidity, and contaminant levels, enabling predictive maintenance and rapid response to contamination events. This IoT-driven approach ensures continuous water quality monitoring, reduces wastage, and supports sustainable water resource management.
Cost Analysis: Potable Water vs Smart Water
The cost analysis of potable water versus smart water reveals significant differences influenced by technology integration and infrastructure requirements. Potable water systems incur ongoing expenses related to purification, distribution, and maintenance, typically ranging from $1 to $3 per 1,000 gallons depending on region and treatment methods. Smart water solutions, leveraging IoT sensors and real-time monitoring, may have higher initial capital costs but reduce long-term operational expenses by optimizing resource management, leak detection, and consumption patterns, resulting in cost savings up to 20-30% over conventional potable water systems.
Environmental Impact of Water Solutions
Potable water systems often require extensive energy for treatment and distribution, contributing to higher carbon emissions and resource depletion. Smart water technologies utilize real-time monitoring and data analytics to optimize water usage, reduce waste, and enhance efficiency, significantly lowering environmental footprints. Implementing smart water solutions leads to sustainable water management by minimizing chemical use and preventing leakages, thereby preserving natural ecosystems.
Future Trends in Water Industry Technology
Potable water innovation is rapidly evolving with the integration of smart water technologies that enhance monitoring and management through real-time data analytics and IoT sensors. Future trends emphasize AI-driven water quality assessment and predictive maintenance to ensure safe, efficient distribution and minimize contamination risks. Sustainable water infrastructure incorporating smart meters and automated leak detection systems are transforming resource conservation in urban and industrial sectors worldwide.
Consumer Adoption and Market Outlook
Potable water remains the primary choice for consumers due to regulatory standards ensuring safety and accessibility, while smart water, embedded with IoT technology, is gaining traction for its enhanced quality monitoring and personalization features. Market forecasts predict a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 8% for smart water devices from 2024 to 2030, driven by increasing health awareness and technological advancement. Consumer adoption trends highlight a shift towards premium products with integrated digital capabilities, signaling a transformative outlook for the water industry.
Related Important Terms
IoT-Enabled Water Monitoring
IoT-enabled water monitoring systems enhance potable water safety by providing real-time data on quality parameters such as pH, turbidity, and contamination levels, enabling immediate response to potential hazards. Smart water solutions integrate sensors and analytics to optimize water usage, reduce waste, and ensure sustainable management of potable water resources.
Digital Twin Hydro-Systems
Digital Twin Hydro-Systems revolutionize potable water management by creating precise virtual replicas of physical water infrastructure, enabling real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized resource allocation. These advanced digital models enhance the efficiency and safety of drinking water distribution networks, reducing contamination risks and operational costs while supporting sustainable water management practices.
Real-Time Water Quality Sensors
Real-time water quality sensors enable continuous monitoring of potable water by detecting contaminants such as pathogens, heavy metals, and chemical pollutants, ensuring safety and compliance with health standards. In contrast, smart water systems integrate these sensors with IoT technology to provide dynamic data analytics, predictive maintenance, and efficient water resource management.
Microbial Sensing Networks
Potable water systems rely on traditional microbial testing methods with time-intensive sampling and laboratory analysis, while smart water networks integrate real-time microbial sensing technologies that enable continuous monitoring of pathogens and contaminants. Microbial sensing networks use advanced biosensors and IoT connectivity to rapidly detect water quality fluctuations, enhancing early warning capabilities and ensuring safer water distribution.
Automated Leak Detection
Potable water systems ensure safe drinking water quality while smart water networks integrate automated leak detection technologies to monitor distribution in real-time, minimizing water loss and preventing infrastructure damage. Automated sensors and IoT-enabled devices promptly identify leaks, optimize maintenance schedules, and enhance the efficiency of potable water delivery systems.
Blockchain Water Tracing
Potable water undergoes rigorous purification to ensure safety for human consumption, while smart water leverages blockchain technology for transparent, immutable water tracing, enhancing quality control and resource management. Blockchain water tracing enables real-time monitoring of water sources, distribution, and usage, reducing contamination risks and promoting sustainable water governance.
Predictive Maintenance Analytics
Predictive maintenance analytics in potable water systems enhances the detection of pipeline leaks, contamination risks, and equipment failures by analyzing real-time sensor data and historical trends. Smart water networks leverage advanced IoT devices and machine learning algorithms to optimize water quality monitoring, reduce operational costs, and ensure consistent delivery of safe drinking water.
Smart Metering Infrastructure
Smart water metering infrastructure enhances potable water management by providing real-time data on consumption, leak detection, and pressure monitoring, enabling efficient resource use and reducing wastage. Integration of IoT sensors and advanced analytics within smart meters facilitates precise demand forecasting and proactive maintenance, optimizing water distribution networks.
AI-Based Contaminant Forecasting
Potable water ensures safety for human consumption by meeting strict health standards, while smart water systems utilize AI-based contaminant forecasting to predict and prevent water quality issues in real time. These advanced AI algorithms analyze sensor data and environmental variables, enabling proactive management of contaminants for improved water safety and resource efficiency.
Smart Distribution Valves
Smart distribution valves in water management enable precise control and real-time monitoring, enhancing efficiency and reducing water loss compared to traditional potable water systems. These valves integrate with IoT technology to optimize flow rates, detect leaks early, and support sustainable water distribution infrastructure.
Potable Water vs Smart Water Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com