Desalinated water is produced by removing salt and impurities from seawater through processes like reverse osmosis, making it suitable for drinking and irrigation. Electrolyzed water, generated by applying an electric current to saline water, has potent antimicrobial properties and is widely used for disinfection and sanitation. Both types of water serve distinct purposes, with desalinated water addressing freshwater scarcity and electrolyzed water enhancing hygiene and safety in various applications.
Table of Comparison
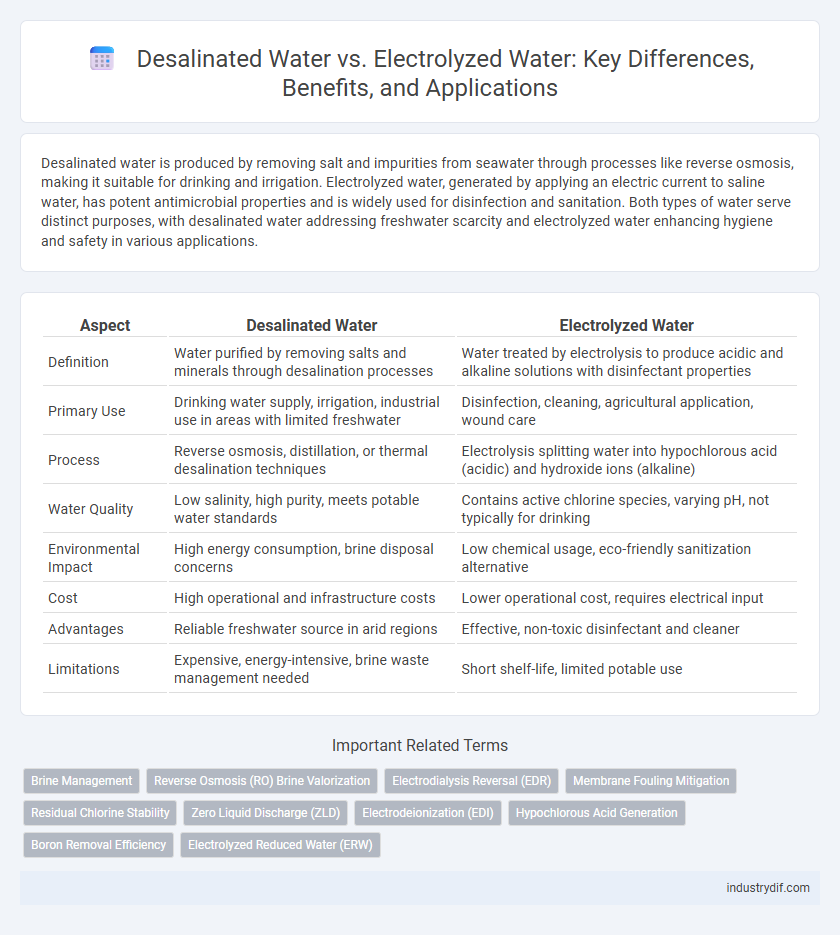
| Aspect | Desalinated Water | Electrolyzed Water |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Water purified by removing salts and minerals through desalination processes | Water treated by electrolysis to produce acidic and alkaline solutions with disinfectant properties |
| Primary Use | Drinking water supply, irrigation, industrial use in areas with limited freshwater | Disinfection, cleaning, agricultural application, wound care |
| Process | Reverse osmosis, distillation, or thermal desalination techniques | Electrolysis splitting water into hypochlorous acid (acidic) and hydroxide ions (alkaline) |
| Water Quality | Low salinity, high purity, meets potable water standards | Contains active chlorine species, varying pH, not typically for drinking |
| Environmental Impact | High energy consumption, brine disposal concerns | Low chemical usage, eco-friendly sanitization alternative |
| Cost | High operational and infrastructure costs | Lower operational cost, requires electrical input |
| Advantages | Reliable freshwater source in arid regions | Effective, non-toxic disinfectant and cleaner |
| Limitations | Expensive, energy-intensive, brine waste management needed | Short shelf-life, limited potable use |
Introduction to Desalinated and Electrolyzed Water
Desalinated water is produced by removing salts and impurities from seawater or brackish water using processes such as reverse osmosis or distillation, making it suitable for drinking and irrigation. Electrolyzed water is generated through the electrolysis of saline water, producing a solution with disinfectant properties primarily used for sanitization and cleaning purposes. Both technologies address water quality challenges but serve distinct applications based on their chemical composition and treatment methods.
Defining Desalinated Water: Process and Applications
Desalinated water is produced through processes like reverse osmosis and distillation, removing salts and impurities from seawater or brackish water to make it suitable for human consumption and irrigation. This method addresses freshwater scarcity in coastal and arid regions by converting saline sources into potable water. Common applications include municipal water supply, agriculture, and industrial uses where freshwater availability is limited.
What is Electrolyzed Water? Generation and Uses
Electrolyzed water is generated by passing an electric current through a saltwater solution, producing a mixture of hypochlorous acid and hydroxide ions, which exhibit strong disinfectant properties. This process, known as electrolysis, results in water effective for microbial sanitation, wound care, and surface cleaning without harmful chemicals. Electrolyzed water is widely used in healthcare settings, food processing, and agriculture for its eco-friendly and non-toxic antimicrobial benefits compared to traditional disinfectants and desalinated water.
Key Differences in Production Methods
Desalinated water is produced by removing salts and impurities from seawater or brackish water through processes such as reverse osmosis or distillation, effectively making it suitable for human consumption and irrigation. Electrolyzed water is generated by applying an electric current to a saline solution, causing chemical reactions that produce disinfectant agents like hypochlorous acid, commonly used for sanitation purposes. The primary difference lies in desalination focusing on purification by physical separation, whereas electrolysis involves chemical alteration to create antimicrobial properties.
Water Quality: Purity and Safety Comparison
Desalinated water undergoes reverse osmosis or distillation, effectively removing salts, minerals, and contaminants to achieve high purity levels suitable for drinking. Electrolyzed water, produced through electrolysis, contains active chlorine species that provide strong antimicrobial properties but may introduce residual chemicals affecting taste and safety perception. Evaluating water quality requires balancing the near-complete contaminant removal in desalinated water against the disinfection advantages and potential chemical residues present in electrolyzed water.
Industrial Applications: Desalinated vs Electrolyzed Water
Desalinated water, produced through processes like reverse osmosis, is essential in industrial applications requiring large volumes of purified water free from salts and minerals, such as boiler feedwater and manufacturing cooling systems. Electrolyzed water, generated by the electrolysis of saline solutions, serves primarily as a disinfectant and cleaning agent in food processing, pharmaceutical production, and surface sanitization due to its strong oxidizing properties. Industries prioritize desalinated water for processes demanding high water purity and electrolyzed water for its antimicrobial efficacy and eco-friendly sanitization capabilities.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Desalinated water production relies heavily on energy-intensive reverse osmosis or thermal distillation processes, leading to significant carbon emissions and brine waste that can harm marine ecosystems. Electrolyzed water, generated through electrolysis of saline or tap water, offers a low-energy, chemical-free alternative with minimal byproducts and reduced ecological footprint. Sustainable water management favors electrolyzed water for its potential to decrease reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate environmental degradation linked to conventional desalination methods.
Cost Analysis: Desalination vs Electrolysis
Desalinated water production involves high capital and operational costs due to energy-intensive processes like reverse osmosis or thermal distillation, often priced around $0.50 to $3.00 per cubic meter depending on scale and technology. Electrolyzed water, generated through electrolysis of saline or brackish water, incurs expenses primarily from electricity consumption and electrode maintenance, generally lower but variable based on energy prices and system efficiency. Evaluating cost-effectiveness requires comparing local energy costs, water quality needs, and infrastructure investments, with desalination favored for large-scale freshwater supply and electrolysis suited for smaller, specialized applications.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Desalinated water must adhere to stringent regulatory standards such as the World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulations to ensure safe removal of salts and contaminants. Electrolyzed water, used primarily for disinfection, is subject to compliance with standards set by agencies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) to verify appropriate pH levels and residual chlorine concentration. Both water types require rigorous quality control testing to meet health and safety benchmarks for public and industrial use.
Future Trends in Advanced Water Treatment Technologies
Desalinated water production is increasingly driven by innovations in reverse osmosis and energy recovery systems, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs for large-scale potable water supply. Electrolyzed water technology is gaining traction for its multifunctional applications, including disinfection and wastewater treatment, enabled by advancements in electrode materials and electrochemical cell design. Future trends indicate a convergence of these technologies with AI-driven process optimization and renewable energy integration to address global water scarcity sustainably.
Related Important Terms
Brine Management
Desalinated water production generates highly concentrated brine, posing significant environmental challenges for disposal and necessitating advanced brine management techniques like zero liquid discharge systems and brine dilution to protect marine ecosystems. In contrast, electrolyzed water produces minimal brine byproducts, offering a more sustainable alternative with reduced impact on salt balance and easier waste handling in water treatment processes.
Reverse Osmosis (RO) Brine Valorization
Reverse osmosis (RO) brine valorization transforms concentrated desalinated water waste into valuable resources by extracting minerals and enabling sustainable water reuse. Electrolyzed water, unlike RO brine, undergoes electrochemical activation to enhance antimicrobial properties but does not address brine disposal or recovery of salts inherent in RO processes.
Electrodialysis Reversal (EDR)
Electrodialysis Reversal (EDR) technology efficiently removes salts and ions from brackish water by periodically reversing the polarity, minimizing membrane fouling and scaling, which enhances the desalination process compared to traditional methods. EDR provides a sustainable alternative to producing potable water with lower energy consumption and operational costs than conventional reverse osmosis systems used in desalinated water production.
Membrane Fouling Mitigation
Desalinated water systems primarily face membrane fouling due to high concentrations of salts and organic matter, requiring advanced pre-treatment techniques like ultrafiltration and chemical dosing to mitigate fouling and maintain membrane permeability. Electrolyzed water reduces membrane fouling risks by generating reactive species that disrupt biofilm formation and degrade contaminants, enhancing membrane lifespan and filtration efficiency in water treatment applications.
Residual Chlorine Stability
Desalinated water typically exhibits low residual chlorine stability due to the removal of minerals that buffer chlorine degradation, whereas electrolyzed water maintains higher residual chlorine levels, enhancing disinfection efficacy over extended periods. The stable presence of active chlorine species in electrolyzed water ensures prolonged antimicrobial effects compared to the rapid depletion seen in desalinated water.
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD)
Desalinated water, produced through reverse osmosis or thermal processes, often faces challenges in achieving Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) due to brine management and high energy consumption, whereas electrolyzed water systems enhance ZLD feasibility by generating minimal waste streams and enabling onsite reuse of purified water. Advanced electrolyzed water technologies optimize resource recovery and reduce environmental impact, positioning them as efficient solutions for sustainable water treatment in water-scarce regions.
Electrodeionization (EDI)
Electrodeionization (EDI) combines ion exchange membranes and electricity to remove ionized species from water, producing ultra-pure water without chemical regenerants, distinguishing it from traditional desalinated water processes like reverse osmosis or thermal distillation. EDI is highly efficient for water treatment in industries requiring continuous, high-quality water such as pharmaceuticals, power generation, and microelectronics, offering lower operational costs and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional desalination methods.
Hypochlorous Acid Generation
Desalinated water typically undergoes reverse osmosis to remove salts, whereas electrolyzed water is produced by passing an electric current through saltwater, generating hypochlorous acid (HOCl), a potent disinfectant. Hypochlorous acid generation in electrolyzed water offers effective microbial control with low chemical residue, making it a preferred method for sanitation compared to chemically treated desalinated water.
Boron Removal Efficiency
Desalinated water, particularly from reverse osmosis plants, typically achieves boron removal rates of 90-95%, while electrolyzed water processes generally demonstrate lower efficiency, often below 70% in boron reduction. Advanced membrane technologies and optimized electrolysis parameters are critical for improving boron removal in electrolyzed water systems compared to conventional desalination methods.
Electrolyzed Reduced Water (ERW)
Electrolyzed Reduced Water (ERW) is generated through water electrolysis, producing alkaline water rich in molecular hydrogen with potent antioxidant properties that support cellular health. Unlike desalinated water which primarily removes salts and impurities, ERW enhances hydration and may offer therapeutic benefits due to its negative oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) and bioactive hydrogen content.
Desalinated Water vs Electrolyzed Water Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com