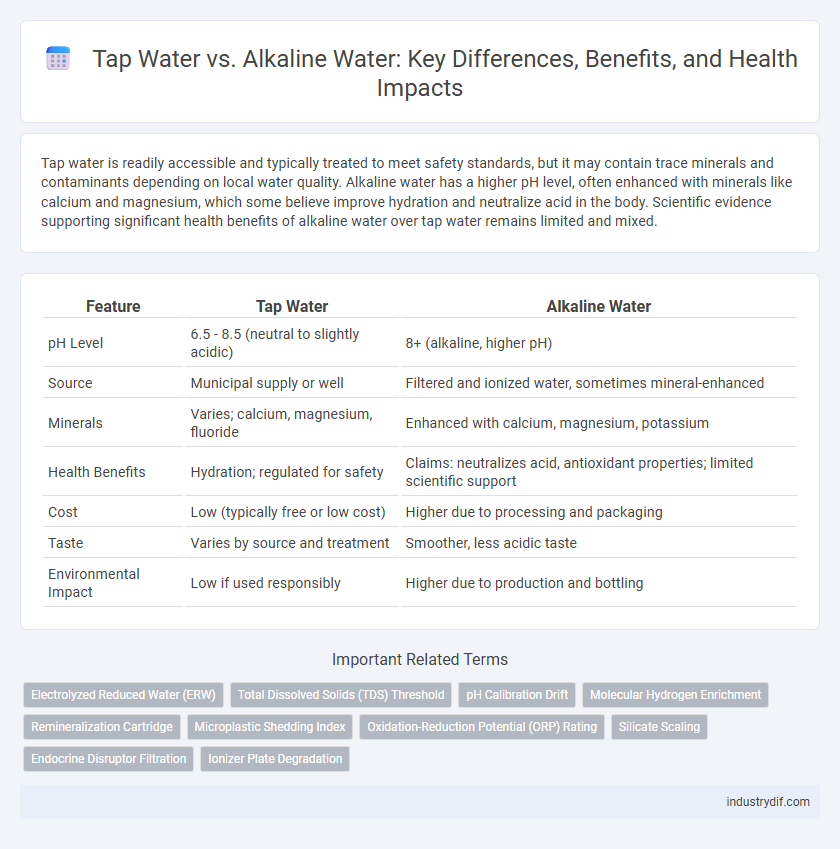
Tap water is readily accessible and typically treated to meet safety standards, but it may contain trace minerals and contaminants depending on local water quality. Alkaline water has a higher pH level, often enhanced with minerals like calcium and magnesium, which some believe improve hydration and neutralize acid in the body. Scientific evidence supporting significant health benefits of alkaline water over tap water remains limited and mixed.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tap Water | Alkaline Water |
|---|---|---|
| pH Level | 6.5 - 8.5 (neutral to slightly acidic) | 8+ (alkaline, higher pH) |
| Source | Municipal supply or well | Filtered and ionized water, sometimes mineral-enhanced |
| Minerals | Varies; calcium, magnesium, fluoride | Enhanced with calcium, magnesium, potassium |
| Health Benefits | Hydration; regulated for safety | Claims: neutralizes acid, antioxidant properties; limited scientific support |
| Cost | Low (typically free or low cost) | Higher due to processing and packaging |
| Taste | Varies by source and treatment | Smoother, less acidic taste |
| Environmental Impact | Low if used responsibly | Higher due to production and bottling |
Understanding Tap Water Composition
Tap water typically contains minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and sodium, along with trace amounts of chlorine and fluoride added for disinfection and dental health. The exact composition varies based on geographical location and local water treatment processes, impacting taste and mineral content. Understanding these components helps consumers evaluate potential health benefits and risks compared to alkaline water, which is characterized by a higher pH and added minerals for alkalinity.
What Is Alkaline Water?
Alkaline water has a higher pH level than regular tap water, typically ranging from 8 to 9.5, due to added minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium which increase its alkalinity. This elevated pH is believed to neutralize acid in the bloodstream, potentially offering health benefits such as improved hydration and reduced acid reflux.
pH Levels: Tap Water vs Alkaline Water
Tap water typically has a neutral pH level around 7, varying slightly depending on the source and treatment process. Alkaline water generally features a higher pH, ranging from 8 to 10, which proponents claim can help neutralize acid in the bloodstream. The elevated pH level in alkaline water is achieved through ionization or adding minerals such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium.
Filtration Methods and Standards
Tap water undergoes municipal filtration processes such as sediment filtration, chlorination, and sometimes fluoridation to meet safety standards established by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Alkaline water is typically filtered using reverse osmosis or activated carbon filters followed by ionization to increase pH levels, complying with Food and Drug Administration (FDA) guidelines for bottled water quality. Both filtration methods target contaminants but differ in treatment objectives: tap water focuses on basic purification and regulatory compliance, while alkaline water emphasizes pH balance and mineral content enhancement.
Health Benefits: Myth vs Science
Tap water provides essential minerals like calcium and magnesium necessary for hydration and bodily functions, while alkaline water, with its higher pH, is often marketed for detoxification and acid reflux relief despite limited scientific evidence supporting these claims. Studies show the body's natural buffering systems maintain pH balance regardless of water intake, making the health benefits of alkaline water largely anecdotal. Consuming tap water from safe sources remains a reliable, scientifically validated method for maintaining hydration and overall health.
Potential Risks and Contaminants
Tap water may contain contaminants such as chlorine, lead, and microorganisms that pose health risks if not properly treated, whereas alkaline water, despite its higher pH, can contain impurities depending on the source and filtration process. Consuming alkaline water excessively may disrupt the body's natural acid-base balance, potentially causing metabolic alkalosis. Both types require regular testing and filtration to minimize exposure to harmful substances and ensure safety for daily hydration.
Cost Comparison: Tap Water vs Alkaline Water
Tap water typically costs less than $0.01 per gallon, making it one of the most affordable hydration options available, while alkaline water averages around $1.00 to $3.00 per gallon depending on brand and packaging. The significant price difference is due to alkaline water undergoing additional filtration and mineral enhancement processes. For long-term daily consumption, tap water offers substantial cost savings compared to alkaline water's premium pricing.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Tap water generally has a lower environmental impact compared to alkaline water due to minimal processing and local distribution, which reduces energy consumption and carbon emissions. Alkaline water production often involves additional filtration, mineralization, and packaging in plastic bottles, contributing to greater resource use and waste generation. Lifecycle assessments reveal that tap water's reliance on existing infrastructure and limited bottling processes makes it a more sustainable choice for reducing environmental footprints.
Regulatory Guidelines and Quality Control
Tap water is regulated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) under the Safe Drinking Water Act, ensuring strict safety standards and regular testing for contaminants like lead, chlorine, and bacteria. Alkaline water, often marketed as a health product, falls under less stringent regulatory oversight by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and lacks mandatory quality control measures present in municipal tap water systems. Consumers seeking consistent water quality should consider the rigorous testing protocols and contaminant limits that govern tap water compared to the variable standards for alkaline water products.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences show a growing shift toward alkaline water due to perceived health benefits, including improved hydration and acid-base balance. Market trends indicate a surge in alkaline water sales driven by premium branding and increased availability in retail and online stores. Tap water remains dominant in daily use for its accessibility and cost-effectiveness but faces challenges from concerns over contamination and taste.
Related Important Terms
Electrolyzed Reduced Water (ERW)
Electrolyzed Reduced Water (ERW) is a type of alkaline water produced through electrolysis, which increases its pH and antioxidant properties by generating molecular hydrogen and reducing oxidation-reduction potential. Compared to regular tap water, ERW offers enhanced hydration benefits and may help neutralize free radicals, potentially improving cellular health and reducing oxidative stress.
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) Threshold
Tap water typically contains Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) levels ranging from 50 to 500 mg/L, which can affect taste and mineral content, while alkaline water generally maintains a lower TDS threshold, around 30 to 100 mg/L, promoting a cleaner, softer taste and enhanced hydration benefits due to its balanced mineral composition. Monitoring TDS levels is crucial in both water types to ensure safety, optimal taste, and health advantages, as excessively high TDS levels in tap water may indicate contamination or poor water quality.
pH Calibration Drift
Tap water typically has a pH around 7, but calibration drift in pH meters can cause inaccurate readings when measuring its neutrality. Alkaline water, with a pH typically between 8 and 9, requires frequent recalibration of pH meters to maintain precise monitoring and avoid measurement errors due to drift.
Molecular Hydrogen Enrichment
Tap water typically contains minimal molecular hydrogen, whereas alkaline water is often enriched with higher concentrations of molecular hydrogen, which acts as a potent antioxidant. Studies suggest that molecular hydrogen-enriched alkaline water can reduce oxidative stress and inflammation more effectively than regular tap water.
Remineralization Cartridge
Remineralization cartridges in alkaline water filters restore essential minerals like calcium and magnesium that are typically removed during the reverse osmosis process, enhancing both taste and health benefits. Tap water generally lacks this targeted mineral restoration, often resulting in lower pH and fewer vital minerals compared to alkaline water treated with a remineralization cartridge.
Microplastic Shedding Index
Tap water often contains higher levels of microplastic particles compared to alkaline water, which typically undergoes additional filtration processes that reduce microplastic shedding. The Microplastic Shedding Index highlights that alkaline water's enhanced purification methods result in substantially lower microplastic contamination, making it a safer choice for minimizing exposure to environmental pollutants.
Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP) Rating
Tap water typically has a positive oxidation-reduction potential (ORP), indicating oxidizing properties that may contribute to free radical formation, whereas alkaline water often exhibits a negative ORP, signifying antioxidant potential that can help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body. Monitoring the ORP rating is crucial for evaluating water's impact on oxidative stress and overall health benefits.
Silicate Scaling
Tap water often contains higher levels of silicates that can contribute to scaling on surfaces and appliances, leading to reduced efficiency and increased maintenance costs. Alkaline water typically has lower silicate concentrations, minimizing silicate scaling and preserving the longevity of plumbing systems and water-using devices.
Endocrine Disruptor Filtration
Tap water often contains trace amounts of endocrine-disrupting chemicals such as BPA, phthalates, and parabens that standard municipal filtration systems may not fully remove. Alkaline water filtration systems typically incorporate advanced technologies like reverse osmosis and activated carbon filters designed to reduce or eliminate these harmful endocrine disruptors, potentially offering a safer alternative for hormonal health.
Ionizer Plate Degradation
Ionizer plate degradation in alkaline water machines occurs due to mineral buildup and frequent use, reducing the efficiency of electrolysis and lowering the water's pH over time. Tap water with high hardness accelerates this process, necessitating regular maintenance to preserve ionizer plate performance and ensure consistent alkaline water quality.
Tap Water vs Alkaline Water Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com