Effective wastewater management involves treating and recycling water from domestic, industrial, and agricultural sources to reduce environmental pollution and conserve resources. Brine management specifically addresses the disposal and treatment of highly concentrated saltwater byproducts from desalination and industrial processes, requiring advanced techniques to prevent soil and water contamination. Understanding the distinct challenges and solutions for wastewater versus brine management is essential for sustainable water resource management and environmental protection.
Table of Comparison
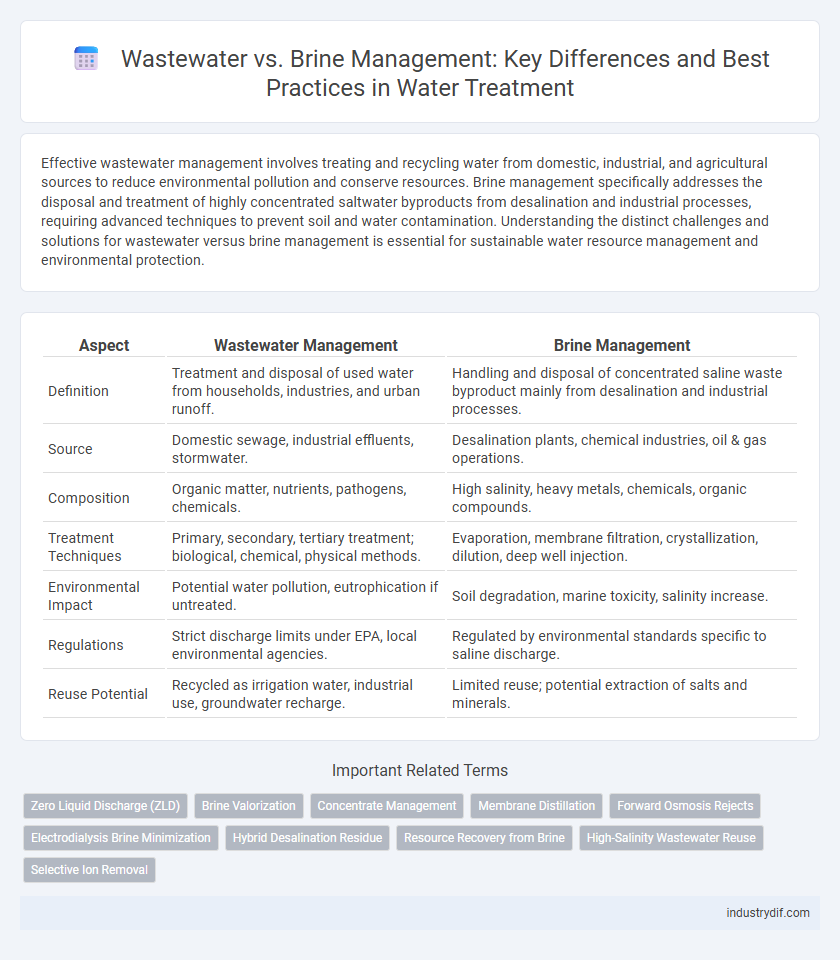
| Aspect | Wastewater Management | Brine Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Treatment and disposal of used water from households, industries, and urban runoff. | Handling and disposal of concentrated saline waste byproduct mainly from desalination and industrial processes. |
| Source | Domestic sewage, industrial effluents, stormwater. | Desalination plants, chemical industries, oil & gas operations. |
| Composition | Organic matter, nutrients, pathogens, chemicals. | High salinity, heavy metals, chemicals, organic compounds. |
| Treatment Techniques | Primary, secondary, tertiary treatment; biological, chemical, physical methods. | Evaporation, membrane filtration, crystallization, dilution, deep well injection. |
| Environmental Impact | Potential water pollution, eutrophication if untreated. | Soil degradation, marine toxicity, salinity increase. |
| Regulations | Strict discharge limits under EPA, local environmental agencies. | Regulated by environmental standards specific to saline discharge. |
| Reuse Potential | Recycled as irrigation water, industrial use, groundwater recharge. | Limited reuse; potential extraction of salts and minerals. |
Introduction to Wastewater and Brine
Wastewater consists of used water from domestic, industrial, and agricultural sources containing contaminants that require treatment before environmental discharge. Brine, a highly concentrated saline byproduct primarily generated during desalination and certain industrial processes, poses unique disposal challenges due to its high salt content and environmental toxicity. Effective management of both wastewater and brine involves advanced treatment technologies to minimize ecological impact and promote sustainable water reuse.
Key Differences Between Wastewater and Brine
Wastewater primarily consists of used water from domestic, industrial, and commercial sources containing organic and inorganic contaminants, whereas brine is a highly concentrated saline solution typically generated from desalination or industrial processes. Wastewater treatment focuses on reducing biological and chemical pollutants to safe levels for discharge or reuse, while brine management involves handling high-salinity effluents that require specialized treatment to prevent environmental harm. Key differences include their composition, treatment methods, and environmental impact, with brine posing greater challenges due to its high salt content and potential toxicity.
Sources of Wastewater in Industry
Industrial wastewater primarily originates from manufacturing processes, cooling systems, and cleaning operations across sectors such as chemical production, food processing, and textile manufacturing. Brine, a highly concentrated saline waste, is typically generated from desalination plants, oil and gas extraction, and certain chemical industries. Effective management of these waste streams is crucial to prevent environmental contamination and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Brine Generation Processes
Brine generation primarily occurs during desalination processes such as reverse osmosis and thermal distillation, where high concentrations of salt and chemicals remain after freshwater extraction. Industrial activities like chemical manufacturing and mining also contribute significant brine volumes with complex compositions. Effective brine management requires understanding these generation processes to optimize treatment and disposal strategies while minimizing environmental impact.
Environmental Impacts of Wastewater Discharge
Wastewater discharge introduces contaminants such as heavy metals, nutrients, and pathogens into aquatic ecosystems, leading to eutrophication, biodiversity loss, and water quality degradation. In contrast, managing brine, often a byproduct of desalination, requires careful handling due to its high salinity and potential to disrupt marine habitats through increased salinity levels and chemical additives. Effective treatment and disposal strategies are essential to minimize toxic effects, protect aquatic life, and ensure sustainable water resource management.
Challenges in Brine Management
High salinity and toxic contaminants in brine pose significant challenges for effective wastewater treatment, leading to environmental risks like soil salinization and aquatic toxicity. Advanced treatment methods such as crystallization and membrane filtration demand high energy and operational costs, limiting their widespread adoption. The management of large volumes of concentrated brine also raises disposal and regulatory concerns, necessitating innovative, sustainable solutions for minimizing ecological impact.
Treatment Technologies for Wastewater
Advanced treatment technologies for wastewater include membrane filtration, activated sludge processes, and biological nutrient removal, which effectively reduce contaminants and organic matter. These methods achieve high pollutant removal efficiencies, enabling water reuse and minimizing environmental impact. In contrast to brine management, wastewater treatment prioritizes the removal of biodegradable materials and toxic substances, supporting sustainable water resource management.
Brine Treatment and Disposal Solutions
Brine treatment and disposal solutions are critical components of effective wastewater management, addressing the challenges posed by high salinity and potential environmental hazards. Advanced treatment technologies such as reverse osmosis, thermal evaporation, and crystallization enable the reduction of volume and recovery of valuable salts from brine streams. Proper brine disposal methods, including deep well injection and zero liquid discharge systems, minimize ecological impact while ensuring regulatory compliance in industrial and municipal water treatment facilities.
Regulatory Frameworks for Wastewater and Brine
Regulatory frameworks for wastewater and brine management encompass strict discharge limits, treatment standards, and disposal requirements established by agencies like the EPA and regional environmental authorities. Wastewater regulations focus on biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), total suspended solids (TSS), and toxic contaminants, while brine management addresses high salinity, heavy metal content, and potential impacts on groundwater. Compliance with permits such as the National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) is essential to mitigate environmental risks and ensure sustainable water resource management.
Future Trends in Water and Brine Management
Emerging future trends in wastewater and brine management emphasize advanced treatment technologies such as membrane bioreactors, forward osmosis, and zero-liquid discharge systems to enhance resource recovery and reduce environmental impact. Integration of smart monitoring systems powered by AI and IoT enables real-time management and optimization of brine concentration, minimizing disposal volumes and operational costs. Increasing regulatory pressures and sustainability goals drive innovation towards circular water economy models, promoting reuse of treated wastewater and brine in industrial processes and agriculture.
Related Important Terms
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD)
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) technology effectively manages wastewater and brine by recovering nearly all water from industrial effluents, eliminating liquid discharge to the environment. This process minimizes environmental impact and maximizes resource recovery through advanced treatment methods such as evaporation, crystallization, and membrane filtration.
Brine Valorization
Brine valorization transforms high-salinity brine from wastewater treatment into valuable products such as salts, minerals, and bioenergy, promoting sustainable resource recovery. Advanced techniques like membrane filtration, crystallization, and thermal processes enhance the economic and environmental benefits by reducing disposal volumes and extracting usable materials.
Concentrate Management
Concentrate management in wastewater treatment involves controlling the byproduct brine, which contains high levels of salts and contaminants that require careful disposal or reuse to prevent environmental harm. Advanced techniques such as zero liquid discharge (ZLD) and membrane crystallization optimize resource recovery and minimize brine volume, enhancing sustainability in industrial water management.
Membrane Distillation
Membrane distillation effectively separates contaminants from wastewater and brine by utilizing hydrophobic membranes that allow vapor transfer while retaining dissolved solids, enhancing water recovery and reducing environmental discharge. This technology outperforms traditional methods in energy efficiency and salt rejection rates, making it ideal for sustainable wastewater and brine management in desalination and treatment processes.
Forward Osmosis Rejects
Forward osmosis rejects generate a concentrated waste stream that poses significant challenges in wastewater and brine management due to high salinity and contaminant loads. Effective treatment strategies for these rejects are critical to minimize environmental impact and enable resource recovery in water reuse and desalination processes.
Electrodialysis Brine Minimization
Electrodialysis brine minimization technology effectively reduces the volume and environmental impact of brine generated in wastewater treatment by selectively removing salts and contaminants through ion-exchange membranes. This process enhances resource recovery, lowers disposal costs, and supports sustainable water management practices in industrial and municipal wastewater systems.
Hybrid Desalination Residue
Hybrid desalination residue, a byproduct of combined membrane and thermal desalination processes, poses significant challenges in wastewater vs brine management due to its high salinity and chemical concentration. Effective treatment of this residue requires advanced techniques like zero liquid discharge (ZLD) or innovative brine valorization methods to minimize environmental impact and recover valuable resources.
Resource Recovery from Brine
Resource recovery from brine focuses on extracting valuable minerals such as lithium, magnesium, and potassium, transforming concentrated waste into economically beneficial products. Advanced membrane technologies and crystallization processes enhance the efficiency of brine management, minimizing environmental impact and promoting sustainable water treatment practices.
High-Salinity Wastewater Reuse
High-salinity wastewater reuse involves advanced treatment processes to recover valuable water from brine, reducing environmental discharge and conserving freshwater resources. Technologies such as membrane filtration and crystallization enable efficient management of saline effluents, promoting sustainable water reuse in industrial and agricultural applications.
Selective Ion Removal
Selective ion removal technology enhances wastewater and brine management by targeting specific contaminants like heavy metals, nitrates, and salts, improving water reuse and reducing environmental discharge. Advanced membrane processes such as electrodialysis and ion exchange resins optimize ion selectivity, minimizing energy consumption and operational costs in treatment facilities.
Wastewater vs Brine Management Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com