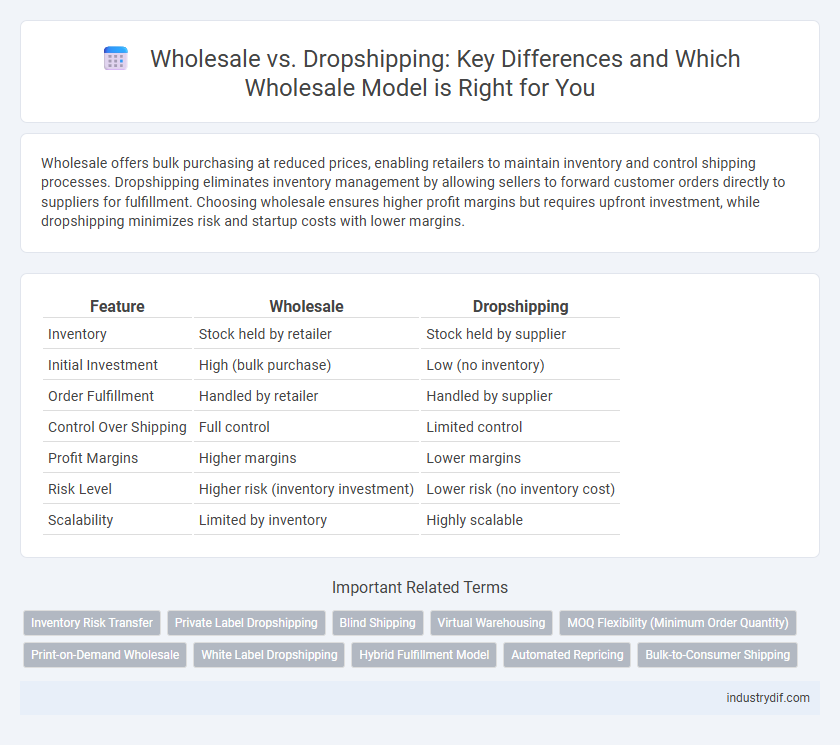
Wholesale offers bulk purchasing at reduced prices, enabling retailers to maintain inventory and control shipping processes. Dropshipping eliminates inventory management by allowing sellers to forward customer orders directly to suppliers for fulfillment. Choosing wholesale ensures higher profit margins but requires upfront investment, while dropshipping minimizes risk and startup costs with lower margins.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wholesale | Dropshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory | Stock held by retailer | Stock held by supplier |
| Initial Investment | High (bulk purchase) | Low (no inventory) |
| Order Fulfillment | Handled by retailer | Handled by supplier |
| Control Over Shipping | Full control | Limited control |
| Profit Margins | Higher margins | Lower margins |
| Risk Level | Higher risk (inventory investment) | Lower risk (no inventory cost) |
| Scalability | Limited by inventory | Highly scalable |
Understanding Wholesale and Dropshipping
Wholesale involves purchasing large quantities of products directly from manufacturers or distributors at discounted prices, allowing businesses to maintain inventory and control over shipping and fulfillment. Dropshipping eliminates the need for inventory by partnering with suppliers who directly ship products to customers, enabling lower upfront costs but often resulting in reduced profit margins and less control over delivery. Understanding the operational differences and financial implications of wholesale versus dropshipping is essential for choosing the best e-commerce model.
Key Differences Between Wholesale and Dropshipping
Wholesale involves purchasing products in bulk directly from manufacturers at reduced prices, requiring inventory storage and upfront investment, while dropshipping allows retailers to sell products without holding stock by forwarding orders to suppliers who ship directly to customers. Key differences include inventory management responsibilities, capital requirements, and control over shipping processes, with wholesale demanding more hands-on involvement compared to the low-risk, low-investment model of dropshipping. Profit margins in wholesale can be higher due to bulk discounts, whereas dropshipping profits are often lower but benefit from minimal operational overhead.
Pros and Cons of Wholesale
Wholesale offers the advantage of lower per-unit costs due to bulk purchasing, enabling higher profit margins and better control over inventory management. However, it requires significant upfront capital investment and storage space, posing risks if products do not sell as expected. Businesses benefit from stronger supplier relationships and faster shipping times but must handle order fulfillment and logistics independently.
Pros and Cons of Dropshipping
Dropshipping offers low startup costs and minimal inventory management, making it accessible for new entrepreneurs, but it often results in lower profit margins due to supplier pricing and shipping fees. The model allows for a wide product range without upfront investment, yet it relies heavily on third-party suppliers, causing potential issues with product quality control and longer shipping times. Scalability is easier in dropshipping compared to wholesale, but lack of control over inventory and customer experience can impact brand reputation.
Supplier Relationships in Wholesale vs Dropshipping
Wholesale involves establishing direct and often long-term relationships with manufacturers or distributors, ensuring better pricing, reliable inventory, and consistent product quality. Dropshipping relies on third-party suppliers who ship products directly to customers, resulting in less control over inventory and variable supplier reliability. Strong supplier relationships in wholesale enable businesses to negotiate favorable terms and enhance supply chain efficiency, unlike the more transactional and distant supplier interactions common in dropshipping.
Inventory Management: Wholesale vs Dropshipping
Wholesale involves purchasing large quantities of products to store and manage inventory directly, allowing for greater control over stock levels and fulfillment speed. Dropshipping eliminates the need for inventory storage by relying on suppliers to ship products directly to customers, reducing upfront costs but potentially slowing delivery times. Efficient inventory management in wholesale requires robust warehousing and demand forecasting systems, whereas dropshipping depends heavily on supplier reliability and real-time stock updates.
Profit Margins and Pricing Strategies
Wholesale typically offers higher profit margins due to bulk purchasing discounts, allowing retailers to price competitively while maintaining profitability. Dropshipping involves lower upfront costs but often comes with thinner margins since suppliers set retail prices, limiting pricing flexibility. Effective pricing strategies in wholesale prioritize volume sales and inventory turnover, whereas dropshipping relies on niche targeting and marketing to optimize smaller margins.
Order Fulfillment and Logistics Comparison
Wholesale requires businesses to purchase and store inventory upfront, enabling faster order fulfillment through direct shipment from warehouses. Dropshipping eliminates the need for inventory storage by shipping products directly from suppliers to customers, often resulting in longer delivery times and less control over logistics. Wholesale offers greater reliability and consistency in supply chain management, while dropshipping relies heavily on supplier efficiency and coordination.
Scalability and Business Growth Potential
Wholesale offers greater scalability and higher profit margins by allowing businesses to purchase inventory in bulk at discounted rates, enabling faster order fulfillment and stronger supplier relationships. Dropshipping limits scalability due to reliance on third-party suppliers for inventory and shipping, often resulting in thinner margins and less control over product quality and delivery times. Businesses aiming for sustainable growth typically prefer wholesale for its potential to build brand loyalty and manage large order volumes efficiently.
Choosing the Right Model: Wholesale or Dropshipping
Choosing between wholesale and dropshipping hinges on factors like inventory management, capital investment, and control over product quality. Wholesale requires upfront inventory purchases and storage, offering higher profit margins and direct shipping control, whereas dropshipping minimizes initial investment by fulfilling orders directly from suppliers, reducing risk but often decreasing profit margins. Analyzing your business goals, cash flow, and customer experience preferences will guide the optimal model selection.
Related Important Terms
Inventory Risk Transfer
Wholesale requires businesses to purchase and store inventory upfront, resulting in higher inventory risks and capital investment. Dropshipping eliminates inventory risk by allowing retailers to sell products without holding stock, as suppliers handle storage and shipping directly.
Private Label Dropshipping
Private Label Dropshipping combines the benefits of wholesale by offering bulk product access with the flexibility of dropshipping, allowing retailers to brand products without managing inventory. This model reduces upfront costs and eliminates storage needs while enabling customization and direct supplier-to-customer shipping for seamless order fulfillment.
Blind Shipping
Blind shipping in wholesale allows retailers to send products directly from suppliers to customers without revealing the supplier's identity, enhancing brand consistency and customer trust. Unlike dropshipping, wholesale blind shipping often involves bulk purchase discounts and greater inventory control, making it ideal for businesses seeking cost efficiency and streamlined logistics.
Virtual Warehousing
Virtual warehousing in wholesale offers centralized inventory management that reduces storage costs and enables faster order fulfillment compared to dropshipping's reliance on third-party suppliers. This system enhances stock visibility and control, allowing wholesalers to optimize supply chain efficiency and maintain better profit margins.
MOQ Flexibility (Minimum Order Quantity)
Wholesale typically requires purchasing large quantities to meet Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) standards, which ensures lower per-unit costs but demands significant upfront investment. Dropshipping offers greater MOQ flexibility by allowing retailers to sell products without holding inventory, enabling orders in smaller quantities or even single units directly from suppliers.
Print-on-Demand Wholesale
Print-on-demand wholesale enables businesses to purchase customizable products in bulk directly from manufacturers, reducing inventory risks and allowing for faster fulfillment compared to dropshipping. This method enhances profit margins and brand control by eliminating third-party intermediaries and providing consistent product quality.
White Label Dropshipping
White label dropshipping combines the benefits of wholesale purchasing with branded product customization, allowing retailers to sell products under their own brand without holding inventory. This model reduces upfront costs and inventory risks while providing greater control over product presentation and customer experience compared to traditional wholesale.
Hybrid Fulfillment Model
The hybrid fulfillment model combines wholesale's bulk purchasing advantages with dropshipping's direct-to-customer shipping efficiency, optimizing inventory management and reducing overhead costs. This approach enables businesses to maintain stock for high-demand products while leveraging suppliers for less predictable items, enhancing scalability and customer satisfaction.
Automated Repricing
Automated repricing in wholesale enables real-time price adjustments based on market demand, competitor pricing, and inventory levels, maximizing profit margins and sales velocity. Dropshipping's reliance on supplier price changes limits repricing control, making wholesale a more efficient option for dynamic pricing strategies.
Bulk-to-Consumer Shipping
Wholesale involves purchasing large quantities of products directly from manufacturers or distributors at discounted rates, enabling bulk-to-consumer shipping that reduces per-unit shipping costs and ensures faster delivery times. Dropshipping bypasses inventory holding by shipping products individually from suppliers to consumers, often resulting in higher shipping expenses and longer fulfillment periods.
Wholesale vs Dropshipping Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com