Wholesale involves bulk purchasing and long-term supply agreements, ensuring consistent inventory for businesses at lower prices per unit. Quick commerce prioritizes speed, offering rapid delivery of smaller quantities to meet immediate consumer demands. While wholesale emphasizes cost efficiency and volume, quick commerce caters to convenience and speed in the modern retail landscape.
Table of Comparison
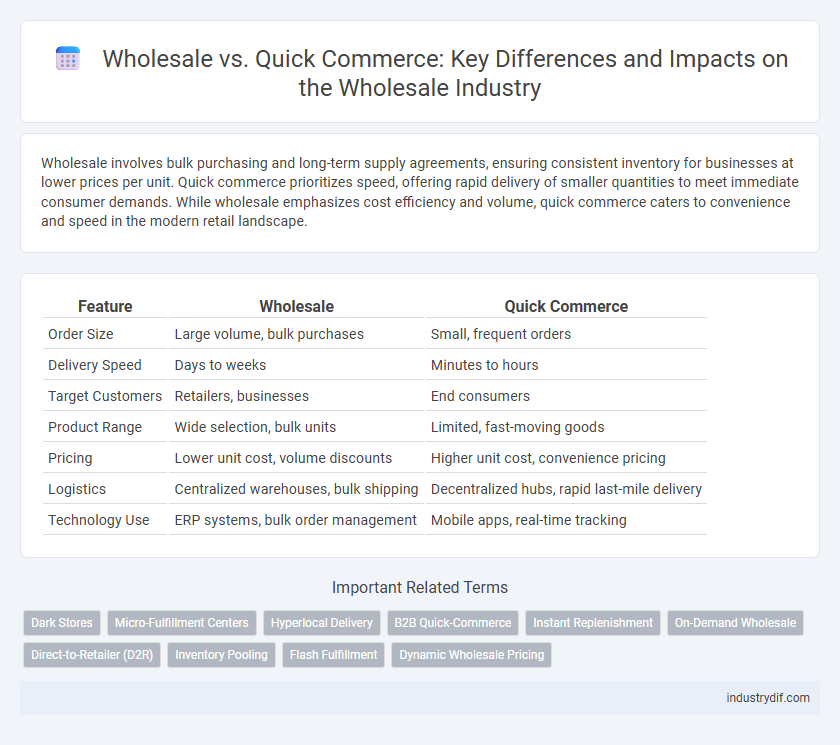
| Feature | Wholesale | Quick Commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Order Size | Large volume, bulk purchases | Small, frequent orders |
| Delivery Speed | Days to weeks | Minutes to hours |
| Target Customers | Retailers, businesses | End consumers |
| Product Range | Wide selection, bulk units | Limited, fast-moving goods |
| Pricing | Lower unit cost, volume discounts | Higher unit cost, convenience pricing |
| Logistics | Centralized warehouses, bulk shipping | Decentralized hubs, rapid last-mile delivery |
| Technology Use | ERP systems, bulk order management | Mobile apps, real-time tracking |
Understanding Wholesale: Key Concepts and Models
Wholesale involves selling goods in large quantities to retailers or businesses, enabling bulk purchasing at lower prices compared to retail. Key models include traditional wholesale distribution, where products move from manufacturers to wholesalers and then retailers, and direct wholesale, which eliminates intermediaries to enhance efficiency. Understanding these models helps businesses optimize supply chains and improve inventory management in competitive markets.
What is Quick Commerce? Speed, Technology, and Trends
Quick Commerce (Q-commerce) revolutionizes wholesale distribution by leveraging advanced technology and ultra-fast delivery systems to meet rising consumer expectations for speed and convenience. This model utilizes AI-driven inventory management, real-time data analytics, and optimized last-mile logistics to ensure rapid order fulfillment, typically within minutes to a few hours. Emerging trends highlight the integration of micro-fulfillment centers and automated warehouses, positioning quick commerce as a critical evolution in wholesale supply chain innovation.
Wholesale vs Quick Commerce: Core Differences
Wholesale involves bulk purchasing and large-volume transactions primarily catering to retailers or businesses, emphasizing cost efficiency and long-term supply contracts. Quick Commerce prioritizes speed and convenience by delivering small quantities of goods rapidly, targeting end consumers with on-demand needs. The core difference lies in Wholesale's focus on scale and price advantages versus Quick Commerce's emphasis on delivery speed and immediacy.
Customer Experience in Wholesale and Quick Commerce
Wholesale offers customers bulk purchasing options with competitive pricing, ideal for businesses seeking cost efficiency and inventory optimization. Quick commerce prioritizes rapid delivery and convenience, enhancing customer experience through speed and real-time order tracking. Both models cater to different needs: wholesale emphasizes volume and value, while quick commerce focuses on immediacy and service agility.
Logistics and Fulfillment: Bulk vs Instant Delivery
Wholesale logistics prioritizes bulk shipment and consolidated inventory management, enabling cost-efficient distribution to retailers and businesses. Quick commerce fulfillment emphasizes instant delivery, leveraging localized warehouses and real-time inventory tracking to meet consumer demand rapidly. The contrasting supply chain models reflect wholesale's focus on scale and speed optimization in quick commerce.
Pricing Strategies: Volume Discounts vs Convenience Premiums
Wholesale pricing strategies emphasize volume discounts, offering significant price reductions as order quantities increase, which incentivize bulk purchases and optimize supply chain efficiency. In contrast, quick commerce prioritizes convenience premiums, charging higher prices for rapid delivery and immediate product availability, catering to consumers' demand for speed over cost savings. These divergent approaches reflect the wholesale focus on cost-effectiveness and the quick commerce emphasis on service speed and accessibility.
Supply Chain Efficiency in Wholesale and Quick Commerce
Wholesale supply chains optimize bulk purchasing and centralized distribution, reducing per-unit costs and enhancing inventory management efficiency. Quick commerce relies on rapid fulfillment through localized micro-fulfillment centers, prioritizing speed over scale and requiring agile, real-time inventory systems. The efficiency in wholesale stems from economies of scale and predictable demand, while quick commerce demands advanced logistics technology to manage frequent, small orders with accelerated delivery timelines.
Market Segmentation: Target Customers and Business Models
Wholesale focuses on bulk transactions primarily targeting retailers, manufacturers, and large businesses aiming to reduce costs per unit through volume purchases. Quick commerce targets individual consumers and small businesses with rapid delivery models, emphasizing convenience and speed in urban areas. Wholesale business models rely on extensive inventory management and long-term supply contracts, while quick commerce utilizes technology-driven logistics and on-demand fulfillment to meet immediate customer needs.
Technology Integration: Platforms, Automation, and Analytics
Wholesale leverages robust technology integration through advanced platforms that streamline inventory management, order processing, and supplier coordination, enhancing operational efficiency at scale. Automation tools in wholesale optimize repetitive tasks such as invoicing and stock replenishment, reducing errors and increasing throughput. Analytics-driven insights enable wholesalers to forecast demand, optimize pricing strategies, and improve customer segmentation, creating competitive advantages over quick commerce models.
Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of Wholesale and Quick Commerce
Future trends in wholesale emphasize digital transformation, integrating AI-driven inventory management, and expanding real-time data analytics to optimize supply chain efficiency. Quick commerce is reshaping consumer expectations with ultra-fast delivery and hyper-local inventory sourcing, pushing wholesale suppliers toward agile, tech-enabled operations. The convergence of wholesale and quick commerce will drive innovation in seamless omnichannel experiences and dynamic fulfillment strategies.
Related Important Terms
Dark Stores
Dark stores serve as a pivotal infrastructure in quick commerce by enabling rapid order fulfillment and localized inventory management, contrasting with traditional wholesale models focused on bulk distribution and long supply chains. The strategic placement of dark stores optimizes last-mile delivery efficiency, reducing delivery times and enhancing the customer experience compared to conventional wholesale operations.
Micro-Fulfillment Centers
Micro-fulfillment centers in wholesale enable rapid inventory turnover by integrating automated storage and retrieval systems within urban hubs, significantly reducing delivery times compared to traditional quick commerce models. These centers optimize bulk product handling and streamline supply chains, enhancing scalability and cost-efficiency for wholesalers targeting high-demand, local markets.
Hyperlocal Delivery
Wholesale prioritizes bulk orders and inventory management, catering to businesses seeking cost-effective supplies, while quick commerce emphasizes rapid delivery within hyperlocal areas to meet immediate consumer demand. Hyperlocal delivery in quick commerce leverages proximity logistics and real-time inventory updates, drastically reducing delivery times compared to traditional wholesale distribution channels.
B2B Quick-Commerce
B2B quick commerce revolutionizes wholesale by enabling rapid delivery of bulk orders with real-time inventory management, enhancing supply chain efficiency for businesses. This model leverages digital platforms to provide instant access to wholesale products, reducing lead times and operational costs compared to traditional wholesale channels.
Instant Replenishment
Wholesale focuses on bulk purchasing with scheduled deliveries, contrasting with quick commerce's model of instant replenishment that prioritizes rapid, small-quantity restocking to meet immediate consumer demand. Instant replenishment in quick commerce enhances inventory turnover and reduces stockouts, offering a competitive edge over traditional wholesale's longer supply cycles.
On-Demand Wholesale
On-demand wholesale revolutionizes traditional bulk purchasing by enabling retailers to order smaller quantities with rapid fulfillment times, bridging the gap between wholesale efficiency and quick commerce speed. This model leverages real-time inventory data and agile supply chains to meet fluctuating demand without the long lead times typical of conventional wholesale.
Direct-to-Retailer (D2R)
Direct-to-Retailer (D2R) models in wholesale streamline supply chains by enabling manufacturers to deliver products directly to retailers, reducing intermediaries and enhancing inventory control. Quick Commerce complements this by accelerating delivery speeds and fulfilling smaller, frequent orders, optimizing stock replenishment for retailers seeking rapid market responsiveness.
Inventory Pooling
Inventory pooling in wholesale enables centralized stock management across multiple locations, reducing excess inventory and improving order fulfillment efficiency. Unlike quick commerce, which relies on hyper-localized, just-in-time inventory for rapid delivery, wholesale inventory pooling leverages bulk purchasing and shared resources to optimize supply chain costs and availability.
Flash Fulfillment
Wholesale primarily involves bulk purchasing and inventory management, optimizing cost-efficiency for retailers, while Quick Commerce leverages Flash Fulfillment to enable ultra-fast delivery within hours by utilizing localized micro-warehouses and real-time inventory tracking. Flash Fulfillment transforms traditional supply chains by prioritizing speed and customer convenience, making it essential for time-sensitive product distribution in competitive markets.
Dynamic Wholesale Pricing
Dynamic wholesale pricing leverages real-time data analytics and market demand to adjust bulk product prices, optimizing profit margins and inventory turnover in wholesale operations. Unlike quick commerce, which emphasizes rapid last-mile delivery, dynamic wholesale pricing focuses on flexible, volume-based pricing strategies to enhance competitive advantage in bulk procurement.
Wholesale vs Quick Commerce Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com